Portal:Thailand
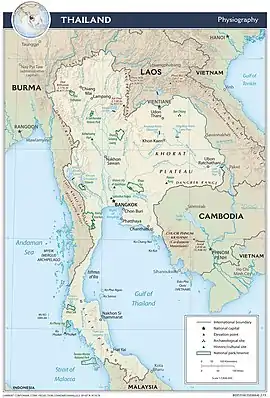
 Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 70 million, it spans 513,120 square kilometres (198,120 sq mi). Thailand is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea; it also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast, and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the nation's capital and largest city. Apart from a brief period of parliamentary democracy in the mid-1970s, Thailand has periodically alternated between democracy and military rule. Since the 2000s, the country has been caught in continual bitter political conflict between supporters and opponents of Thaksin Shinawatra, which resulted in two coups (in 2006 and 2014), along with the establishment of its current constitution, a nominally democratic government after the 2019 Thai general election, and large pro-democracy protests in 2020–2021 which included unprecedented demands to reform the monarchy. Since 2019, it has been nominally a parliamentary constitutional monarchy; in practice, however, structural advantages in the constitution have ensured the military's continued influence in politics. Thailand is a middle power in global affairs and a founding member of ASEAN, and ranks very high in the Human Development Index. It has the second-largest economy in Southeast Asia and the 24th-largest in the world by PPP and ranks 85th by nominal GDP per capita. Thailand is classified as a newly industrialised economy, with manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism as leading sectors. (Full article...) Selected articles -General imagesThe following are images from various Thailand-related articles on Wikipedia.
List articles
More Thailand-related lists
CategoriesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Thailand Thailand-related lists Buildings and structures in Thailand Thai culture Economy of Thailand Education in Thailand Environment of Thailand Geography of Thailand Government of Thailand Health in Thailand History of Thailand Organizations based in Thailand Thai people Politics of Thailand Society of Thailand Images of Thailand Thailand stubs
| |||||||||
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Sources
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals







.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)

.jpeg.webp)





.jpg.webp)





_-_img_08.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)







.jpg.webp)
















