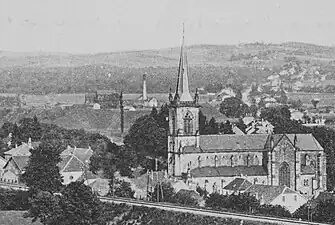Saint-Joseph Coal Mine
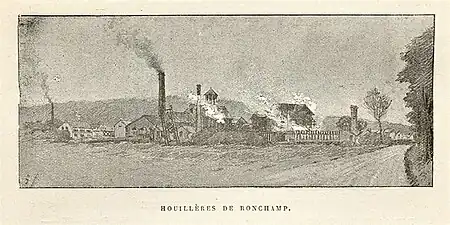
The Saint-Joseph Coal Mine is one of the main shafts of the Ronchamp coal mine, in the Ronchamp commune, within the French region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. It was one of the most productive coal mines in the Ronchamp coalfield during the second half of the 19th century. Throughout this period, it was the center of activity for the mining company, with the installation of a coking plant and a coal-washing plant, before being replaced by the Chanois shaft. The Saint Joseph shaft was hit by several disasters. On August 10, 1859, a firedamp explosion killed twenty-nine people. On May 8, 1860, another explosion destroyed the underground tunnels and the roof of the surface recette building.
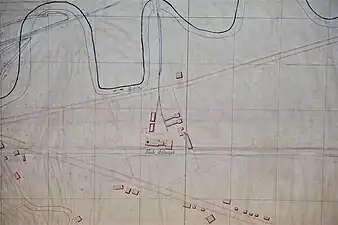
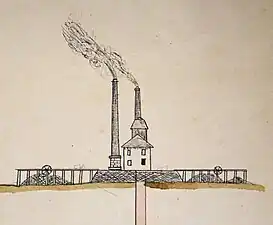
 Overview of the Saint-Joseph well facilities, with the Notre-Dame Mine Shaft in the background on the left. | |
| Location | |
|---|---|
 Saint-Joseph Coal Mine | |
| Location | Ronchamp commune, Haute-Saône department, Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region |
| Country | France |
| Coordinates | 47°41′50″N 06°38′47″E[1] |
| Production | |
| Products | Coal |
| Type | Coal mine |
| Greatest depth | 453 m (1,486 ft) |
| History | |
| Discovered | July 24th, 1850 |
| Opened | October 14th, 1855 |
| Active | 1855-1895 |
| Closed | 1896 |
| Owner | |
| Company | Ronchamp coal mines |
After the closure of the Saint-Joseph shaft in 1895, the buildings were demolished and replaced by a small sawmill, whose buildings, now used as shops for building materials, still exist into the early 21st century. Some slag heaps and an old railway track still remain.
Excavation
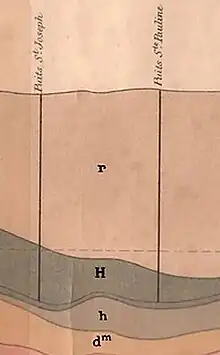
In 1830, Mr. Thirria, a state mining engineer working in Vesoul, had already foreseen the need to excavate a shaft 1,200 meters south-west of shaft no. 1.[2] The sinking of the shaft finally began on July 24, 1850, with a cross-section of 2.15 meters x 3.05 meters divided into two sections, one for extraction (2.15 m x 2.25 m), the other for ventilation (2.15 m x 0.8 m).[3] The old 24-horsepower[4] Saint-Louis shaft extraction machine was used to deepen the shaft at an average rate of seven meters per month.[5] It was to have been fitted with Mr. Méhu's cleat machine and would have assisted the Saint-Charles shaft, which was the only working shaft in the coalfield at the time.[6] It was rectangular in shape, 2.15 meters wide and 3.05 meters long; the shaft had two compartments, one of which was reserved for ventilation. A cast-iron casing made up of sixty cylindrical rings was built with a base at a depth of 150 meters and a height of 89 meters. The rings are made up of several segments, the horizontal and vertical joints are made of lead-concrete and, as the rings are installed, cement concrete is poured between the casing and the ground. Strong releases of firedamp were observed in the coal beds.[7]
When the shaft was sunk, numerous difficulties were encountered in ventilating the workings at the bottom, despite the use of an intake chimney and a plank shaft. Ventilation was improved in 1856, when the toc-feu system was replaced by two Duvergier ventilators.[7][8]
Exploitation
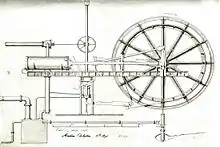
On October 14, 1855, the shaft was sunk to a depth of 441.64 meters, after crossing the first 3.30-metre thick vein of coal; the second layer was sought out through three unsuccessful test pits at the bottom.[5] A 120 hp[9] steam engine with two horizontal cylinders 0.75 meters in diameter and two meters in stroke was purchased from Le Creusot for the extraction operation.[3] It was powered by six generators consisting of a cylinder ten meters long and 1.11 meters high, heated directly by the flames from the diameter hearth, which could consume up to seventeen tonnes of coal a day.[10]
In 1858, the Saint-Joseph shaft was linked to the coal mines' rail network by a railway line that transported coal via the Paris-Est to the Mulhouse-Ville line.[11]
The next year, the steam engine boilers were replaced by six Mulhouse generators with a larger heating surface, saving five tonnes of coal a day thanks to their 50 m2 heating surface (the old ones had only 17 m2).[10] Two-story iron cages (corresponding to two levels of revenue at the bottom and daylight) fitted with Duvergier and then Fontaine parachutes (following accidents) were used to transport 800-kilogram minecarts. A fourteen-meter-high headframe made of fir and oak supported wheels 3.50 meters in diameter through which aloe cables passed.[12]
The same year, iron cables were tested at Saint Joseph under unfavorable conditions (heavy water infiltration), but the results were not satisfactory.[13] In May 1859, 200 tonnes of coal extracted from the Saint-Joseph shaft were sent to the Dornach railway station to be tested by the Société Industrielle de Mulhouse (calorific value and composition tests).[14]
On August 10, 1859, a firedamp explosion killed twenty-nine people in the west works. Work did not resume in this sector until 1874.[7] On April 23, 1860, at 11 a.m., a flaming blast of firedamp was caused by a pierced sieve. The shaft was closed until May 8 for safety reasons, but this was not sufficient, as a violent detonation occurred at 3 am on May 9. This was followed by another at 9.30 am, so violent that it took out the dam made of earth and trays, as well as the entire roof of the building. The decision was taken to drown the workings of the well to extinguish the fire. A few days later, the water began to be drained, with a volume in excess of 90,000 m3.[7]
On September 21, a connecting gallery was dug with the Saint-Charles shaft, which provided ventilation.[7] In June 1861, the Saint-Joseph shaft was the most productive in the coalfield, extracting 6,258 tonnes of coal during the month, compared with 2,585 tonnes from the Saint-Charles shaft, 2,622 tonnes from the Sainte-Barbe shaft, and 502 tonnes from the Sainte-Pauline shaft.[15] Production totaled 75,774.7 tonnes in 1861, 67,567.1 tonnes in 1862, and 34,460.8 tonnes in 1863.[16]
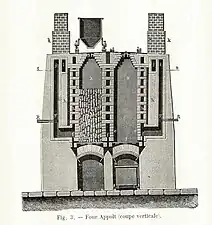
By 1862, a three-story cage had been installed. In the same year, large-volume vertical Appolt furnace were built, followed by horizontal Belgian coke ovens. These were later replaced by more sophisticated ovens next to the washing plant.[7]
In 1868, 50,000 tonnes of coal were extracted at Saint-Joseph, and the following year production rose to 66,000 tonnes, making it the company's most productive shaft.[17] In 1878, engineers noticed that water from the Rahin was invading the well.[18] In 1895, mining ceased for good at the Saint-Joseph shaft.[7] The coking plant was replaced in 1898 by the Chanois coking plant.[19]
Reconversion
At the beginning of the 20th century, the Saint Joseph shaft facilities were demolished and replaced by the Union Industrielle sawmill, which employed around twenty people in 1918. By 1938, it was producing 6,000 tonnes of timber. At that time, the factory was powered by a 120-hp electric motor.[20] The facilities also included a cabinet-making shop and a panel beater. The complex later became a shop selling building materials.[20][21]
At the beginning of the 21st century, the industrial buildings that once housed a sawmill and subsequently the shop were still in existence. They were included in the general inventory of cultural heritage on March 11, 2010. The well is located beneath one of the buildings on the industrial site, between the RN19 and the D4.[20][22]
Terrils and railway
The Saint-Joseph shaft had many slag heaps, which were exploited after the mines closed in 1958 and almost disappeared at the end of the 20th century. They are crossed by an old railway line built in 1858 and used until the conversion of the Union sawmill. It is part of the Ronchamp coal mines rail network and runs over a wooden bridge that no longer exists as of the beginning of the 21st century.[23][24]
References
- - Puits du Chanois . BRGM is the leading French public body in the field of earth sciences for the management of soil and subsoil resources and risks.
- François Mathet 1882, p. 120.
- François Mathet 1882, p. 192.
- François Mathet 1882, p. 116.
- François Mathet 1882, p. 191.
- Parietti 1999 (1), p. 8.
- (fr) "Histoire du puits Saint-Joseph" archive, on Les Amis du Musée de la Mine archive.
- Parietti 2001, p. 30.
- Édouard Thirria 1869, p. 186.
- François Mathet 1882, p. 193.
- Société de l'industrie minérale 1882, p. 676.
- François Mathet 1882, p. 194.
- (fr) "Tests de câbles en fer" archive.
- Société industrielle de Mulhouse 1860, p. 132.
- Parietti 1999 (1), p. 34.
- Michel Godard 2012, p. 336.
- Parietti 1999 (2), p. 18.
- Parietti 1999 (1), p. 33.
- Jean-Jacques Parietti 2001, p. 83.
- Notice no IA70000153 archive, Mérimée data base, ministère français de la Culture.
- (fr) "Le site du puits Saint-Joseph en 2006" archive, on http://culture.gouv.fr/ archive.
- (fr) "Situation et vestige du puits Saint-Joseph" archive, on http://www.abamm.org/ archive.
- (fr) "La voie ferrée et le terril du puits Saint-Joseph" archive, on http://www.abamm.org/ archive.
- (fr) "Le pont de la voie ferrée du puits Saint-Joseph" archive, on http://www.abamm.org/ archive.
See also
Related articles
External links
Bibliography
- (fr) Jean-Jacques Parietti, Les Houillères de Ronchamp vol. I : La mine, Vesoul, Éditions Comtoises, 2001, 87 p. (ISBN 2-914425-08-2).
- (fr) Jean-Jacques Parietti, Les Houillères de Ronchamp vol. II : Les mineurs, Noidans-lès-Vesoul, fc culture & patrimoine, 2010, 115 p. (ISBN 978-2-36230-001-1).
- (fr) Jean-Jacques Parietti, Le puits Saint-Charles, Ronchamp, Association des amis du musée de la mine, coll. "Les dossiers de la Houillère" (no 3), 1999 (1), 55 p. (BNF 37621655).
- (fr) Jean-Jacques Parietti, Le puits d'Eboulet, Association des amis du musée de la mine, coll. "Les dossiers de la Houillère" (no 5), 1999 (2) (read online archive).
- (fr) Société industrielle de Mulhouse, Bulletin, Volume 30, Part 1, 1860 (read online archive).
- (fr) Édouard Thirria, Manuel à l'usage de l'habitant du département de la Haute-Saône, 1869 (read online archive), p. 182-186.
- (fr) François Mathet, Mémoire sur les mines de Ronchamp, Société de l'industrie minérale, 1882 (read online archive).
- (fr) Société de l'industrie minérale, Bulletin trimestriel, Saint-Étienne, 1882 (read online archive).
- (fr) [PDF] Michel Godard, Enjeux et impacts de l'exploitation minière du bassin houiller de Ronchamp (1810-1870), UTBM, May 16, 2012 (read online archive).