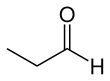
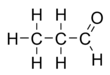
Propionaldehyde
Propionaldehyde or propanal is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CHO. It is the 3-carbon aldehyde. It is a colourless, flammable liquid with a slightly fruity odour. It is produced on a large scale industrially.
| |||
 | |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Propionaldehyde | |||
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanal | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.204 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1275 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 58.080 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Pungent, fruity | ||
| Density | 0.81 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −81 °C (−114 °F; 192 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 46 to 50 °C (115 to 122 °F; 319 to 323 K) | ||
| 20 g/100 mL | |||
| -34.32·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Viscosity | 0.6 cP at 20 °C | ||
| Structure | |||
| C1, O: sp2
C2, C3: sp3 | |||
| 2.52 D | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   | |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H315, H318, H332, H335[1] | |||
| P210, P261, P280, P304+P340+P312, P305+P351+P338, P310, P403+P235[1] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −26 °C (−15 °F; 247 K) | ||
| 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related aldehydes |
Acetaldehyde Butyraldehyde | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Production
Propionaldehyde is mainly produced industrially by hydroformylation of ethylene:
- CO + H2 + C2H4 → CH3CH2CHO
In this way, several hundred thousand tons are produced annually.[2]
Laboratory preparation
Propionaldehyde may also be prepared by oxidizing 1-propanol with a mixture of sulfuric acid and potassium dichromate. The reflux condenser contains water heated at 60 °C, which condenses unreacted propanol, but allows propionaldehyde to pass. The propionaldehyde vapor is immediately condensed into a suitable receiver. In this arrangement, any propionaldehyde formed is immediately removed from the reactor, thus it does not get over-oxidized to propionic acid.[3]
Reactions
Propionaldehyde exhibits the reactions characteristic of alkyl aldehydes, e.g. hydrogenation, aldol condensations, oxidations, etc. It is the simplest aldehyde with a prochiral methylene such that α-functionalized derivatives (CH3CH(X)CHO) are chiral.
Uses
It is predominantly used as a precursor to trimethylolethane (CH3C(CH2OH)3) through a condensation reaction with formaldehyde. This triol is an important intermediate in the production of alkyd resins. It is used in the synthesis of several common aroma compounds (cyclamen aldehyde, helional, lilial). Other applications include reduction to propanol and oxidation to propionic acid.[2]
Laboratory uses
Propionaldehyde is a common reagent, being a building block to many compounds.[4] Many of these uses exploit its participation in condensation reactions.[5] With tert-butylamine it gives CH3CH2CH=N-t-Bu, a three-carbon building block used in organic synthesis.[6]
Extraterrestrial occurrence
Propionaldehyde along with acrolein has been detected in the molecular cloud Sagittarius B2 near the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, about 26,000 light years from Earth.[7][8][9]
Measurements by the COSAC and Ptolemy instruments on comet 67/P's surface, revealed sixteen organic compounds, four of which were seen for the first time on a comet, including acetamide, acetone, methyl isocyanate and propionaldehyde.[10][11][12]
References
- Record of Propanal in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 22 March 2020.
- Hensel, A. (2018). "Propanal". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_157.pub3.
- Hurd, Charles D.; Meinert, R. N. (1932). "Propionaldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 12: 64. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.012.0064.
- Wehrli, Pius A.; Chu, Vera (1978). "Y-Ketoesters from Aldehydes Via Diethyl Acylsuccinates: Ethyl 4-Oxohexanoate". Organic Syntheses. 58: 79. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.058.0079.
- Sessler, Jonathan L.; Mozaffari, Azadeh; Johnson, Martin R. (1992). "3,4-Diethylpyrrole and 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-Octaethylporphyrin". Org. Synth. 70: 68. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.070.0068.
- Peralta, M. M. "Propionaldehyde t-Butylimine" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289X.
- Scientists Discover Two New Interstellar Molecules: Point to Probable Pathways for Chemical Evolution in Space, National Radio Astronomy Observatory, June 21, 2004
- Two newly found space molecules. By: Goho, Alexandra, Science News, 00368423, 7/24/2004, Vol. 166, Issue 4
- Chemical Precursors to Life Found in Space Scientists say that a universal prebiotic chemistry may be at work
- Jordans, Frank (30 July 2015). "Philae probe finds evidence that comets can be cosmic labs". The Washington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- "Science on the Surface of a Comet". European Space Agency. 30 July 2015. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- Bibring, J.-P.; Taylor, M.G.G.T.; Alexander, C.; Auster, U.; Biele, J.; Finzi, A. Ercoli; Goesmann, F.; Klingehoefer, G.; Kofman, W.; Mottola, S.; Seidenstiker, K.J.; Spohn, T.; Wright, I. (31 July 2015). "Philae's First Days on the Comet - Introduction to Special Issue". Science. 349 (6247): 493. Bibcode:2015Sci...349..493B. doi:10.1126/science.aac5116. PMID 26228139.