Thrust vectoring
Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket, or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to control the attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle.

In rocketry and ballistic missiles that fly outside the atmosphere, aerodynamic control surfaces are ineffective, so thrust vectoring is the primary means of attitude control. Exhaust vanes and gimbaled engines were used in the 1930s by Robert Goddard.
For aircraft, the method was originally envisaged to provide upward vertical thrust as a means to give aircraft vertical (VTOL) or short (STOL) takeoff and landing ability. Subsequently, it was realized that using vectored thrust in combat situations enabled aircraft to perform various maneuvers not available to conventional-engined planes. To perform turns, aircraft that use no thrust vectoring must rely on aerodynamic control surfaces only, such as ailerons or elevator; aircraft with vectoring must still use control surfaces, but to a lesser extent.
In missile literature originating from Russian sources,[1] thrust vectoring is often referred to as gas-dynamic steering or gas-dynamic control.
Methods
Rockets and ballistic missiles
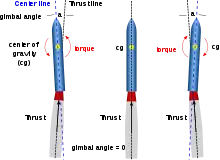


Nominally, the line of action of the thrust vector of a rocket nozzle passes through the vehicle's centre of mass, generating zero net torque about the mass centre. It is possible to generate pitch and yaw moments by deflecting the main rocket thrust vector so that it does not pass through the mass centre. Because the line of action is generally oriented nearly parallel to the roll axis, roll control usually requires the use of two or more separately hinged nozzles or a separate system altogether, such as fins, or vanes in the exhaust plume of the rocket engine, deflecting the main thrust. Thrust vector control (TVC) is only possible when the propulsion system is creating thrust; separate mechanisms are required for attitude and flight path control during other stages of flight.
Thrust vectoring can be achieved by four basic means:[2][3]
- Gimbaled engine(s) or nozzle(s)
- Reactive fluid injection
- Auxiliary "Vernier" thrusters
- Exhaust vanes, also known as jet vanes
Gimbaled thrust
Thrust vectoring for many liquid rockets is achieved by gimbaling the whole engine. This involves moving the entire combustion chamber and outer engine bell as on the Titan II's twin first-stage motors, or even the entire engine assembly including the related fuel and oxidizer pumps. The Saturn V and the Space Shuttle used gimbaled engines.[2]
A later method developed for solid propellant ballistic missiles achieves thrust vectoring by deflecting only the nozzle of the rocket using electric actuators or hydraulic cylinders. The nozzle is attached to the missile via a ball joint with a hole in the centre, or a flexible seal made of a thermally resistant material, the latter generally requiring more torque and a higher power actuation system. The Trident C4 and D5 systems are controlled via hydraulically actuated nozzle. The STS SRBs used gimbaled nozzles.[4]
Propellant injection
Another method of thrust vectoring used on solid propellant ballistic missiles is liquid injection, in which the rocket nozzle is fixed, but a fluid is introduced into the exhaust flow from injectors mounted around the aft end of the missile. If the liquid is injected on only one side of the missile, it modifies that side of the exhaust plume, resulting in different thrust on that side and an asymmetric net force on the missile. This was the control system used on the Minuteman II and the early SLBMs of the United States Navy.
Vernier thrusters
An effect similar to thrust vectoring can be produced with multiple vernier thrusters, small auxiliary combustion chambers which lack their own turbopumps and can gimbal on one axis. These were used on the Atlas and R-7 missiles and are still used on the Soyuz rocket, which is descended from the R-7, but are seldom used on new designs due to their complexity and weight. These are distinct from reaction control system thrusters, which are fixed and independent rocket engines used for maneuvering in space.
Exhaust vanes
One of the earliest methods of thrust vectoring in rocket engines was to place vanes in the engine's exhaust stream. These exhaust vanes or jet vanes allow the thrust to be deflected without moving any parts of the engine, but reduce the rocket's efficiency. They have the benefit of allowing roll control with only a single engine, which nozzle gimbaling does not. The V-2 used graphite exhaust vanes and aerodynamic vanes, as did the Redstone, derived from the V-2. The Sapphire and Nexo rockets of the amateur group Copenhagen Suborbitals provide a modern example of jet vanes. Jet vanes must be made of a refractory material or actively cooled to prevent them from melting. Sapphire used solid copper vanes for copper's high heat capacity and thermal conductivity, and Nexo used graphite for its high melting point, but unless actively cooled, jet vanes will undergo significant erosion. This, combined with jet vanes' inefficiency, mostly precludes their use in new rockets.
Tactical missiles and small projectiles
Some smaller sized atmospheric tactical missiles, such as the AIM-9X Sidewinder, eschew flight control surfaces and instead use mechanical vanes to deflect rocket motor exhaust to one side.
By using mechanical vanes to deflect the exhaust of the missile's rocket motor, a missile can steer itself even shortly after being launched (when the missile is moving slowly, before it has reached a high speed). This is because even though the missile is moving at a low speed, the rocket motor's exhaust has a high enough speed to provide sufficient forces on the mechanical vanes. Thus, thrust vectoring can reduce a missile's minimum range. For example, anti-tank missiles such as the Eryx and the PARS 3 LR use thrust vectoring for this reason.[5]
Some other projectiles that use thrust-vectoring:
- 9M330[6]
- Strix mortar round uses twelve midsection lateral thruster rockets to provide terminal course corrections[5]
- AAD uses jet vanes
- Astra (missile)[7]
- Akash (missile)[8]
- BrahMos[9]
- QRSAM uses jet vanes
- MPATGM uses jet vanes
- Barak 8 uses jet vanes
- A-Darter uses jet vanes
- ASRAAM uses jet vanes
- R-73 (missile) uses jet vanes
- HQ-9 uses jet vanes
- PL-10 (ASR) uses jet vanes
- MICA (missile) uses jet vanes
- PARS 3 LR uses jet vanes
- Aster missile family combines aerodynamic control and the direct thrust vector control called "PIF-PAF"
- AIM-9X uses four jet vanes inside the exhaust, that move as the fins move.
- 9M96E uses a gas-dynamic control system enables maneuver at altitudes of up to 35km at forces of over 20g, which permits engagement of non-strategic ballistic missiles.[10]
- 9K720 Iskander is controlled during the whole flight with gas-dynamic and aerodynamic control surfaces.
- Dongfeng subclasses/JL-2/JL-3 ballistic missiles (allegedly fitted with TVC control) [11]
Aircraft
Most currently operational vectored thrust aircraft use turbofans with rotating nozzles or vanes to deflect the exhaust stream. This method allows designs that can deflect thrust through as much as 90 degrees relative to the aircraft centreline. If an aircraft uses thrust vectoring for VTOL operations the engine must be sized for vertical lift, rather than normal flight, which results in a weight penalty. Afterburning (or Plenum Chamber Burning, PCB, in the bypass stream) is difficult to incorporate and is impractical for take-off and landing thrust vectoring, because the very hot exhaust can damage runway surfaces. Without afterburning it is hard to reach supersonic flight speeds. A PCB engine, the Bristol Siddeley BS100, was cancelled in 1965.
Tiltrotor aircraft vector thrust via rotating turboprop engine nacelles. The mechanical complexities of this design are quite troublesome, including twisting flexible internal components and driveshaft power transfer between engines. Most current tiltrotor designs feature two rotors in a side-by-side configuration. If such a craft is flown in a way where it enters a vortex ring state, one of the rotors will always enter slightly before the other, causing the aircraft to perform a drastic and unplanned roll.

Thrust vectoring is also used as a control mechanism for airships. An early application was the British Army airship Delta, which first flew in 1912.[12] It was later used on HMA (His Majesty's Airship) No. 9r, a British rigid airship that first flew in 1916[13] and the twin 1930s-era U.S. Navy rigid airships USS Akron and USS Macon that were used as airborne aircraft carriers, and a similar form of thrust vectoring is also particularly valuable today for the control of modern non-rigid airships. In this use, most of the load is usually supported by buoyancy and vectored thrust is used to control the motion of the aircraft. The first airship that used a control system based on pressurized air was Enrico Forlanini's Omnia Dir in 1930s.
A design for a jet incorporating thrust vectoring was submitted in 1949 to the British Air Ministry by Percy Walwyn; Walwyn's drawings are preserved at the National Aerospace Library at Farnborough.[14] Official interest was curtailed when it was realised that the designer was a patient in a mental hospital.
Now being researched, Fluidic Thrust Vectoring (FTV) diverts thrust via secondary fluidic injections.[15] Tests show that air forced into a jet engine exhaust stream can deflect thrust up to 15 degrees. Such nozzles are desirable for their lower mass and cost (up to 50% less), inertia (for faster, stronger control response), complexity (mechanically simpler, fewer or no moving parts or surfaces, less maintenance), and radar cross section for stealth. This will likely be used in many unmanned aerial vehicle (UAVs), and 6th generation fighter aircraft.
Vectoring nozzles
Thrust-vectoring flight control (TVFC) is obtained through deflection of the aircraft jets in some or all of the pitch, yaw and roll directions. In the extreme, deflection of the jets in yaw, pitch and roll creates desired forces and moments enabling complete directional control of the aircraft flight path without the implementation of the conventional aerodynamic flight controls (CAFC). TVFC can also be used to hold stationary flight in areas of the flight envelope where the main aerodynamic surfaces are stalled.[16] TVFC includes control of STOVL aircraft during the hover and during the transition between hover and forward speeds below 50 knots where aerodynamic surfaces are ineffective.[17]
When vectored thrust control uses a single propelling jet, as with a single-engined aircraft, the ability to produce rolling moments may not be possible. An example is an afterburning supersonic nozzle where nozzle functions are throat area, exit area, pitch vectoring and yaw vectoring. These functions are controlled by four separate actuators.[16] A simpler variant using only three actuators would not have independent exit area control.[16]
When TVFC is implemented to complement CAFC, agility and safety of the aircraft are maximized. Increased safety may occur in the event of malfunctioning CAFC as a result of battle damage.[16]
To implement TVFC a variety of nozzles both mechanical and fluidic may be applied. This includes convergent and convergent-divergent nozzles that may be fixed or geometrically variable. It also includes variable mechanisms within a fixed nozzle, such as rotating cascades[18] and rotating exit vanes.[19] Within these aircraft nozzles, the geometry itself may vary from two-dimensional (2-D) to axisymmetric or elliptic. The number of nozzles on a given aircraft to achieve TVFC can vary from one on a CTOL aircraft to a minimum of four in the case of STOVL aircraft.[17]
Definitions
- Axisymmetric
- Nozzles with circular exits.
- Conventional aerodynamic flight control (CAFC)
- Pitch, yaw-pitch, yaw-pitch-roll or any other combination of aircraft control through aerodynamic deflection using rudders, flaps, elevators and/or ailerons.
- Converging-diverging nozzle (C-D)
- Generally used on supersonic jet aircraft where nozzle pressure ratio (npr) > 3. The engine exhaust is expanded through a converging section to achieve Mach 1 and then expanded through a diverging section to achieve supersonic speed at the exit plane, or less at low npr.[20]
- Converging nozzle
- Generally used on subsonic and transonic jet aircraft where npr < 3. The engine exhaust is expanded through a converging section to achieve Mach 1 at the exit plane, or less at low npr.[20]
- Effective Vectoring Angle
- The average angle of deflection of the jet stream centreline at any given moment in time.
- Fixed nozzle
- A thrust-vectoring nozzle of invariant geometry or one of variant geometry maintaining a constant geometric area ratio, during vectoring. This will also be referred to as a civil aircraft nozzle and represents the nozzle thrust vectoring control applicable to passenger, transport, cargo and other subsonic aircraft.
- Fluidic thrust vectoring
- The manipulation or control of the exhaust flow with the use of a secondary air source, typically bleed air from the engine compressor or fan.[21]
- Geometric vectoring angle
- Geometric centreline of the nozzle during vectoring. For those nozzles vectored at the geometric throat and beyond, this can differ considerably from the effective vectoring angle.
- Three-bearing swivel duct nozzle (3BSD[17])
- Three angled segments of engine exhaust duct rotate relative to one another about duct centreline to produce nozzle thrust axis pitch and yaw.[22]
- Three-dimensional (3-D)
- Nozzles with multi-axis or pitch and yaw control.[16]
- Thrust vectoring (TV)
- The deflection of the jet away from the body-axis through the implementation of a flexible nozzle, flaps, paddles, auxiliary fluid mechanics or similar methods.
- Thrust-vectoring flight control (TVFC)
- Pitch, yaw-pitch, yaw-pitch-roll, or any other combination of aircraft control through deflection of thrust generally issuing from an air-breathing turbofan engine.
- Two-dimensional (2-D)
- Nozzles with square or rectangular exits. In addition to the geometrical shape 2-D can also refer to the degree-of-freedom (DOF) controlled which is single axis, or pitch-only, in which case round nozzles are included.[16]
- Two-dimensional converging-diverging (2-D C-D)
- Square, rectangular, or round supersonic nozzles on fighter aircraft with pitch-only control.
- Variable nozzle
- A thrust-vectoring nozzle of variable geometry maintaining a constant, or allowing a variable, effective nozzle area ratio, during vectoring. This will also be referred to as a military aircraft nozzle as it represents the nozzle thrust vectoring control applicable to fighter and other supersonic aircraft with afterburning. The convergent section may be fully controlled with the divergent section following a pre-determined relationship to the convergent throat area.[16] Alternatively, the throat area and the exit area may be controlled independently, to allow the divergent section to match the exact flight condition.[16]
Methods of nozzle control
- Geometric area ratios
- Maintaining a fixed geometric area ratio from the throat to the exit during vectoring. The effective throat is constricted as the vectoring angle increases.
- Effective area ratios
- Maintaining a fixed effective area ratio from the throat to the exit during vectoring. The geometric throat is opened as the vectoring angle increases.
- Differential area ratios
- Maximizing nozzle expansion efficiency generally through predicting the optimal effective area as a function of the mass flow rate.
Methods of thrust vectoring
- Type I
- Nozzles whose baseframe mechanically is rotated before the geometrical throat.
- Type II
- Nozzles whose baseframe is mechanically rotated at the geometrical throat.
- Type III
- Nozzles whose baseframe is not rotated. Rather, the addition of mechanical deflection post-exit vanes or paddles enables jet deflection.
- Type IV
- Jet deflection through counter-flowing or co-flowing (by shock-vector control or throat shifting)[21] auxiliary jet streams. Fluid-based jet deflection using secondary fluidic injection.[21]
- Additional type
- Nozzles whose upstream exhaust duct consists of wedge-shaped segments which rotate relative to each other about the duct centreline.[17][22][23]
Operational examples
Aircraft

An example of 2D thrust vectoring is the Rolls-Royce Pegasus engine used in the Hawker Siddeley Harrier, as well as in the AV-8B Harrier II variant.
Widespread use of thrust vectoring for enhanced maneuverability in Western production-model fighter aircraft didn't occur until the deployment of the Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor fifth-generation jet fighter in 2005, with its afterburning, 2D thrust-vectoring Pratt & Whitney F119 turbofan.[24]
While the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II uses a conventional afterburning turbofan (Pratt & Whitney F135) to facilitate supersonic operation, its F-35B variant, developed for joint usage by the US Marine Corps, Royal Air Force, Royal Navy, and Italian Navy, also incorporates a vertically mounted, low-pressure shaft-driven remote fan, which is driven through a clutch during landing from the engine. Both the exhaust from this fan and the main engine's fan are deflected by thrust vectoring nozzles, to provide the appropriate combination of lift and propulsive thrust. It is not conceived for enhanced maneuverability in combat, only for VTOL operation, and the F-35A and F-35C do not use thrust vectoring at all.
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI, produced by India under licence at Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, is in active service with the Indian Air Force. The TVC makes the aircraft highly maneuverable, capable of near-zero airspeed at high angles of attack without stalling, and dynamic aerobatics at low speeds. The Su-30MKI is powered by two Al-31FP afterburning turbofans. The TVC nozzles of the MKI are mounted 32 degrees outward to longitudinal engine axis (i.e. in the horizontal plane) and can be deflected ±15 degrees in the vertical plane. This produces a corkscrew effect, greatly enhancing the turning capability of the aircraft.[25]
A few computerized studies add thrust vectoring to extant passenger airliners, like the Boeing 727 and 747, to prevent catastrophic failures, while the experimental X-48C may be jet-steered in the future.[26]
Other
Examples of rockets and missiles which use thrust vectoring include both large systems such as the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster (SRB), S-300P (SA-10) surface-to-air missile, UGM-27 Polaris nuclear ballistic missile and RT-23 (SS-24) ballistic missile and smaller battlefield weapons such as Swingfire.
The principles of air thrust vectoring have been recently adapted to military sea applications in the form of fast water-jet steering that provide super-agility. Examples are the fast patrol boat Dvora Mk-III, the Hamina class missile boat and the US Navy's Littoral combat ships.[26]
List of vectored thrust aircraft
Thrust vectoring can convey two main benefits: VTOL/STOL, and higher maneuverability. Aircraft are usually optimized to maximally exploit one benefit, though will gain in the other.
For VTOL ability
Vectoring in two dimensions
- McDonnell Douglas F-15 STOL/MTD (experimental)
- Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor (pitch only)[28]
- Chengdu J-20 (earlier variants with WS-10C,[29] pitch and roll)
- McDonnell Douglas X-36 (yaw only)[27]
- Me 163 B experimentally used a rocket steering paddle for the yaw axis
- Lockheed Martin F-22A Raptor
Vectoring in three dimensions
- McDonnell Douglas F-15 ACTIVE (experimental)
- Mitsubishi X-2 (experimental)
- McDonnell Douglas F-18 HARV (experimental)
- General Dynamics F-16 VISTA (experimental)
- Rockwell-MBB X-31 (experimental)
- Chengdu J-10B TVC testbed (experimental)
- Mikoyan MiG-35 (MiG-29OVT, not in production aircraft)
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI /MKM/ MKA/ SM (pitch and roll)
- Sukhoi Su-37
- Sukhoi Su-35S
- Sukhoi Su-57
Other
- 23 class airship, a series of British, World War 1 airships
- Airship Industries Skyship 600 modern airship
- Zeppelin NT modern, thrust–vectoring airship
References
- "AA-11 ARCHER R-73". Archived from the original on 2 September 2016. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- George P. Sutton, Oscar Biblarz, Rocket Propulsion Elements, 7th Edition.
- Michael D. Griffin and James R. French, Space Vehicle Design, Second Edition.
- "Reusable Solid Rocket Motor—Accomplishments, Lessons, and a Culture of Success" (PDF). ntrs.nasa.gov. 27 September 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- "Anti-tank guided missile developments". Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- "Combat Vehicle Tor 9A330". State company "UKROBORONSERVICE". Archived from the original on 31 March 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- "First test of air-to-air missile Astra Mk II likely on February 18". Archived from the original on 2 June 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- "Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) System-Airforce Technology". Archived from the original on 5 March 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- "Explained: From Pinaka to Astra, the new weapons DAC has approved 'for defence of borders'". Archived from the original on 2 June 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- "S-400 SA-20 Triumf". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 5 December 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- "China's ballistic missile industry" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- Mowthorpe, Ces (1998). Battlebags: British Airships of the First World War. Wrens Park. p. 11. ISBN 0-905778-13-8.
- Abbott, Patrick (1989). The British Airship at War. Terence Dalton. p. 84. ISBN 0-86138-073-8.
- "STOCK IMAGE - A 1949 jet deflection vectored-thrust propulsion concept by www.DIOMEDIA.com". Diomedia. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- P. J. Yagle; D. N. Miller; K. B. Ginn; J. W. Hamstra (2001). "Demonstration of Fluidic Throat Skewing for Thrust Vectoring in Structurally Fixed Nozzles". Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power. 123 (3): 502–508. doi:10.1115/1.1361109. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2007.
- "Thrust Vectoring Nozzle for Modern Military Aircraft" Daniel Ikaza, ITP, presented at NATO R&T Organization Symposium, Braunschweig, Germany, 8–11 May 2000
- "F-35B Integrated Flight Propulsion Control Development" Walker, Wurth, Fuller, AIAA 2013-44243, AIAA Aviation, August 12–14, 2013, Los Angeles, CA 2013 International Powered Lift Conference"
- "The X-Planes, Jay Miller, Aerofax Inc. for Orion Books, ISBN 0-517-56749-0, Chapter 18, The Bell X-14
- "Propulsion System For A Vertical And Short Takeoff And Landing Aircraft" Bevilaqua and Shumpert, U.S. Patent Number 5,209,428
- "Nozzle Selection and Design Criteria" Gambell, Terrell, DeFrancesco, AIAA 2004-3923
- "Experimental Study of an Axisymmetric Dual Throat Fluidic Thrust Vectoring Nozzle for Supersonic Aircraft application" Flamme, Deere, Mason, Berrier, Johnson, https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20070030933.pdf Archived 2017-08-15 at the Wayback Machine
- "F-35B Lightning II Three-Bearing Swivel Nozzle - Code One Magazine". codeonemagazine.com. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- "Variable Vectoring Nozzle For Jet Propulsion Engines" Johnson, U.S. Patent 3,260,049
- "F-22 Raptor fact sheet." U.S. Air Force, March 2009. Retrieved: 10 July 2014.
- "Air Attack - Fighters and more". www.air-attack.com. Archived from the original on 17 September 2010.
- Gal-Or, Benjamin (2011). "Future Jet Technologies". International Journal of Turbo and Jet Engines. online. 28: 1–29. doi:10.1515/tjj.2011.006. ISSN 2191-0332. S2CID 111321951.
- Sweetmano, Bill (1999). Joint Strike Fighter: Boeing X-32 vs Lockheed Martin X-35. Enthusiast Color Series. MBI. ISBN 0-7603-0628-1.
- Barham, Robert (June 1994). "Thrust Vector Aided Maneuvering of the YF-22 Advanced Tactical Fighter Prototype". AIAA Biennial Flight Test Conference Proceedings. Hilton Head, SC. doi:10.2514/6.1994-2105. AIAA-94-2105-CP. Archived from the original on 26 June 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- "China's J-20 stealth fighters are getting an engine upgrade, source says". South China Morning Post. 15 March 2022. Archived from the original on 13 April 2022. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
8. Wilson, Erich A., "An Introduction to Thrust-Vectored Aircraft Nozzles", ISBN 978-3-659-41265-3
External links
 Media related to Thrust vectoring at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Thrust vectoring at Wikimedia Commons


