Portal:Ancient Egypt
|
THE ANCIENT EGYPT PORTAL
Showcased content about Ancient Egypt The golden funeral mask of king Tutankhamun, a symbol for many of ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt was a civilization in Northeast Africa situated in the Nile Valley. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology) with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Menes (often identified with Narmer). The history of ancient Egypt occurred as a series of stable kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. Egypt reached the pinnacle of its power in the New Kingdom, ruling much of Nubia and a sizable portion of the Levant, after which it entered a period of slow decline. During the course of its history, Egypt was invaded or conquered by a number of foreign powers, including the Hyksos, the Nubians, the Assyrians, the Achaemenid Persians, and the Macedonians under Alexander the Great. The Greek Ptolemaic Kingdom, formed in the aftermath of Alexander's death, ruled Egypt until 30 BC, when, under Cleopatra, it fell to the Roman Empire and became a Roman province. The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River valley for agriculture. The predictable flooding and controlled irrigation of the fertile valley produced surplus crops, which supported a more dense population, and social development and culture. With resources to spare, the administration sponsored mineral exploitation of the valley and surrounding desert regions, the early development of an independent writing system, the organization of collective construction and agricultural projects, trade with surrounding regions, and a military intended to assert Egyptian dominance. Motivating and organizing these activities was a bureaucracy of elite scribes, religious leaders, and administrators under the control of a pharaoh, who ensured the cooperation and unity of the Egyptian people in the context of an elaborate system of religious beliefs.[1] The many achievements of the ancient Egyptians include the quarrying, surveying, and construction techniques that supported the building of monumental pyramids, temples, and obelisks; a system of mathematics, a practical and effective system of medicine, irrigation systems, and agricultural production techniques, the first known planked boats, Egyptian faience and glass technology, new forms of literature, and the earliest known peace treaty, made with the Hittites. Ancient Egypt has left a lasting legacy. Its art and architecture were widely copied, and its antiquities were carried off to far corners of the world. Its monumental ruins have inspired the imaginations of travelers and writers for millennia. A newfound respect for antiquities and excavations in the early modern period by Europeans and Egyptians has led to the scientific investigation of Egyptian civilization and a greater appreciation of its cultural legacy. (Full article...) Selected article -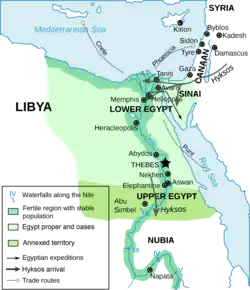 The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht. The concept of the Middle Kingdom as one of three golden ages was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition evolved significantly throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. Some scholars also include the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt wholly into this period, in which case the Middle Kingdom would end around 1650 BC, while others only include it until Merneferre Ay around 1700 BC, last king of this dynasty to be attested in both Upper and Lower Egypt. During the Middle Kingdom period, Osiris became the most important deity in popular religion. The Middle Kingdom was followed by the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, another period of division that involved foreign rule of Lower Egypt by the Hyksos of West Asia. (Full article...)Selected picture
The Great Sphinx of Giza, partially excavated, with two pyramids in the background. Did you know...
News5th September 2018. Rock-cut Tomb discovered in a 4,000-year-old Elite Cemetery August 2018: in the tomb of the mayor of Memphis Ptahmose who dates around 1300 BC was found well preserved cheese, more than 3000 years old. Selected biography -Seth-Peribsen (also known as Ash-Peribsen, Peribsen and Perabsen) is the serekh name of an early Egyptian monarch (pharaoh), who ruled during the Second Dynasty of Egypt (c. 2890 – c. 2686 BC). His chronological position within this dynasty is unknown and it is disputed who ruled both before and after him. The duration of his reign is also unknown. Peribsen's name is unusual, in that Set, not Horus, was his patron deity. This goes against the Egyptian tradition of a king choosing the falcon-shaped deity Horus as his royal patron. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various ancient Egypt-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsWikiProjects
Main topics
Notable Pharaohs
CategoriesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Ancient Egypt Early Dynastic Period of Egypt Old Kingdom of Egypt First Intermediate Period of Egypt Middle Kingdom of Egypt Second Intermediate Period of Egypt New Kingdom of Egypt Third Intermediate Period of Egypt Late Period of ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt-related lists 1st millennium BC in Egypt 2nd millennium BC in Egypt 3rd millennium BC in Egypt 4th millennium BC in Egypt Ancient Egyptian architecture Dynasties of ancient Egypt Ancient Egyptians Egyptology Foreign contacts of ancient Egypt Geography of ancient Egypt Historians of ancient Egypt Ancient Jewish Egyptian history Ancient Egyptian language Ancient Egyptian medicine Military history of ancient Egypt Nomes of ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt in popular culture Ancient Egyptian science Ancient Egyptian society Ancient Egyptian technology Works about ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt stubs Recognized content
Featured articles
Good articles
Did you know? articles
Featured pictures
In the News articlesMain page featured articles
Picture of the day pictures
Things to do
WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Sources
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|







_-_2009.jpg.webp)





.JPG.webp)








.jpg.webp)

















.svg.png.webp)




