Random amplification of polymorphic DNA
Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), pronounced "rapid",[1] is a type of polymerase chain reaction (PCR), but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random.[2] The scientist performing RAPD creates several arbitrary, short primers (10–12 nucleotides), then proceeds with the PCR using a large template of genomic DNA, hoping that fragments will amplify. By resolving the resulting patterns, a semi-unique profile can be gleaned from an RAPD reaction.
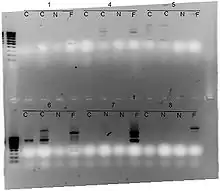
No knowledge of the DNA sequence of the targeted genome is required, as the primers will bind somewhere in the sequence, but it is not certain exactly where. This makes the method popular for comparing the DNA of biological systems that have not had the attention of the scientific community, or in a system in which relatively few DNA sequences are compared (it is not suitable for forming a cDNA databank). Because it relies on a large, intact DNA template sequence, it has some limitations in the use of degraded DNA samples. Its resolving power is much lower than targeted, species-specific DNA comparison methods, such as short tandem repeats. In recent years, RAPD has been used to characterize, and trace, the phylogeny of diverse plant and animal species.
Introduction
RAPD markers are decamer (10 nucleotides long) DNA fragments from PCR amplification of random segments of genomic DNA with a single primer of arbitrary nucleotide sequence and which are able to differentiate between genetically distinct individuals, although not necessarily in a reproducible way. It is used to analyze the genetic diversity of an individual by using random primers. Due to problems in experiment reproducibility, many scientific journals do not accept experiments merely based on RAPDs anymore. RAPD requires only one primer for amplification.
How it works
After amplification with PCR, samples are loaded into a gel (either agarose or polyacrylamide) for gel electrophoresis. The differing sizes created through random amplification will separate along the gel in a repeatable manner depending on the sample source. This creates a distinct DNA fingerprint.
Unlike traditional PCR analysis, RAPD does not require any specific knowledge of the DNA sequence of the target organism: the identical 10-mer primers will or will not amplify a segment of DNA, depending on positions that are complementary to the primers' sequence. For example, no fragment is produced if primers annealed too far apart or 3' ends of the primers are not facing each other. Therefore, if a mutation has occurred in the template DNA at the site that was previously complementary to the primer, a PCR product will not be produced, resulting in a different pattern of amplified DNA segments on the gel.
Limitations
- Nearly all RAPD markers are dominant, i.e. it is not possible to distinguish whether a DNA segment is amplified from a locus that is heterozygous (1 copy) or homozygous (2 copies). Codominant RAPD markers, observed as different-sized DNA segments amplified from the same locus, are detected only rarely.
- PCR is an enzymatic reaction, therefore, the quality and concentration of template DNA, concentrations of PCR components, and the PCR cycling conditions may greatly influence the outcome. Thus, the RAPD technique is notoriously laboratory dependent and needs carefully developed laboratory protocols to be reproducible.
- Mismatches between the primer and the template may result in the total absence of PCR product as well as in a merely decreased amount of the product. Thus, the RAPD results can be difficult to interpret, unlike traditional PCR analysis.
References
- "Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD)". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2020-11-10.
- "rDNA: Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD)". www.rvc.ac.uk. Retrieved 2016-06-03.
External links
- RAPD+Technique at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)