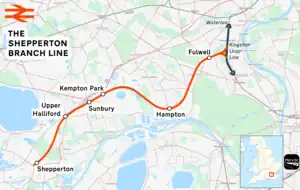
Shepperton branch line
The Shepperton branch line is a railway line connecting Shepperton to the Kingston loop railway line by a triangular junction between Strawberry Hill and Teddington stations. The line crosses from eastern Surrey into Greater London, England.
| Shepperton branch line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 The line curving away from Upper Halliford | |||
| Overview | |||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Locale | |||
| Termini | |||
| Stations | 6 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Commuter rail, Heavy rail | ||
| System | National Rail | ||
| Services | 1 | ||
| Operator(s) | South Western Railway | ||
| Depot(s) | Wimbledon | ||
| Rolling stock | |||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1 November 1864 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Number of tracks | 2 | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 750 V DC third rail | ||
| Operating speed | 60 mph (97 km/h) | ||
| |||
Shepperton branch line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
It opened in 1864, and was chiefly used for residential travel, but it was not until electrification in 1916 that a frequent and comfortable train service was provided. The outer (western) end of the branch still retains a semi-rural air.
Kempton Park Racecourse was opened on a site alongside the line in 1878, and platform facilities were grudgingly provided, for members only at first. However racegoers later provided a lucrative business revenue; special arrangements were made before and after World War II to enable travel to and from the course by very large numbers of people in a short space of time on race days. For some time Hampton Waterworks was dependent on the line for the delivery of coal. The line continues in use today as a moderately busy suburban line.
History
First proposals
The London and South Western Railway opened its Kingston branch line from Twickenham on 1 July 1863. At this stage the Kingston line was a single-ended branch, but on 1 January 1869 an extension railway was constructed to what is now New Malden station on the Surbiton main line, forming a circular loop line.[1][2]
In 1861 a Metropolitan & Thames Valley Railway (M&TVR) had been proposed. Its supporters had agreed on the desirability of constructing a railway to connect the towns of Isleworth, Richmond, Twickenham, Hampton, Sunbury, Shepperton and the valley of the River Thames via the Great Western Railway (GWR) and the LSWR. Such a line would, they said, enable London workers from the overcrowded and unhealthy portion of the City of London to easily reach and live in healthier and more inviting localities.[3][4]
The line would be built on the mixed gauge (with rails for both the broad gauge, and what became the standard gauge, then known as narrow gauge). The promoters wanted to connect to the LSWR at all practicable points, and they said they would negotiate with the with the GWR for the building or leasing of the railway.[5]
The promoters presented a Bill for their line in the 1862 session of Parliament. They sought a line from the Brentford branch line of the GWR, to Richmond Bridge, joining the LSWR at Twickenham. In addition they proposed a line from Chertsey through Twickenham to Isleworth. In total this amounted to about 14 miles.[5]
The GWR offered to help with getting the Bill through Parliament, and to work the line for half its gross receipts. The M&TVR turned this down on 11 March 1862, as they wanted help raising capital for the construction, rather than a commercial deal for the later operation of the railway. They turned now to the LSWR. The difficulty in raising capital must have been starkly clear to them, for in the negotiation they abandoned their intentions for lines north of Twickenham. At the same time the LSWR was anxious to prevent the GWR from achieving such an easy entry onto LSWR territory, and an agreement was reached on 1 May 1862.[5][4]
The Thames Valley Railway
The agreement was that the LSWR would work the line in perpetuity, and an income-sharing formula was agreed. The company name was changed to the Thames Valley Railway (TVR), and it was authorised by an Act of 17 July 1862; authorised share capital was to be £110,000.[6] The line would run from the LSWR Kingston branch at what was later Strawberry Hill station, via Hampton to the Charlton road at Shepperton. It would be six and a half miles (10.5 km) long. Many of the supporters of the original scheme were appalled at the reduction of the ambitious project to a short branch of the LSWR, and declined to continue any association with the business.[7]
A contractor was appointed, Aird and Son. In October 1864 they offered to finance and build an extension from Shepperton to the LSWR Chertsey line, if TVR directors would give public support. Aird and Son had already substantially financed the original line. The TVR agreed, and so a Thames Valley and London & South Western Junction Railway Bill was prepared, ready for the 1865 Parliamentary session. However the LSWR had no wish to encourage a line that would compete with their own main line, and the LSWR refused permission for the necessary junction. The idea was dropped in December 1864.[4][7]

The line, to Shepperton only, opened on 1 November 1864;[6] it was a single line, operated by train staff, from Thames Valley Junction to Shepperton. Thames Valley Junction was later the site of Strawberry Hill station, from 1 December 1873.[8] Intermediate stations on the line were stations at Fulwell, Hampton and Sunbury to Shepperton. Passing loops were provided at Thames Valley Junction, Hampton, Sunbury and Shepperton itself. In practice the Up platform at Shepperton was little used and soon fell into disuse.[4] There were seven passenger trains and one goods train each way on weekdays, and four passenger trains on Sundays to Twickenham only. This was later increased to ten and five passenger trains respectively.[7]
Absorption by the LSWR
Amalgamation started to be thought of, and on 21 December 1864 the TVR accepted a LSWR offer of £100,910, in 4+1⁄2 per cent preference stock. In fact, Aird & Son held £100,000 of TVR capital of £110,000: the appeal for share subscriptions from the general public had clearly not gone well. The amalgamation was ratified by an Act of 5 July 1865.[7][6]
Infrastructure improvements
The LSWR doubled the line between Thames Valley Junction the Kingston branch and Fulwell, probably in 1867.[7] The doubling was extended from Fulwell to Sunbury on 17 July 1878, and to Shepperton on 9 December 1878. Kempton Park Racecourse opened on 18 July 1878.[7] The north-facing connection at Strawberry Hill was a limitation, and an LSWR Act of 4 July 1890 authorised a 24 chain west-to-south curve from Fulwell Junction (western apex) to Shacklegate Junction (southern apex) for direct running from Shepperton towards Kingston: it came into use on 1 July 1894. This was primarily for goods traffic, but race trains usually worked over the rather longer route to Waterloo via Kingston. The curve was not used by ordinary passenger trains until 1 June 1901 when a single down working (6:07 pm from Waterloo) was routed this way.[7][4]
Inside the triangle formed by the three junctions a locomotive depot known as Strawberry Hill Depot was built to replace the small shed at Twickenham, to service the Shepperton and Kingston lines. It was opened in the 1890s and enlarged in 1908 to accommodate 50 locomotives, mostly tanks; the depot eventually employed over 500 staff, but it was in turn replaced by a new depot at Feltham marshalling yard in 1922. From 1916 part of the site was used as an electric train depot; enlarged in 1936, it could accommodate up to eleven 8-car trains overnight.[4]
Kempton Park racecourse station
In the mid-1870s the Kempton Manor Estate was acquired in order to build a new racecourse, which became Kempton Park Racecourse. In 1877 the developers asked the LSWR to provide a passenger station, but in October the LSWR refused, fearing that the special traffic would necessitate doubling the track. However on reflection, the potential income from racegoers induced the Company to double the line between Fulwell and Hampton, and then on to Sunbury. The racecourse opened for its first race on 18 July 1878. On 5 September 1878 the LSWR allowed a simple platform on the down line, adjacent to the grandstand, for members of the racecourse only. It was not provided with any special facilities, but on 2 April 1879, an up platform was reluctantly approved. The station continued to be for members only.[7][4]
Complete rebuilding of Kempton Park racecourse station was undertaken in 1890, and in its final form it had three platforms sheltered by long canopies and connected by a covered footbridge. The third platform was an up loop and was never electrified. It was removed in 1964.[9][10]
The down platform was built extra-long in order to receive two LSWR first-class only Members' Special trains, composed of American Line saloons. A covered way connected the station to the racecourse. Some further improvements were carried out in 1930. After 1890 the station was opened to the public on race days, when it was served by the branch trains as well as the race specials, but it could not be used other than to gain access to and from the racecourse.[4] For many years therefore the station was only open on race days, but from 6 March 2006 trains called there in the ordinary way, a public access having been created.[11]
Electrification
At the end of the first decade of the twentieth century, the passenger service in the suburban area was uncomfortable, dirty, old-fashioned and slow. While the railway had been the only means of residential travel, this had to be tolerated by the public, but the widespread introduction of street tramways changed that fundamentally. The LSWR decided to install electric traction throughout the suburban area, and a very large investment scheme was undertaken. It was to use the third-rail system, electrified at 660 V DC. Stage one was announced in 1913 and would take two years to implement, at an estimated cost of £1.16 million. The Kingston Loop and the Shepperton Branch were included in stage one.[12]
The Shepperton branch and the Kingston Loop received their first electric passenger trains on Sunday 30 January 1916. For the first time, almost all the service was routed via Kingston, a change made to balance the Hounslow Loop Line service with the Richmond line and to give a combined 10-minute headway all day between Waterloo and Teddington. This was a revolutionary improvement, with 35 trains a day each way, every day of the week. On weekdays they ran at 30-minute intervals between 5:55 am and 10:55 pm, with an extra down train from Wimbledon at 5:09 am and another at 11:53 pm from Waterloo. The headcode was "S". On Sundays, trains worked every half hour between Twickenham and Shepperton with head code S. Rushhour trains were lengthened from three to six cars, and there were extra steam (later electric) trains via Richmond. After 1919 all weekday trains ran via Kingston with peak-hour trains running non-stop from Norbiton to Wimbledon covering the Shepperton-Waterloo run in 44 minutes. Stabling at Shepperton was improved in 1925 by the installation of an electrified siding and cleaning stage.[13][14]
Radical improvements to the timetable were brought in on 10 July 1967 when the basic all-day half-hourly service ran from end to end in 44 minutes, later increased to 45, by omitting stops nearer Waterloo.[14]
For many years after electrification steam locomotives continued to work freight and certain race specials. In LSWR days race trains were operated from various parts of the system but the post-grouping service was invariably to and from Waterloo. Until September 1939, first-class race trains made up from SECR and LBSCR compartment stock hauled by LSWR M7 0-4-4T locomotives, ran between the electric services, whilst other race trains were electrically-worked.[14]
The branch goods locomotive was employed in term time to haul a school train between Hampton and Twickenham until 1939. Occasionally a steam engine was brought in when electric traction was in difficulty. For example in the summer of 1957, a night of heavy rain inundated the line at Fulwell and an M7 was called in to operate a shuttle service between Teddington and Hampton for most of the following day.[14]
Hampton waterworks
The private water companies which had established themselves at Hampton twelve years before the opening of the branch received their coal via Thames river barges and horse carts, but the East London Waterworks Company which had come to Sunbury in the late 1860s used the LSWR.[9]
The Metropolitan Water Board took over the installations in June 1904 and it decided to build a 2 foot (0.61 m) gauge railway system with transhipment sidings alongside the LSWR up line at Kempton Park and at the riverside at Hampton.[9] The 3+1⁄2 miles (5.6 km) system opened in 1915, and was worked by three Kerr, Stuart 0-4-2T locomotives named Hampton, Kempton and Sunbury, supplemented by the 0-4-2T named Hurst some years later. Eventually there were about 140 tipping, hopper and other wagons. With the declining use of coal at the pumping stations there was no work for the railway and in 1947 it was closed down.[9][15]
Wartime

In 1914-18 there was a large military camp at Sunbury, and the racecourse was used as a motor transport store, both bringing extra work to the line. During World War II Italian prisoners of war were kept in a camp at Kempton Park, and they were brought in using 8-car sets of Maunsell corridor coaches. British Thermostats built a war factory near the point where the line passed under the Feltham-Walton road, and to serve this a concrete platform with small brick buildings called Upper Halliford Halt was opened on the down side east of the road on 1 May 1944. There was no need at this time for an up line platform as during the war years the branch was worked as a single track, the other line serving as a parking place for crippled wagons. An up platform and concrete footbridge followed after the war.[9]
Race day working
Faulkner, writing in 1955, described the special working on the branch on race days.[16]
Some steam -hauled specials were operated with all-first-class coaches. These could not be stacked in amongst the electric trains and had to be returned to Strawberry Hill immediately, complicating the working.[17]
Using this system coupled with the additional signalboxes to shorten the sections, electric race-trains were operated at intervals as close as four minutes at the busiest times (Easter Mondays). A standby steam locomotive was stationed at Sunbury in case of emergency. Increased car ownership and television killed this business and by the later 1950s single-line working was seen only on Easter Mondays. A few special trains continued to run to Kempton Park until the early 1960s. Horsebox traffic, once a great feature on the day before·the·first races, and the day following the last ones, with steam locomotives working through from the LNER and other lines, also dwindled to nothing as horse owners turned to the more convenient motor boxes.[9]
Stations
Stations on the line are:
- Fulwell; opened 1 November 1864; still open;
- Hampton; opened 1 November 1864; still open;
- Kempton Park; opened as Sunbury Racecourse 18 July 1878, unadvertised for members only; opened to general public in 1890; renamed Kempton Park 1891; open on race days only; full public service began 6 March 2006; still open;
- Sunbury; opened 1 November 1864; still open;
- Upper Halliford; opened 1 May 1944 as Upper Halliford Halt; Halt suffix removed 5 May 1969; still open;
- Shepperton; opened 1 November 1864; still open.[18]
Passenger train service
The passenger train service on the line is (December 2022) typically half-hourly to London Waterloo via Kingston, hourly on Sundays. A small number of rush-hour trains run via Twickenham and Richmond.[19]
References
- R A Williams, The London and South Western Railway: volume 2: Growth and Consolidation, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1973, ISBN 0 7153 5940 1, page 38
- Alan A Jackson, London's Local Railways, David & Charles, Newton Abbot, 1978, ISBN 0 7153 7479 6, page 57
- M&TVR Prospectus, quoted in Williams, volume 2, page 39
- Jackson, pages 64 to 66
- Williams, volume 2, pages 39 and 40
- Donald J Grant, Directory of the Railway Companies of Great Britain, Matador, Kibworth Beauchamp, 2017, ISBN 978 1785893 537, page 560
- Williams, volume 2, pages 40 to 43
- M E Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England, Wales and Scotland: A Chronology, version 5.04, September 2022, Railway and Canal Historical Society, electronic download, page 433
- Jackson, pages 71 to 73
- Vic Mitchell and Keith Smith, Kingston and Hounslow Loops, Middleton Press, Midhurst, 1990, 0 906520 83 5, plate 52
- M E Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England, Wales and Scotland: A Chronology, version 5.04, September 2022, Railway and Canal Historical Society, electronic download, page 260
- David Brown, Southern Electric, volume 1, Development of the London Suburban Network and Its Trains, Capital Transport Publishing, Crowthorne, 2009, ISBN 978-1854143303, page 25
- Brown, volume 1, pages 28 and 29
- Jackson, pages 70 and 71
- Mitchell and Smith, "Hampton Waterworks"
- J N Faulkner, Easter Monday at Kempton Park, Railway Magazine, April 1955, pages 275 and 276
- Mitchell and Smith, plate 53
- Quick
- South Western publicity