The Atlas of Middle-earth
The Atlas of Middle-earth by Karen Wynn Fonstad is an atlas of J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional realm of Middle-earth.[1][2] It was published in 1981, following Tolkien's major works The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion. It provides many maps at different levels of detail, from whole lands to cities and individual buildings, and of major events like the Battle of the Pelennor Fields. The maps are grouped by period, namely the First, Second, and Third Ages of Middle-earth, with chapters on The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings. A final chapter looks at geographic themes such as climate, vegetation, population, and languages around Middle-earth.
 Dust wrapper, first edition | |
| Author | Karen Wynn Fonstad |
|---|---|
| Illustrator | Karen Wynn Fonstad |
| Cover artist | Alan Lee (Second edition) |
| Country | United States |
| Subject | Middle-earth |
| Genre | Atlas |
| Publisher | Houghton Mifflin |
Publication date | 1981 |
| Media type | Hardcover |
| Pages | 190 (210 with notes) |
| ISBN | 0-395-53516-6 |
| OCLC | 24142309 |
| 823/.912 20 | |
| LC Class | G3122.M5 F6 1991 |
The atlas has been warmly received by Tolkien scholars, who have called it both authorized and magisterial, providing in particular a comprehensive set of thematic maps of Middle-earth.
Context
Karen Wynn Fonstad earned a master's degree in Geography, specializing in cartography, from the University of Oklahoma, and worked as Director of Cartographic Services at the University of Wisconsin–Oshkosh before she focused on raising children and writing atlases of fictional worlds.[3][2]
Middle-earth is the fictional world created by the philologist and fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien and presented in his bestselling books The Hobbit (1937) and The Lord of the Rings (1954–1955).[4] Tolkien provided overview maps for each book.[5]
Book
Publication history
The Atlas of Middle-earth was first published in hardback by Houghton Mifflin in the United States in 1981. A revised and updated second edition was published in 1991, after Christopher Tolkien had edited and published eight volumes of The History of Middle-earth following his father's death. HarperCollins republished the revised edition in London in 1994, reprinting it in 1999, 2016, and 2017.[6]
Approach
The Atlas of Middle-earth provides many detailed maps of the lands described in Tolkien's books. The maps are treated as if they are of real landscapes, drawn according to the rules of a real atlas. For each area the history of the land is taken into account, as well as geography on a larger scale; from there maps are drawn.[7] Fonstad's discussion includes suggestions as to the geology that could explain various formations, and points that are contradictory between multiple accounts. Fonstad explains in the atlas, and in her article about it, how she came to decide on such matters. For example, she compares the western Emyn Muil with its two ridges to the Weald with its pair of inward-facing downs (an anticline).[2]
City maps and floor plans for important buildings are included. For example, the city of Minas Tirith is mapped on a single page, the main map giving a perspective view of the whole city, while three insets show the nearly-circular plan of the city, a plan of the citadel in the innermost circle, and a labelled cutaway drawing of the White Tower at the centre of the citadel. A page of text describes the city's geography.[8] Further maps are given of significant events, such as the Battle of the Pelennor Fields in front of Minas Tirith.[9]
Content
The maps are organised first by period, with chapters on the First, Second, and Third Ages of Middle-earth.[10] A chapter covers regional maps, and a short chapter focuses on The Hobbit.[11] A major chapter follows the action in The Lord of the Rings.[12] The book ends with a chapter of thematic maps, illustrating the landforms, climate, vegetation, population, and languages of Middle-earth.[13]
Reception
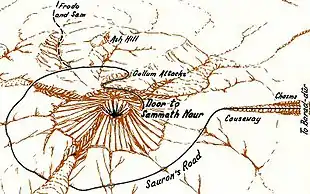
The Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger records that she persuaded Fonstad to write an account for Tolkien Studies of how she researched and created the maps for her Atlas of Middle-earth. Fonstad, while seriously ill, accordingly prepared her last article, "Writing 'TO' the Map" in her final months. Flieger stated "We mourn her passing and we honor her work".[2] The editor of Tolkien Studies, David Bratman, notes that the atlas provides historical, geological, and battle maps, with a detailed commentary and explanation of how Fonstad approached the mapping task from the available evidence.[14] Michael Brisbois, also in Tolkien Studies, describes the atlas as "authorized",[15] while the cartographers Ina Habermann and Nikolaus Kuhn take Fonstad's maps as defining Middle-earth's geography.[16] The Tolkien scholar Luke Shelton calls the book the more popular of the two atlases of Middle-earth, the other being Barbara Strachey's more specific Journeys of Frodo. In his view, the book isn't perfect "but it is certainly helpful", not least as it covers the First and Second Ages.[17]
Stentor Danielson, a Tolkien scholar, notes that Tolkien did not provide the same "detailed textual history" to contextualise his maps as he did for his writings. Danielson suggests that this has assisted the tendency among Tolkien's fans to treat his maps as "geographical fact".[7] He calls Fonstad's atlas "magisterial",[7] and comments that like Tolkien, Fonstad worked from the assumption that the maps, like the texts, "are objective facts" which the cartographer must fully reconcile. He gives as an instance the work that she did to make the journey of Thorin's company in The Hobbit consistent with the map, something that Tolkien found himself unable to do. Danielson writes that in addition, Fonstad created "the most comprehensive set" of thematic maps of Middle-earth, presenting geographic data including political boundaries, climate, population density, and the routes of characters or armies.[7]
See also
References
- Beahm, George (2004). The Essential J. R. R. Tolkien Sourcebook. p. 42. ISBN 978-1-56414-702-8.
- Fonstad, Karen Wynn (with prefatory note by Verlyn Flieger) (2006). "Writing "TO" the Map". Tolkien Studies. 3 (1): 133–136. doi:10.1353/tks.2006.0018. ISSN 1547-3163. S2CID 170599010.
- "About the Author", The Atlas of Pern, New York: Del Rey Books, 1984. Back endpapers.
- Bratman, David (2013) [2007]. "History of Middle-earth: Overview". In Drout, Michael D. C. (ed.). J.R.R. Tolkien Encyclopedia. Routledge. pp. 273–274. ISBN 978-0-415-86511-1.
- Campbell, Alice (2013) [2007]. "Maps". In Drout, Michael D. C. (ed.). The J. R. R. Tolkien Encyclopedia: Scholarship and Critical Assessment. Routledge. pp. 405–408. ISBN 978-0-415-86511-1.
- "'The Atlas of Tolkien's Middle-earth' (editions)". WorldCat. Retrieved 16 January 2023.
- Danielson, Stentor (21 July 2018). "Re-reading the Map of Middle-earth: Fan Cartography's Engagement with Tolkien's Legendarium". Journal of Tolkien Research. 6 (1). ISSN 2471-934X.
- Fonstad1991, pp. 138–139.
- Fonstad1991, pp. 151–153.
- Fonstad1991, pp. 1–33, 37–47, 51–65.
- Fonstad1991, pp. 69–93, 97–113.
- Fonstad1991, pp. 117–176.
- Fonstad1991, pp. 179–189.
- Bratman, David (2007). "Studies in English on the works of J.R.R. Tolkien". The Tolkien Estate. Retrieved 29 October 2021.
- Brisbois, Michael J. (2005). "Tolkien's Imaginary Nature: An Analysis of the Structure of Middle-earth". Tolkien Studies. Project Muse. 2 (1): 197–216. doi:10.1353/tks.2005.0009. ISSN 1547-3163. S2CID 170238657.
- Habermann, Ina; Kuhn, Nikolaus (2011). "Sustainable Fictions – Geographical, Literary and Cultural Intersections in J. R. R. Tolkien'sThe Lord of the Rings". The Cartographic Journal. 48 (4): 263–273. doi:10.1179/1743277411y.0000000024. ISSN 0008-7041. S2CID 140630128.
- Shelton, Luke (19 February 2021). "The Best (And Worst) Reference Books For Tolkien". Luke Shelton. Retrieved 29 October 2021.
Sources
- Fonstad, Karen Wynn (1991). The Atlas of Middle-earth. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 0-618-12699-6.
