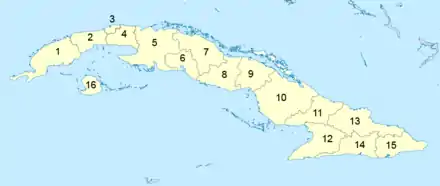
Provinces of Cuba
Administratively, Cuba is divided into 15 provinces and one special municipality (the Isla de la Juventud). The current structure has been in place since August 2010, when the then-La Habana Province was divided into Artemisa Province and Mayabeque Province.
| Administrative Divisions of Cuba | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Cuba |
| Number | 15 Provinces 1 Special Municipality |
| Populations | 81,486 (Isla de la Juventud) – 2,130,517 (La Habana) |
| Areas | 281.18 square miles (728.3 km2) (La Habana) – 5,951.31 square miles (15,413.8 km2) (Camagüey Province) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
List of provinces
From west to east, Cuba's provinces are:
History
1879–1976


The provinces were created in 1879 by the Spanish colonial government. From 1879 to 1976, Cuba was divided into six provinces, which maintained with little changes the same boundaries and capital cities, although with modifications in official names. These "historical" provinces are the following (from west to east):
- Pinar del Río
- La Habana, included the city of Havana, current Mayabeque, some municipalities of current Artemisa Province (prior to 1970: 5 municipalities; from 1970 to 2011, 8 municipalities, including Artemisa city itself). Isla de Pinos ("Isle of Pines") was considered a "special municipality" in the Province of La Habana.
- Matanzas
- Las Villas (before 1940 named "Santa Clara"), contained the present-day provinces of Cienfuegos, Villa Clara, Sancti Spíritus, and Southern Matanzas Province.
- Camagüey (before 1899 named "Puerto Príncipe"), contained the present-day provinces of Camagüey and Ciego de Ávila, as well as two municipalities of current Las Tunas Province (prior to 1970).
- Oriente (before 1905 named "Santiago de Cuba"), contained the present-day provinces of Las Tunas, Granma, Holguín, Santiago de Cuba and Guantánamo
1976–present
.png.webp)
In December 1976, the original six provinces were reconstituted into 14 provinces plus one special municipality:[1]
Isla de Pinos was renamed Isla de la Juventud on 3 August 1978.[2]
In August 2010, the Cuban National Assembly split the then-La Habana Province into two new provinces: Artemisa (which incorporated three eastern municipalities of neighboring Pinar del Río) and Mayabeque. The new provinces started functioning from January 1, 2011.[3] Havana City Province (Ciudad de La Habana Province) recovered its original name, La Habana Province.
Demographics
Pop. = Population. Source: Cuba census 2002 [4]
| Province | Capital | Pop. (2012) | Pop. (%) | Area (km2) | Area (%) | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camagüey | Camagüey | 768,311 | 7.02 | 15,386.16 | 13.2 | 50.22 |
| Ciego de Ávila | Ciego de Ávila | 424,750 | 3.68 | 6,971.64 | 5.6 | 60.70 |
| Cienfuegos | Cienfuegos | 400,768 | 3.54 | 4,188.61 | 3.9 | 94.54 |
| La Habana | La Habana (Havana) | 2,154,454 | 19.70 | 728.26 | 0.7 | 3,053.49 |
| Granma | Bayamo | 830,645 | 7.36 | 8,374.24 | 7.9 | 98.20 |
| Guantánamo | Guantánamo | 506,369 | 4.54 | 6,167.97 | 6.0 | 82.22 |
| Holguín | Holguín | 1,027,683 | 9.14 | 9,215.72 | 8.5 | 109.90 |
| Isla de la Juventud† | Nueva Gerona | 84,263 | 0.77 | 2,419.27 | 2.1 | 35.78 |
| Artemisa | Artemisa | 487,339 | 4.49 | 4,003.24 | 3.75 | 125.5 |
| Las Tunas | Las Tunas | 525,729 | 4.70 | 6,592.66 | 6.0 | 79.77 |
| Matanzas | Matanzas | 679,314 | 6.00 | 11,791.82 | 10.0 | 56.80 |
| Mayabeque | San José de las Lajas | 371,198 | 3.41 | 3,743.81 | 3.49 | 102.2 |
| Pinar del Río | Pinar del Río | 585,452 | 5.32 | 8,883.74 | 8.32 | 67.00 |
| Sancti Spíritus | Sancti Spíritus | 462,114 | 4.12 | 6,777.28 | 6.3 | 68.33 |
| Santiago de Cuba | Santiago de Cuba | 1,053,837 | 9.27 | 6,227.78 | 5.9 | 168.32 |
| Villa Clara | Santa Clara | 783,708 | 7.31 | 8,441.81 | 7.6 | 97.17 |
| Cuba | La Habana | 11,163,934 | 109,884.01 | 101.72 |
† Special municipality
Presidents of the People's Power Provincial Councils
The following are the presidents of the Provincial People's Councils in each province in the country (local governments).[5]
The Provincial People's Councils replaced the Provincial Assemblies in the 2019 Constitution and are made up of provincial representatives elected by the municipal assemblies or councils.
| Province | President of the Provincial Council |
|---|---|
| Camagüey | Jesús Arturo García Collazo |
| Ciego de Ávila | Agustín Gregorio Arza Pascual |
| Cienfuegos | Rolando Díaz González |
| La Habana | Reinaldo García Zapata |
| Granma | Jesús Antonio Infante López |
| Guantánamo | Luis Fernando Navarro Fernández |
| Holguín | Alberto Olivera Fis |
| Isla de la Juventud† | Roberto Unger Pérez |
| Mayabeque | Armando Cuellar Domínguez |
| Artemisa | Raúl Rodríguez Cartaya |
| Las Tunas | Víctor Luis Rodríguez Carballosa |
| Matanzas | Nilo Tomás Díaz Fundora |
| Pinar del Río | Vidal Pérez Baños |
| Sancti Spíritus | Fidel Pérez Luzbert |
| Santiago de Cuba | Rolando Yero García |
| Villa Clara | Alexander Rodriguez Rosada |
† Special municipality
See also
- Politics of Cuba
- Demographics of Cuba
- List of places in Cuba
- Municipalities of Cuba
- List of West Indian first-level country subdivisions, a list of first-level country subdivisions within the Caribbean in order of total area
- ISO 3166-2:CU, which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of the country
References
- Goodsell, James Nelson (December 12, 1976). "Cuba's citizens to have a say". The Columbian. Vancouver, Washington. The Christian Science Monitor. p. 47. Retrieved September 2, 2023 – via newspapers.com.
- "Cuba has New Name for 'Treasure Island'" (PDF). New York Times. 4 August 1978. Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- Proponen en Pleno del Partido dos nuevas provincias cubanas: Artemisa y Mayabeque (+ Infografía) - Cubadebate
- Cuba Census 2002 Archived 2008-01-17 at the Wayback Machine Population table
- "Presidentes de las Asambleas Provinciales del Poder Popular en cada provincia" (in Spanish). Parlamento Cubano. Archived from the original on 2007-06-09. Retrieved 2007-02-10.
External links
- Cuba at GeoHive
- "Provinces of Cuba". Statoids.
.svg.png.webp)