Cherokee County, Oklahoma
Cherokee County is a county located in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 47,078.[1] Its county seat is Tahlequah,[2] which is also the capital of the Cherokee Nation.[3]
Cherokee County | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Oklahoma | |
 Oklahoma's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 35°55′N 95°00′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1907 |
| Named for | Cherokee Nation |
| Seat | Tahlequah |
| Largest city | Tahlequah |
| Area | |
| • Total | 776 sq mi (2,010 km2) |
| • Land | 749 sq mi (1,940 km2) |
| • Water | 27 sq mi (70 km2) 3.5% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 47,078 |
| • Density | 61/sq mi (23/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
Cherokee County comprises the Tahlequah, OK micropolitan statistical area, which is included in the Tulsa-Muskogee-Bartlesville, OK combined statistical area.
History


According to a historian, Cherokee County was established in 1907.[4] However, the Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture, states that it was created from the Tahlequah District of the Cherokee Nation in 1906.[3][lower-alpha 1]
The Cherokee moved to this area as a result of the forced relocation brought about by the Indian Removal Act of 1830, also known as Trail Of Tears. The first significant settlements were at the site of Park Hill, where there was already a mission community, and Tahlequah, which became the seat of Cherokee government. However, the Civil War divided the tribe and caused many of the early structures to be destroyed. Non-Indians began moving into the area illegally starting in the mid-1870s, and became the majority by the 1890s.[3]
In 1851, the Cherokee Male Seminary opened in Tahlequah and the Cherokee Female Seminary opened in Park Hill. The latter burned down in 1887 and was rebuilt in Tahlequah. A 1910 fire destroyed the Male Seminary. The Female Seminary became Northeastern State Normal School after statehood in 1907 and is now part of Northeastern State University.[3]
During 1901 – 1903, The Ozark and Cherokee Central Railway, which later became part of the St. Louis and San Francisco Railway was the first to build a track in the county. It boosted the shipment of farm products through the 1920s, but declined during the Great Depression. All rail service ceased in 1942.[3]
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 776 square miles (2,010 km2), of which 749 square miles (1,940 km2) is land and 2.7 square miles (7.0 km2) (3.5%) is water.[5]
The county lies in the foothills of the Ozark Mountains. It includes most of Tenkiller Lake and part of Fort Gibson Lake. The principal river running through it is the Illinois River. Grand River (Oklahoma) forms part of its western boundary.[3]
Major highways
Adjacent counties
- Delaware County (north)
- Adair County (east)
- Sequoyah County (south)
- Muskogee County (southwest)
- Wagoner County (west)
- Mayes County (northwest)
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1910 | 16,778 | — | |
| 1920 | 19,872 | 18.4% | |
| 1930 | 17,470 | −12.1% | |
| 1940 | 21,030 | 20.4% | |
| 1950 | 18,989 | −9.7% | |
| 1960 | 17,762 | −6.5% | |
| 1970 | 23,174 | 30.5% | |
| 1980 | 30,684 | 32.4% | |
| 1990 | 34,049 | 11.0% | |
| 2000 | 42,521 | 24.9% | |
| 2010 | 46,987 | 10.5% | |
| 2020 | 48,078 | 2.3% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790-1960[7] 1900-1990[8] 1990-2000[9] 2010[10] | |||
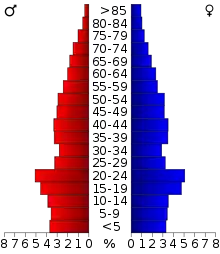
As of the census of 2000, there were 42,521 people, 16,175 households, and 11,079 families residing in the county.[11] The population density was 57 people per square mile (22 people/km2). There were 19,499 housing units at an average density of 26 units per square mile (10/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 56.41% White, 1.20% Black or African American, 32.42% Native American, 0.27% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 2.10% from other races, and 7.56% from two or more races. 4.14% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 92.7% spoke English, 3.8% Spanish and 2.7% Cherokee as their first language. At the publication of the 2020 census, its population grew to 48,078.[1]
In 2000, there were 16,175 households, out of which 32.70% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.50% were married couples living together, 11.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 31.50% were non-families. 25.30% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.52 and the average family size was 3.04. In the county, the population was spread out, with 26.30% under the age of 18, 14.60% from 18 to 24, 25.70% from 25 to 44, 21.50% from 45 to 64, and 12.00% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32 years. For every 100 females there were 96.30 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 92.10 males.
As of 2000, the median income for a household in the county was $26,536, and the median income for a family was $32,369. Males had a median income of $25,993 versus $21,048 for females. The per capita income for the county was $13,436. About 17.00% of families and 22.90% of the population were below the poverty line, including 28.40% of those under age 18 and 13.80% of those age 65 or over. In 2021, the median household income was an estimated $47,421.[12]
Education
Primary & secondary education
Public K-12 school districts in the county include:[13]
K-12 school districts:
- Fort Gibson Public Schools
- Hulbert Public Schools
- Kansas Public Schools
- Locust Grove Public Schools
- Oaks-Mission Public Schools
- Tahlequah Public Schools
- Westville Public Schools
Elementary school districts:
- Briggs Public School
- Grand View Public School
- Keys Public Schools
- Lowrey Public School
- Norwood Public School
- Peggs Public School
- Shady Grove Public School
- Tenkiller Public School
- Woodall Public School
Bureau of Indian Education (BIE)-affiliated tribal school:
Colleges

Northeastern State University is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of Oklahoma as well as one of the oldest institutions of higher learning west of the Mississippi River.[14] Tahlequah is home to the capital of the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma and about 25 percent of the students at NSU identify themselves as American Indian.[15] The university has many courses focused on Native American linguistics, and offers Cherokee language Education as a major.[16] Cherokee can be studied as a second language, and some classes are taught in Cherokee for first language speakers as well.[17]
Politics
Despite the county being home to a significant Native American population and a historically wide Democratic registration advantage, the county has voted Republican in every presidential elections in the 21st century. Donald Trump beat Joe Biden 63%-34% in 2020. However, the county still will on occasion support local Democrats, as it narrowly voted for Democrat Drew Edmondson over Republican Kevin Stitt in the 2018 gubernatorial race.[18]
| Voter Registration and Party Enrollment as of May 31, 2023[19] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Number of voters | Percentage | |||
| Democratic | 10,590 | 40.15% | |||
| Republican | 10,845 | 41.12% | |||
| Others | 4,938 | 18.72% | |||
| Total | 26,373 | 100% | |||
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 11,223 | 63.36% | 6,027 | 34.02% | 464 | 2.62% |
| 2016 | 9,994 | 60.61% | 5,456 | 33.09% | 1,040 | 6.31% |
| 2012 | 8,162 | 57.05% | 6,144 | 42.95% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2008 | 9,186 | 56.08% | 7,194 | 43.92% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2004 | 9,569 | 52.60% | 8,623 | 47.40% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2000 | 6,918 | 47.82% | 7,256 | 50.15% | 294 | 2.03% |
| 1996 | 5,046 | 36.84% | 6,817 | 49.77% | 1,833 | 13.38% |
| 1992 | 4,977 | 32.94% | 6,794 | 44.96% | 3,340 | 22.10% |
| 1988 | 5,838 | 46.99% | 6,483 | 52.18% | 103 | 0.83% |
| 1984 | 7,614 | 58.50% | 5,307 | 40.78% | 94 | 0.72% |
| 1980 | 5,594 | 49.47% | 5,215 | 46.12% | 499 | 4.41% |
| 1976 | 4,443 | 42.06% | 6,006 | 56.85% | 115 | 1.09% |
| 1972 | 7,080 | 69.37% | 2,899 | 28.40% | 227 | 2.22% |
| 1968 | 3,971 | 47.32% | 2,554 | 30.44% | 1,866 | 22.24% |
| 1964 | 3,467 | 43.80% | 4,449 | 56.20% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1960 | 3,571 | 57.06% | 2,687 | 42.94% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1956 | 3,277 | 52.28% | 2,991 | 47.72% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1952 | 3,326 | 50.70% | 3,234 | 49.30% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1948 | 2,785 | 39.59% | 4,249 | 60.41% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1944 | 3,336 | 49.33% | 3,415 | 50.50% | 12 | 0.18% |
| 1940 | 4,128 | 50.98% | 3,952 | 48.80% | 18 | 0.22% |
| 1936 | 2,917 | 42.25% | 3,966 | 57.44% | 21 | 0.30% |
| 1932 | 2,275 | 32.93% | 4,633 | 67.07% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1928 | 2,963 | 54.49% | 2,446 | 44.98% | 29 | 0.53% |
| 1924 | 2,622 | 49.84% | 2,454 | 46.65% | 185 | 3.52% |
| 1920 | 2,524 | 56.48% | 1,859 | 41.60% | 86 | 1.92% |
| 1916 | 1,379 | 42.37% | 1,594 | 48.97% | 282 | 8.66% |
| 1912 | 962 | 43.67% | 1,094 | 49.66% | 147 | 6.67% |
Economy
Since statehood, the economy of Cherokee County has been based on agriculture, especially production of corn, wheat and vegetables. However, the percentage of the population engaged in farming has declined from 62 percent in 1940 to 4.4 percent in 1990. This is largely due to increased urbanization around Tahlequah since World War II. Agriculture remains very important. In 2002, this county ranked first in Oklahoma for the value of nursery and greenhouse crops and seventh in the state for poultry and eggs.[3] Illinois River and Lake Tenkiller tourism are perhaps of greater economic impact than agriculture, and both have lodging, water sports and recreation outfitters, fishing equipment and guides, eating and drinking establishments, campgrounds, festival events, and organizations for the conservation of resources.
Major non-agricultural employers in the county now include the Cherokee Nation government and Northeastern State University,[3]
NRHP sites
The following sites in Cherokee County are listed on the National Register of Historic Places:
|
Notable citizens
- Bamboo Harvester, the horse who played television's Mr. Ed
- Sam Claphan, football player
- Robert Conley, author of numerous books about the Cherokee Indians
- Alice Brown Davis, Principal Chief of the Seminole Tribe of Oklahoma
- Wilma Mankiller, first female Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation
- Jackson Narcomey, Muscogee Creek artist
- Wilson Rawls, author of Where the Red Fern Grows and Summer of the Monkeys
- Hastings Shade, Cherokee traditionalist and author
- Sonny Sixkiller, Cherokee football player
- Wes Studi, Cherokee actor
Notes
- Both of these statements are correct. All modern counties in the former Indian Territory became operational when Oklahoma officially became a state on November 16, 1907. The tribal governments became ineffective during the preceding years, while the new counties were being designated in the Oklahoma Constitution.
References
- "Cherokee County, Oklahoma". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 11, 2023.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 9, 2015. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Burnett, Amanda. "Cherokee County," Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture, 2009. Accessed March 28, 2015.
- Columbia-Lippincott Gazetteer. p. 386
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 27, 2010. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved April 27, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "Quickfacts: Cherokee County, OK". U.S. Census Bureau.
- "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Cherokee County, OK" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 10, 2022. Retrieved July 20, 2022. - Text list
- "General Information". NSU. Archived from the original on August 28, 2009. Retrieved February 20, 2008.
- Agnew, Brad. Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture. "Northeastern State University.""Northeastern State University". Archived from the original on November 19, 2012. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- + auElement.html() +. "NSU, Cherokee Nation Partner to Train and Hire Language Instructors - ICTMN.com". Indiancountrytodaymedianetwork.com. Archived from the original on August 13, 2015. Retrieved July 17, 2015.
- "Cherokee". Ethnologue.
- "Oklahoma Governor Election Results 2018: Live Midterm Map by County & Analysis". Politico.
- "Voter Registration Totals". OK Elections Interactive Statistics Beta. May 31, 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2023.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 28, 2018.
- United States Department of the Interior. National Park Service. "Park Hill Mission Cemetery - National Register of Historic Places Registration Form." December 6, 2006. Accessed March 4, 2016.