Typhoon Ketsana
Typhoon Ketsana, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Ondoy, was the second-most devastating tropical cyclone of the 2009 Pacific typhoon season, causing $1.15 billion in damages and 665 fatalities, only behind Morakot earlier in the season, which caused 789 deaths and damages worth $6.2 billion. Ketsana was the sixteenth tropical storm, and the eighth typhoon of the season. It was the most devastating tropical cyclone to hit Manila,[1] surpassing Typhoon Patsy (Yoling) in 1970.
 Ketsana prior to peak intensity on September 28 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | September 24, 2009 |
| Dissipated | September 30, 2009 |
| Typhoon | |
| 10-minute sustained (JMA) | |
| Highest winds | 130 km/h (80 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 960 hPa (mbar); 28.35 inHg |
| Category 2-equivalent typhoon | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 165 km/h (105 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 955 hPa (mbar); 28.20 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 665 direct |
| Missing | 439 |
| Damage | $1.15 billion (2009 USD) |
| Areas affected | Philippines, China, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 2009 Pacific typhoon season | |
Ketsana formed early about 860 km (530 mi) to the northwest of Palau on September 23, 2009. The depression remained weak and was downgraded to a low pressure area later that day by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and after drifting through extremely favorable conditions, it intensified the next day and was categorized as Tropical Depression by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) and was given the name Ondoy after entering the Philippine Area of Responsibility. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert on the depression. It was then upgraded to a tropical depression by the JMA later that morning before the JTWC followed suit early on September 25, designating the depression as 17W. Soon, Ketsana was upgraded to a tropical storm before passing over the Philippines. As it moved into the South China Sea the storm intensified while moving toward the west, and was categorized as a Severe Tropical Storm by the JMA.
President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo declared a "state of calamity" encompassing most of Luzon after at least 86 people were initially reported dead in landslides and other incidents.[2] Flood water levels reached a record 20 feet (6.1 m) in rural areas. As of October 24, 2013, at least 464 deaths in the Philippines were officially reported from the typhoon.[3][4][5][6][7][8][9]
Meteorological history

Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On September 23, 2009, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), reported that a seasonal tropical depression had formed about 860 km (530 mi) to the northwest of Palau.[10] The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) then reported later that day that the depression had a developing low-level circulation center and was in a favorable environment with low vertical wind shear.[11] The JMA then reported that the depression had weakened into an area of low pressure.[12] However, early the next day, as deep convection started to consolidate around the low-level circulation center, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) reported that the low-pressure area had become a tropical depression and assigned it a local name of Ondoy.[13][14] Later that morning, the JTWC issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert as central convection had continued to organize around a consolidating elongated but exposed low-level circulation center.[15] The JMA then re-upgraded Ondoy to a tropical depression later that morning before the JTWC followed suit early on September 25, designating it as Tropical Depression 17W when it was located about 400 nm east of Manila in the Philippines.[16][17] At this stage, the system was moving along the southern side of the subtropical ridge and had good poleward outflow into a tropical upper tropospheric trough (TUTT) cell.[17]

Throughout September 25 the intensification of Ondoy was hampered by the system moving into an area of moderate vertical wind shear and by an upper-level trough of pressure that was moving over the system.[18] But later that day the JTWC upgraded it to a tropical storm despite its low level circulation center being partially exposed.[19] The JMA followed suit early the next day, assigning the international name of Ketsana and the international designation of 0916 to the storm.[20] PAGASA then reported that Ketsana had made landfall on Northern Luzon near the boundary of the Philippine provinces of Aurora and Quezon. As a result of making landfall, its low-level circulation center had become fully exposed, but as the storm moved into the South China Sea, it dramatically deepened and expanded while moving west and was upgraded to a severe tropical storm by the JMA early on September 27.
During September 27, Ketsana gradually developed further and was upgraded to a typhoon by the JTWC and the JMA early the next day, as multiple convective bands were continuing to consolidate more tightly around the low-level circulation center, leading to the formation of a disorganized eye. Typhoon Ketsena then intensified quickly under favorable conditions, reaching peak windspeeds later that day of 165 km/h (103 mph) (1-min winds) and 140 km/h (87 mph) (10-min winds) which made it a Category 2 typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson scale. Ketsana then made a second landfall on Quảng Nam in Vietnam, at 0600 UTC on September 29 at its peak intensity. It then rapidly weakened into a Severe Tropical Storm, with the JTWC issuing its last advisory later that day; however, the JMA continued to monitor Ketsana as a Severe Tropical Storm until later that day, when it downgraded it to a Tropical Storm before further downgrading it to a Tropical Depression early the next day when the center of the depression was located over Laos. The JMA monitored the storm as a weak tropical depression until late on September 30, when it released its final advisory.
Preparations
Philippines
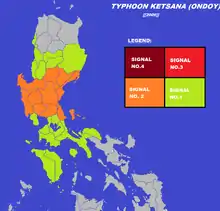
On September 24, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) placed the provinces of Aurora, northern Quezon, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, and Catanduanes under Public Storm Warning Signal#1 which meant that winds of 30–60 km/h (19–37 mph) were expected to affect those areas within 36 hours. PAGASA raised public storm signal no. 2 for the provinces of Catanduanes, Camarines Norte and Camarines Sur, and Polillo Island in Quezon.[21] On September 28, PAGASA lifted all public storm signals in the country as Ketsana left the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) the same day.[22] After the floods struck, some were critical of the government's failure to predict the scale of the disaster or to lessen the damage it caused.[8]
Highest Public Storm Warning Signal
| PSWS# | Luzon | Visayas | Mindanao |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Pangasinan, Nueva Vizcaya, Quirino, Aurora, Nueva Ecija, Zambales, Tarlac, Pampanga, Bulacan, Northern portion of Quezon including Polillo Island | None | None |
| 1 | Metro Manila, Bataan, Rizal, Cavite, Laguna, Batangas, Camarines Norte, Marinduque, Mindoro Provinces, Lubang Island, Ilocos Sur, La Union, Benguet, Isabela, Mt. Province, Ifugao, Southern portion of Quezon | None | None |
China
Late on September 27, both the Hong Kong Observatory and the Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau placed Hong Kong and Macau under the Standby Signal No.1.[23][24] The Bureau then considered hoisting the Strong Wind Signal 3, but decided it was not needed for Hong Kong, while Macau hoisted it early the next day. These warnings were kept in force until later that day when all warnings were lowered.[23] On September 29 it was announced that parts of southern China would be placed under an orange warning with certain regional meteorological bureaus entering a level 3 emergency response.
Vietnam
On September 27, the Vietnam National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting[25] issued a public storm warning signal named "Number 9." The Vietnamese government evacuated some 170,000 people. The government instructed residents to secure their homes with fortified hard wood and sandbag roofs. Also, authorities mobilized several thousand military personnel and police to help residents evacuate from the typhoon's path. Fishing vessels were called to return to their ports.[26] This caused thousands of crops to fail.
Impact
Philippines
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tropical Storm Ondoy (Ketsana) Rainfall Distribution over Philippines | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement station |
Precipitation | Date | Pre-Post(mm) | |
| (mm) | (in) | |||
| PAGASA Science Garden, Quezon City, NCR | 454.9 mm | 17.91 inches | September 26, 2009 | 94.0 mm |
| Tanay, Rizal, CALABARZON | 331.7 mm | 13.06 inches | September 26, 2009 | 41.5 mm |
| Manila, Metro Manila, NCR | 258.6 mm | 10.18 inches | September 26, 2009 | 41.4 mm |
| Ambulong, Batangas/Laguna, CALABARZON | 234.4 mm | 9.23 inches | September 26, 2009 | 49.5 mm |
| Bagasbas, Daet, Camarines Norte, Bicol | 204.5 mm | 8.05 inches | September 25, 2009 | 5.8 mm |
| Infanta, Quezon, CALABARZON | 176.2 mm | 6.94 inches | September 26, 2009 | 98.6 mm |
| (PSW), Barrio Barretto, Zambales, Central Luzon | 159.3 mm | 6.27 inches | September 26, 2009 | 75.2 mm |
| Subic,W.S., Zambales, Central Luzon | 127.8 mm | 5.03 inches | September 26, 2009 | 50.3 mm |
| Clark AFB, Angeles City, Pampanga, Central Luzon | 109.0 mm | 4.29 inches | September 26, 2009 | 25.4 mm |
| Iba, Zambales, Central Luzon | 103.9 mm | 4.09 inches | September 26, 2009 | 39.9 mm |

Ketsana caused widespread flash flooding in the cities of Manila, Caloocan, Marikina, Malabon, Muntinlupa, Quezon, Makati, Pasay, Pasig, Taguig, Valenzuela, and San Juan. Flooding also occurred in the nearby provinces of Bulacan, Rizal, Laguna, and other Calabarzon areas. Major roads were rendered impassable because of huge flood currents and clogged cars.[28] Air flights were canceled because of heavy rains.
Earlier, power interruptions were reported in Camarines Norte and minor landslides occurred in Camarines Sur.[28]
EDSA was closed because of heavy flooding. Defense secretary and National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council (NDCC) chairman Gilbert Teodoro asked the DOTC to keep MRT and LRT lines operational to accommodate stranded passengers.[29]
On the afternoon of September 26, Gilbert Teodoro declared an overall state of calamity in Metro Manila and the nearby 25 provinces in Luzon hit by the typhoon, allowing officials to utilize emergency funds for relief and rescue. Army troops, police, and civilian volunteers were deployed to rescue victims.[30] The Philippine National Red Cross and Philippine Coast Guard dispatched teams to rescue stranded and trapped people.[31] At that time, the average height of flooding was from two feet to waist high, and in some areas more than six feet.[32] Even Malacañang Palace was opened to those who were in need. The landslides and severe flooding left at least 246 people dead and 38 others missing.[8][27] Public and private roads were clogged by vehicles stuck in floodwater.[8] Thousands of motorists and more than 500 passengers were stranded at the North Luzon Expressway (NLEx). Distress telephone calls and emails from thousands of Metro Manila residents and their worried relatives flooded television and radio stations overnight as most of the power supply, communication, and water supply were lost.[33] Ketsana also caused Ninoy Aquino International Airport (NAIA) closed for almost a day.[34]
The economic region of Metro Manila and many adjoining provinces incurred damages to both infrastructure and agriculture. As of September 28, 2009, total damages from Ketsana were estimated at $100 million.[3][4][8] Internet cafés, entertainment plazas, banks, food stores, building agencies, and stores were soaked with water and mud.[8][35] Many people were warned of leptospirosis.
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
Marikina, part of Metro Manila, was the most devastated region in the Philippines: almost all of the city's area was submerged in water up to ten feet deep and tons of knee-deep mud. During the typhoon, the Marikina River broke its banks and transformed streets into rivers.[36] Marikina residential areas, particularly Provident Village, were badly affected by flooding; at least eight people were found dead.[37] Marikina itself recorded 78 deaths, the highest among Metro Manila cities.[38]
At the height of the flooding, around 100,000 liters of bunker oil from the paper manufacturing firm Noah's Paper Mill in Marikina spilled. Most of the oil battered the city's barangays and a relatively small amount was washed into the basement of the SM City Marikina shopping mall. The spill later complicated rescue efforts in the city.[39] Over a two-day period starting on September 29, the National Power Corporation Flood Forecasting and Warning System released 500 cubic meters per second of stored water from the Angat Dam in Bulacan. The dam had accumulated 100 cubic meters per second when Ketsana hit the province.[40] Mandaluyong also recorded more than 6 feet (1.8 m) of flooding, especially in Gen. Kalentong St., where flooding was more than 10 feet (3.0 m) deep,[41] badly affecting the local campus of Arellano University. The street recorded the highest flooding outside the Marikina area.
In Mindanao, several towns in Cotabato City and nearby Sultan Kudarat municipalities were submerged. The closing of the national highway in Bulalo, Cotabato City led to the isolation of connecting towns for several days.[42]
Vietnam

Ketsana's maximum winds were reported at 167 km/h (104 mph) with gusts as strong as 204 km/h (127 mph) as it crossed over the South China Sea and approached land.[43] Two persons were killed by falling trees and electric lines.[44]
Heavy rains and strong winds lashed a 400 km (250 mi) stretch of coastline from Thừa Thiên–Huế to Quảng Ngãi, with rainfall causing massive flood surges in Huế, Bình Định, and Kon Tum provinces. Record high water levels were reported in rivers of Quảng Ngãi, Kon Tum, and Gia Lai.[45] Airports, schools, communications, and electricity in the affected area were shut down. Strong winds also destroyed parts of the north–south high voltage powerline, the backbone of Vietnam's electricity grid. In total the typhoon killed 179 people in Vietnam, 23 during the first hours after landfall; 8 people were missing and 1,140 injured.[46][26][47][48][49] Total economic losses caused by Ketsana were 16.07 trillion VND (US$896.1 million).[n 2][46][50]
Cambodia
The weakening typhoon struck northeastern Cambodia as one of the most severe storms ever to lash the country, with the worst damage in Kampong Thom Province in central Cambodia. Death tolls reached 43 people.[51] More than 66,000 families were forced from their homes by floodwaters.
Laos
There was major flooding in the southern and central provinces of Laos, and much of the country experienced heavy rain and light flooding. Water was up to knee height in the province of Saravane, and at least 26 people died. The cities of Savannakhet and Pakse were worst affected since they were directly on the pathway of the typhoon and directly on the Mekong River. In the Si Phan Don area in Champassak Province, some people took refugee on the roofs of their houses. The floods devastated rice fields and homes. Attapeu was the worst hit province, with nearly 90% of the province affected.
Thailand
As the weakening Ketsana moved through the country, widespread heavy rainfall and flash flooding were reported in 40 provinces.[52] The heavy rainfall also helped to fill up natural reservoirs within the country.[52] The depression partially damaged 4680 houses and destroyed 44, as well as 820,000 acres (330,000 ha) of agricultural land.[52] Ketsana also injured one person and killed two before moving out of the country as an area of low pressure and dissipating on October 3 over the Andaman Sea.[52] Total damages were estimated at just over $20,000,000.[52] Three dams in Chai-ya-poom were damaged by the heavy rainfall, while in Pattaya nine boats were sunk waves reported to be over two metres high.[53]
Aftermath


The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) documented a record-high amount of rainfall in 24 hours at 455 millimetres (17.9 in). They also reported that Ketsana's rainfall was recorded from 8 am PST/ 0000 (UTC) of Saturday (September 26) to 8 am PST/ 0000 (UTC) of Sunday (September 27). The amount of rainfall recorded for six hours, which was 341.3 millimetres (13.44 in), was comparable to the 24-hour rainfall in 1967.[54] The damage to property was estimated to be P6 billion, including P4.1 billion in damage to infrastructure, P1.9 billion in damage to schools, and P882.525 million in damage to agriculture.[55][56]
According to the Bureau of Agricultural Statistics of the Department of Agriculture (DA), an estimated 126,721 hectares of rice-farming land were destroyed, which would affect almost 3% of the country's annual expected rice production. Added to this, Ketsana devastated some 1,374 hectares of corn plantations.[57]
Some 48 hours after Ketsana struck Metro Manila, the Philippine government appealed to the international community and the United Nations for help.[58] Various United Nations agencies, the United States, the People's Republic of China, and Japan provided emergency assistance to the victims of the typhoon in the Philippines.[59] The United States donated $50,000, while China and Japan gave $10,000 and $20,000 respectively. Australia provided $ 1 million and Thailand also provided humanitarian services.[60][61] Germany donated €500,000[62] as well as Taiwan donated $50,000.[63] The United States also deployed Marines to help rescue victims in the Cainta and Pasig areas, as well as for search and retrieval operations for dead bodies.[64][65][66] Special Forces Operators and other U.S. service members attached to Joint Special Operations Task Force Philippines also assisted in aid efforts.[67] An additional 3,000 U.S. troops were expected to arrive to assist in relief efforts.[68] U.S. Nonprofit international disaster relief organization AmeriCares shipped $3.2 million worth of medical aid for Ketsana survivors.[69] An Israeli search and rescue party, and doctors, nurses, and paramedics were sent to the Philippines.[70]
In the Philippines, the National Disaster Coordinating Council (NDCC) headed the rescue and relief operations for the citizens affected by Ketsana's flooding. There was also a counterpart private-sector effort among companies and NGOs to provide and coordinate relief activities in various areas.
The Philippine Army deployed about 1,000 soldiers in Metro Manila and surrounding provinces to help in operations.[71] The Philippine Red Cross and the Philippine Coast Guard also deployed teams in rubber boats to rescue people stranded in their homes.[8][72] On the Internet, citizens turned to various social networks like Twitter, Facebook, Plurk, and Multiply to share news updates and forward cries for help from people trapped in the floods. Google Maps was used to pinpoint locations of stranded people while various blogs and websites shared information on how to donate money and in-kind goods.[73] Donations arrived from all over the world and were sorely needed.
After Typhoon Ketsana and Typhoon Parma, the government of Japan gave the Philippines a P1.7-billion (3.350 billion yen) grant to improve the country's weather monitoring and information dissemination system.[74][75]
International Aid to the Philippines

.svg.png.webp) Australia:A$11,000,000
Australia:A$11,000,000.svg.png.webp) Canada:C$5,100,000, aid packages, water purification systems [76]
Canada:C$5,100,000, aid packages, water purification systems [76]
 China:$140,000[80]
China:$140,000[80] Japan:$20,000
Japan:$20,000 European Union:€2,000,000[81]
European Union:€2,000,000[81] Germany:€500,000
Germany:€500,000 Israel:Medical Teams
Israel:Medical Teams Malaysia:20 tonnes of food aid.[82]
Malaysia:20 tonnes of food aid.[82] New Zealand:NZ$25,000[83]
New Zealand:NZ$25,000[83] Singapore:$20,000 and 3,200 water purification sets
Singapore:$20,000 and 3,200 water purification sets South Korea:Aid workers[84]
South Korea:Aid workers[84] Taiwan:$50,000
Taiwan:$50,000 Thailand:Humanitarian Services
Thailand:Humanitarian Services United States:$3,250,000
United States:$3,250,000
- US government:$50,000
- US military:USS Tortuga (LSD-46) and USS Harpers Ferry (LSD-49), 3rd Marine Expeditionary Force plus 20 USMC personnel, a helicopter and four Zodiac inflatable boats.[85]
- AmeriCares:$3.2 million
Paracel Islands incident
Vietnamese officials and media reported that Chinese naval forces mistreated Vietnamese fishermen who tried to take shelter from the typhoon in the disputed Paracel Islands. The Chinese Navy allegedly fired on Vietnamese fishing boats when they tried to take shelter at Tru Cau island to escape Typhoon Ketsana and after being allowed to stay on the island for several days, they were robbed and beaten by Chinese forces before leaving.[86] Vietnam and China have an agreement that fishermen from either country can ride out storms in the other's territory.
Nguyen Viet Thang, chairman of the Vietnam Fishery Association, said his organization was preparing an official protest to China over the incidents. Colonel Bui Phu Phu, vice chief of the border guard forces of the fishermen's home province of Quảng Ngãi, confirmed the accusations and said the Ministry of Foreign Affairs should send a protest to China.[87]
An official at the Chinese embassy in Hanoi said China had no comment on the accusations.
Retirement
Due to the damage and deaths caused by the storm, the names Ketsana and Ondoy were later retired. The committee selected the name Champi to replace Ketsana on the Western Pacific basin name lists beginning in 2011. It was first used in the 2015 season. In June 2012, PAGASA chose the name Odette to replace Ondoy, which was first used in 2013. But later in 2021, the name Odette was retired after its usage due to the number of deaths and damages it caused.
Removal of Prisco Nilo
When President Benigno Aquino III took office in June 2010, PAGASA Chief Administrator Prisco Nilo was fired and removed from his post on August 6.[88] The agency accused Nilo of having a supposedly fool-proof forecast of Typhoon Ketsana as the typhoon struck over Metro Manila. Aquino adds lack of disaster preparedness and slow installation of Doppler weather radar and other equipment, and slow voluntary response that left the agency unmodernized.
Nilo left PAGASA after Graciano Yumul, Jr., took Nilo's vacant seat. This similar accusation also happened on the aftermath of Typhoon Conson (Basyang) in July 2010. Nilo was in Australia for his new post as weather forecaster of the Bureau of Meteorology (BOM).
See also
- Typhoons in the Philippines
- Typhoon Vamco (Ulysses, 2020), a devastating Category 4 typhoon that struck Luzon bringing violent rainfall and high flooding, affecting also the capital Metro Manila and the worst floods since Ketsana.
- Tropical Storm Fung-wong (Mario, 2014), a tropical storm that hit Northern Luzon on the 5th anniversary of Typhoon Ketsana.
- Typhoon Rammasun (Glenda, 2014), a destructive typhoon that brought damaging winds over Southern Luzon including Metro Manila.
- Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda, 2013), deadliest tropical cyclone to strike the Philippines in modern history
- Typhoon Nari (Santi, 2013)
- Typhoon Conson (Basyang, 2010)
- Typhoon Parma (Pepeng, 2009), a typhoon that hit Northern Luzon just right after Ketsana devastated the Philippines capital and killed just as many as Ketsana
- Typhoon Durian (Reming, 2006)
- Typhoon Xangsane (Milenyo, 2006)
- Typhoon Angela (Rosing, 1995)
- Typhoon Patsy (Yoling, 1970)
- Typhoon Ruby (Unsang, 1988)
- Typhoon Nesat (Pedring, 2011), a Category 4 typhoon which made landfall the day after the 2nd anniversary of Typhoon Ketsana, which caused widespread blackouts and flooding over Metro Manila.
- Typhoon Doksuri (Maring, 2017), a typhoon that made a similar track.
- Typhoon Noru (Karding, 2022), a Category 5 super-typhoon that hit Northern Luzon on the 13th anniversary of Typhoon Ketsana.
- Typhoons in Central Vietnam
Notes
- Total damages figure includes agriculture, infrastructure, casualties, etc. damages.
- 2009 statistics
References
- "Metro Manila, 25 provinces placed under state of calamity". GMANews.TV. September 26, 2009. Archived from the original on September 29, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Philippines storm leaves 106 dead — report". Independent Online. September 28, 2009. Archived from the original on May 22, 2008. Retrieved September 27, 2009.
- Cerojano, Teresa (September 28, 2009). "140 die in Philippine storm, toll expected to rise". The Washington Times. Associated Press. Retrieved October 1, 2009.
- Evangelista, Katherine (September 28, 2009). "SAYS NDCC: P109-M worth of infrastructure, crops damaged: Death toll up to 100". INQUIRER.net. Archived from the original on September 29, 2009. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- Weaver, Matthew (September 28, 2009). "Philippines storm death toll rises". The Guardian. London. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Philippines 'overwhelmed' as new storm threatens after Ketsana". The Times. London. September 28, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Philippine flood death toll rises". London: The Daily Telegraph. September 28, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- Tharoor, Ishaan (September 29, 2009). "The Manila Floods: Why Wasn't the City Prepared?". Time. Archived from the original on October 2, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Death toll from Ondoy rises to 337". ABS-CBN News. Agence France-Presse. October 9, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "JMA WWJP25 Advisory 2009-09-23 00z". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 23, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and Southern Pacific Oceans 2009-09-23 06z". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 23, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "JMA WWJP25 Advisory 2009-09-23 12 UTC". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 23, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and Southern Pacific Oceans 2009-09-23 14z". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 23, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "PAGASA Tropical Cyclone Advisory 2009-09-24 03z". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. September 24, 2009. Archived from the original on July 26, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert 2009-09-24 04z". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 24, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "JMA WWJP25 Advisory 2009-09-24 06 UTC". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 24, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "Prognastic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W 2009-09-25 03z". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 25, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "Prognastic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W 2009-09-25 15z". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 25, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "Tropical Storm 17W JTWC Advisory 2009-09-25 21z". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 25, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "JMA Tropical Cyclone Advisory: 2009-09-26 00z". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 26, 2009. Archived from the original on May 17, 2008. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- "'Ondoy' intensifies into tropical storm, 4 areas under signal 2". GMA News. September 25, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Pagasa lifts all Storm Signals in RP; more rains to follow as 'Ondoy' exits". GMA News. September 28, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Tropical Cyclone Warning Signals Hoisted in September 2009". Hong Kong observatory. September 29, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Tropical Cyclone advisory Macau 2009-09-27 21z". Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau. September 27, 2009. Archived from the original on August 8, 2009. Retrieved September 27, 2009.
- "Vietnam National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting".
- "Yahoo! News". Ph.news.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on October 1, 2009.
- "Situation Report: Ondoy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 30, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Ubalde, Joseph Holandes (September 26, 2009). "Storm 'Ondoy' makes landfall, causes widespread flooding". GMA News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Ubalde, Joseph Holandes (September 26, 2009). "MRT, LRT open for 24 hours to accommodate stranded commuters". GMA News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Metro Manila, 24 provinces placed under state of calamity". GMA News. September 26, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Andrade, Jeannette (September 27, 2009). "Red Cross rubber boats rescue people on roofs". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on September 30, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Floods rise to 6 feet in Rizal; residents ask for rescue". GMA News. September 26, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Santos, Jose Bimbo (September 29, 2009). "Metro Manila, surrounding areas' power, water supply still below normal". BusinessWorld. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Libu-libong pasahero, na-stranded sa NAIA dahil sa pananalasa Bagyong Ondoy" (in Tagalog). September 27, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Arquiza, Yasmin (September 28, 2009). "Both rich and poor suffered from Ondoy's wrath". GMA News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Leithead, Alastair (September 28, 2009). "Devastation in Manila flood zone". BBC News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- de los Santos, Melissa (September 28, 2009). "8 dead in Provident Village, Marikina City". GMA News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Aragones, Sol (September 28, 2009). "78 dead in devastated Marikina". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Recuenco, Aaron (September 28, 2009). "Oil spill complicates Marikina rescue efforts". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- Kim Tan. "Bulacan residents warned of Angat Dam water release". Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Help for Typhoon Victims in the Philippines". Archived from the original on October 1, 2009.
- Señase, Charlie (September 28, 2009). "'Ondoy' worsens floods in Mindanao town, villages". Inquirer Mindanao. Archived from the original on September 29, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Typhoon Ketsana slams into Vietnam". CNN. September 29, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- en:Typhoon_Ketsana, oldid 1034748289
- "Lũ miền Trung — Tây Nguyên vượt mọi kỷ lục" (in Vietnamese). VietNamNet. September 29, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- 2009 VIETNAM REPORT
- "Typhoon Ketsana kills over 160 in Vietnam". Sify. October 5, 2009. Archived from the original on October 9, 2010. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Chính trị — Xã hội — Bạn đọc Tuổi Trẻ cứu trợ khẩn cấp người dân vùng lũ bị cô lập". Tuoi Tre Online (in Vietnamese). October 1, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "2nd typhoon gathers strength in Southeast Asia". CBC News. October 1, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "LHQ: Bão số 9 làm Việt Nam thiệt hại 785 triệu USD". VietNamNet (in Vietnamese). October 7, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Disaster authority revises toll from Ketsana, warns of food shortages". The Phnom Penh Post. October 26, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- J Weyman (December 18, 2009). "ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee 42nd Session Country Report:Thailand" (PDF). Thai Meteorological Department. World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- Xiong Tong (September 30, 2009). "Several provinces in Thailand hit by Ketsana depression". Xinhua. Archived from the original on October 3, 2009. Retrieved December 30, 2009.
- "Flood blamed on record rainfall". Manila Bulletin. September 28, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Death toll from storm 'Ondoy' continues to rise — NDCC". GMA News.TV. September 28, 2009. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- "'Ondoy' damage P4.6B and counting—NDCC". INQUIRER.net. September 29, 2009. Archived from the original on October 2, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Crop losses surge to four times earlier estimates". GMA News. September 29, 2009. Retrieved September 30, 2009.
- Balana, Cynthia; Jocelyn Uy (September 28, 2009). "Typhoon-Ravaged Philippines Asks for Int'l Help". Inquirer.net. Archived from the original on February 22, 2012. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- dpa (September 28, 2009). "Toll surpasses 200 as Philippines struggles after flood — Summary". Earth Times.org. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- "Thailand to provide humanitarian aid to Philippines". September 29, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "China gives $100,000 more for Ondoy victims". Inquirer.net. September 29, 2009. Archived from the original on October 1, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "Germany gives €500,000 for Ondoy victims". Philippine Daily Inquirer. September 30, 2009. Archived from the original on October 1, 2009. Retrieved October 1, 2009.
- "Taiwan donates US$50,000 for typhoon victims in the Philippines". Taiwan News. September 29, 2009. Retrieved October 1, 2009.
- See, Aie Balagtas (September 29, 2009). "US gives additional $50,000 aid for 'Ondoy' victims". GMA News. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- "US helps with Philippines typhoon". Taiwan News. Associated Press. October 3, 2009. Retrieved October 2, 2009.
- Josh Levs (October 2, 2009). "Filipinos preparing for worst, 'praying' for best from Parma". CNN. Retrieved October 2, 2009.
- Donna Miles; Lt. j.g. Theresa Donnelly (September 30, 2009). "Military Provides Rescue, Humanitarian Support in Pacific". America Forces Press Service. Retrieved October 2, 2009.
Meanwhile, members of Joint Special Operations Task Force Philippines assisted the Armed Forces of the Philippines in rescuing 52 people stranded by massive flooding during Tropical Storm Ketsana earlier this week. The storm, known locally as Tropical Storm Ondoy, struck in the Manila area Sept. 27 and 28. The floods displaced hundreds of thousands of people, and the most recent reports indicate that nearly 100,000 people have been relocated, according to Philippines Disaster Management Services. Members of Navy SEAL teams and Naval Special Boat Teams 12 and 20, and U.S. medical troops attached to the Philippines task force responded, working with the island nation's military and government officials to rescue people from rooftops, deliver food and distribute medical supplies, officials reported.
- Al Labita (October 3, 2009). "US storms troops into the Philippines". Asian Times. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 2, 2009.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - "AmeriCares Sends Aid to the Philippines to Help Typhoon Ketsana Survivors". Reuters. September 28, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- Yael Levy (August 9, 2010). "Israel to aid Philippines in post-storm efforts". Ynetnews.
- "1,000 soldiers join rescue operations in Metro Manila, 3 provinces". The Philippine Star. September 28, 2009. Archived from the original on September 17, 2012. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Red Cross rubber boats rescue people on roofs". INQUIRER.net. September 27, 2009. Archived from the original on September 30, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Calls for help flood cyberspace as 'Ondoy' pummeled Luzon". GMANews.TV. September 27, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Japan gives RP P1.7B for new weather radar - INQUIRER.net, Philippine News for Filipinos". Archived from the original on November 4, 2009. Retrieved August 16, 2010.
- News, ABS-CBN. "PAGASA gets 3 Doppler radars from Japan".
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - "WORLD VISION CANADA | World Vision expands Typhoon Ketsana response across three countries". Newswire.ca. September 30, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Canada pledges $5 million to flood relief in Philippines". InsideToronto. October 1, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Philippines typhoon victims offered Canadian visas". Global Visas. October 2, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- Staff Writer (September 30, 2009). "$100,000 aid for Philippines". Winnipeg Free Press. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "China hikes donation to Philippine storm victims to $140,000". People's Daily Online. September 30, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "EU sends emergency aid to typhoon-hit Philippines". EU Business News. September 29, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Malaysia sends aid to Philippines". NST Online. October 16, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Caritas Aotearoa New Zealand pledges $25,000 to Philippines flooding". Caritas Aotearoa New Zealand. September 29, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "South Korean aid workers and Filipino soldiers..." Getty Images. September 30, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Marines, sailors bring aid to Philippines". ReliefWeb. October 2, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- James Wray and Ulf Stabe (October 14, 2009). "Vietnamese fishermen say they were mistreated by China". Monsters and Critics. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- "Chấm dứt ngay việc cướp tài sản, đánh đập ngư dân VN" (in Vietnamese). VietNamNet. October 16, 2009. Archived from the original on December 20, 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- Sisante, Jam (August 6, 2010). "Aquino replaces PAGASA chief". GMANews.TV. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
External links
- RSMC Tokyo – Typhoon Center
- Best Track Data of Typhoon Ketsana (0916) (in Japanese)
- Best Track Data (Graphics) of Typhoon Ketsana (0916)
- Best Track Data (Text)
- JTWC Best Track Data of Typhoon 17W (Ketsana)
- 17W.KETSANA from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
- ReliefWeb's main page for this event.
- TV Patrol World's news report on the typhoon on YouTube - video from ABS-CBN

