Trams in Leipzig
The Leipzig tramway network (German: Straßenbahnnetz Leipzig) is a network of tramways which together with the S-Bahn Mitteldeutschland forms the backbone of the public transport system in Leipzig, a city in the federal state of Saxony, Germany. Opened in 1872, the network has been operated since 1938 by Leipziger Verkehrsbetriebe (LVB), and is integrated in the Mitteldeutscher Verkehrsverbund (MDV).
| Leipzig tramway network | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Trams at Waldplatz, near Red Bull Arena | |||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Leipzig, Saxony, Germany | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
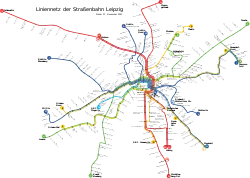
With its 13 lines, route length of 146 km (91 mi) and 522 tram stops, the network is currently the third biggest in Germany, after the Cologne and Berlin tramway networks.
History
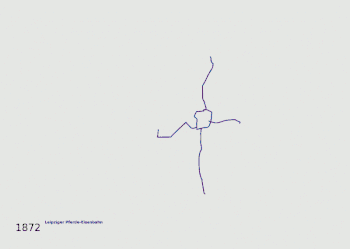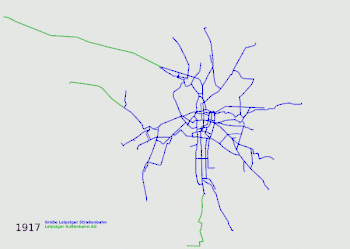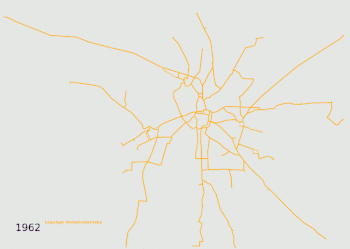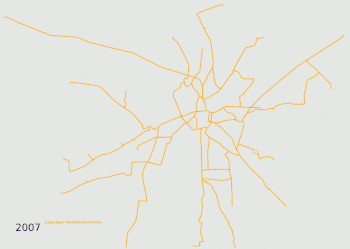 Evolution of the network, the different companies are colour-coded
Evolution of the network, the different companies are colour-coded
Rolling stock
As of 1 January 2020 there were a total of 245 trams and 43 trailers in regular service, consisting of the following:
- 84 Tatra T4D-M (Typ 33c/33d/33h/33i)
- 56 Low floor articulated trams of type NGT8 (Typ 36/36a)
- 49 Low floor articulated trams of type NGTW6 Leoliner (Typ 37/37a/37b)
- 33 Low floor articulated trams of type NGT12-LEI classicXXL (Bombardier Flexity Classic) (Typ 38/38a)
- 23 Low floor articulated trams of type NGT10 Solaris Tramino (Typ 39)
- 43 Low floor trailers of type NB4 (Typ 68a/68b)
In 2018 Leipzig sold 20 used trams to the Ukrainian city Dnipro, to be used on its tram routes.[1]
| By transport mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By size (list) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change of gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By location | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gallery
 Replica of horse tram in operation
Replica of horse tram in operation A 1914/15 postcard depicting a tram
A 1914/15 postcard depicting a tram Some vehicles, such as this horse tram, are preserved in the tram museum
Some vehicles, such as this horse tram, are preserved in the tram museum Trams are used to bring passengers to Leipzig Trade Fair, 1972
Trams are used to bring passengers to Leipzig Trade Fair, 1972 Tatra T4 tram, June 1993
Tatra T4 tram, June 1993 Modern low-floor tram
Modern low-floor tram Service vehicle
Service vehicle
References
- (in Ukrainian) Dnipro tram fleet will be replenished with cars from Germany, National industrial portal (2 October 2021)
- Bauer, Gerhard; Kuschinski, Norbert (1993). Die Straßenbahnen in Ostdeutschland [The Tramways in East Germany]. Vol. Band 1: Sachsen [Volume 1: Saxony]. Aachen, Germany: Schweers + Wall. ISBN 3921679796. (in German)
- Schwandl, Robert (2012). Schwandl's Tram Atlas Deutschland (in German and English) (3rd ed.). Berlin: Robert Schwandl Verlag. pp. 94–97. ISBN 9783936573336.
External links
![]() Media related to Tram transport in Leipzig at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tram transport in Leipzig at Wikimedia Commons
- Leipzig database / photo gallery and Leipzig tram list at Urban Electric Transit – in various languages, including English.
- Leipzig database / photo gallery at Phototrans – in various languages, including English.