Vitré, Ille-et-Vilaine
Vitré (French pronunciation: [vitʁe] ⓘ; Breton: Gwitreg; Gallo: Vitræ) is a commune in the Ille-et-Vilaine department in Brittany in northwestern France.
Vitré
Vitræ | |
|---|---|
 A general view of Vitré | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
Location of Vitré | |
 Vitré  Vitré | |
| Coordinates: 48°07′27″N 1°12′29″W | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Brittany |
| Department | Ille-et-Vilaine |
| Arrondissement | Fougères-Vitré |
| Canton | Vitré |
| Intercommunality | CA Vitré Communauté |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Isabelle Le Callennec[1] (LR) |
| Area 1 | 37.03 km2 (14.30 sq mi) |
| Population | 18,603 |
| • Density | 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 35360 /35500 |
| Elevation | 56–127 m (184–417 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Vitré, a sub-prefecture until 1926, is the seat of a canton of 17,798 inhabitants (2015). It lies on the edge of Brittany, near Normandy, Maine, and Anjou. The town has been designated a ville d'art et d'histoire, a town of artistic and historic significance, by the Ministry of Culture in recognition of its rich cultural inheritance. Vitré is the 37th French city with the most historic buildings and has 14% of the historical monuments of the department.
"If I was not King of France, I want to be bourgeois from Vitré!" Henry IV, King of France, surprised by the richness of the city in 1598.
"The good fortune to see a Gothic city entire, complete, homogeneous, a few of which still remain, Nuremberg in Bavaria and Vittoria in Spain, can readily form an idea; or even smaller specimens, provided that they are well preserved, Vitré in Brittany, Nordhausen in Prussia." Victor Hugo in The Hunchback of Notre Dame, Book third, Chapter 2, A bird's eye view of Paris, 1831
Geography
Situation
The city is located on the slopes of the Vilaine river, along an east–west geographic depression which the national railway on the Paris-Rennes route follows.
Vitré commune is home to around 28,000 inhabitants spread throughout three cantons: Vitré, La Guerche-de-Bretagne and Châteaugiron.
The land area of Vitré: 37.19 km2 (14.36 sq mi). The average altitude of Vitré is approximately 89 m. The highest point, 127 m, is found in the "Ménardières" zone, at Pierre and Marie Curie Street. The lowest point, 67 m, is close to the firm S.V.A.'s location under the viaduct of the ring-road.
Since 1 October 2010, Vitré has withdrawn from the arrondissement of Rennes and joined the arrondissement of Fougères-Vitré.
Climate
Vitré has an oceanic climate slightly degraded (type Cfb according to Koppen Classification). The city is located in climate zone Breton "South East", which includes the portion south and east of the Vilaine.
The winters are wet and mild on average, but occasionally, the annual minimum temperature can be largely negative with some severe frosts.
The days without thawing remain infrequent. The summers are relatively dry, moderately warm and sunny.
The annual maximum temperatures exceed several times a year over 30 °C and few years when this threshold is not reached.
The city has about 1,750 hours of sunshine each year (nearly 2,000 hours in 2003 and 2010). It is located in a region with relatively high relief, well exposed to winds from SW, consequently more humid with annual rainfall heights between 800 and 1000 mm (≈ 900 mm in 2001 and 2002, between 600 and 800 mm between 2003 and 2006).
At temperatures, it is little differentiated from Rennes basin in the valleys of about 12.5 °C. It becomes rather on the hills with an average annual temperature lowered to 10 °C and a certain rigor in winter with high wind exposure. On average, there are 130 rainy days per year, 70 days of fog, 15 stormy days, 9 days and 6 days of snow and hail.
Some continentality that the amplitude of temperature is greater than on the west coast of Brittany, with greater extremes (- 15 °C on 19 January 1985 and 39.5 °C on 5 August 2003 ).
Summer thunderstorms can be very violent as that of 16 July 2003 where 76 mm of water per square meter were found, which caused flooding and significant damage due to hail and gusty winds.
For the most part, these storms from the south of Brittany and in particular the Loire-Atlantique and took charge of Vitre. In the past, notorious storms have devastated parts of the city with the storm Lothar on 26 December 1999 or when the storm 15 October 1987 where a cow had the same flight.
| Climate data for Rennes (1961-2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8 (46) |
9.1 (48.4) |
11.8 (53.2) |
14.3 (57.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
21.2 (70.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.2 (73.8) |
21.1 (70.0) |
16.7 (62.1) |
11.5 (52.7) |
8.7 (47.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
3.5 (38.3) |
5.3 (41.5) |
8.2 (46.8) |
11.1 (52.0) |
13 (55) |
12.8 (55.0) |
11.1 (52.0) |
8.3 (46.9) |
4.8 (40.6) |
3 (37) |
7.1 (44.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 61.5 (2.42) |
51.6 (2.03) |
49.5 (1.95) |
44.3 (1.74) |
58.1 (2.29) |
45.4 (1.79) |
43.5 (1.71) |
46.7 (1.84) |
55.9 (2.20) |
65.5 (2.58) |
67.6 (2.66) |
68.4 (2.69) |
657.9 (25.90) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 67.8 | 81.3 | 131.2 | 162.4 | 182.6 | 222.0 | 214.6 | 204.1 | 185.4 | 111.8 | 88.9 | 74.0 | 1,726.1 |
| Source: Météo France | |||||||||||||
Population
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: EHESS[3] and INSEE (1968-2017)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
At the end of the 14th century the city had between 4–5,000 inhabitants, at a time when Rennes and Nantes had some around 13–14,000. in 1560, Vitré's population is estimated by Arthur de Borderie at 7,800 inhabitants, matching that of the towns of Vannes and Quimper.
At the time of the birth of Madame de Sévigné, about 1620, the city counted 10,000 inhabitants. The population reached 14,000 inhabitants in 1762. This population was contained within the medieval boundaries of the city, which was a third the size of the modern Vitré. In the 18th century, Vitré was the 5th most important city in Brittany after Nantes, Rennes, Brest and Lorient.
In 1789, on the eve of the French Revolution, Vitré's population reached 10,850 inhabitants. In the post-revolution period there was a significant drop in population, to 8,904 inhabitants by 1861. By 1911 a moderate increase brought the figure to 10,613. The First World War and its subsequent economic trials would reduce the population to 8,506. By 1999 the population again had reached 18th century levels, with 15,313 inhabitants and 17,798 in 2015 (+1,1% per annum). The canton of Vitré counted 39,115 inhabitants in 2015 on 382 km2 (102 inhabitants/km2). The greater Vitré-Community counts 80,000 inhabitants on 868 km2.
Inhabitants of Vitré are called Vitréens and vitréennes.
Language
The local dialect in Vitré is Gallo, spoken by some in Upper Brittany. In 2016, 3.9% of children attended bilingual schools in primary education.[5]
History

Early settlement

The site of Vitré was occupied in Gallo-Roman times. The name Vitré comes from the Gallo-Roman name "Victor" or "Victrix", after the owner of a farm in the region. The year 1000 marked the formal birth of Vitré, when the duke of Brittany Geoffrey I bestowed feudal powers upon Riwallon Le Vicaire, who was charged with keeping this strategic area as a buffer zone known as the "Marches of Brittany". A parallel can be drawn with the "Welsh Marches".
A small wooden motte-and-bailey castle, on a feudal mound, was built on the Sainte-Croix hill. The castle was burned down on several occasions, and eventually was bequeathed to the Benedictine monks of Marmoutiers. A stone castle was built in 1070 by Robert Ier on the current site, on a rocky outcrop dominating the Vilaine's river valley. Certain parts of the original stone castle are still visible today.
In the 13th century, the castle was enlarged and equipped with robust towers and curtain walls. The castle integrated into the triangular outcrop of rock on which it was built a structure in the style of the castles of Philip II August. Late in the century, in 1295, the town passed to Guy IX de Laval, on his marriage with the heiress, and afterwards successively belonged to the families of Rieux, Coligny and La Trémoille.[6] During this period, the "Vieil Bourg" including the church of Nôtre-Dame, developed on the eastern side of Vitré. The city was encircled by fortified ramparts and ditches. It was at this time that the "walled city" took its current form. The Baron directed the construction of the "privileged boroughs" around the walled city. These boroughs defined the linear layout of the streets of Vitré's present neighborhoods. Since the 13th century, Vitré has joined together all of the elements of the traditional medieval city: a fortified castle, religious buildings, churches, colleges, and suburbs.
Middle Ages

In the 15th century, the castle was modified to keep up with developments in artillery design. It was decommissioned from a military post to become a comfortable residence for Jeanne of Laval-Châtillon and her son Anne de Montmorency. At the same time, many half-timbered houses and private mansions were built inside the city. These medieval districts are characterized by their sturdy frame construction and their sinuous and dark streets, as well as by a network of lanes. From a defense perspective, these narrow streets were a confusing obstacle to taking the city. The frontages of the houses are made either of half-timbering or stone. The corbellings (projection of the higher floors over the street) helped save space. They shielded pedestrians from bad weather, and they channeled rainwater into the central gutters, helping preserve the wooden facades.
In 1488, during the French invasion of Brittany, Vitré was seized by Charles VIII.[6]
The names of Vitré's streets often originated from the trade guilds in the area: for example, "Baudrairie Street" was a gathering-place for "baudroyors" (leatherworkers), and there is also a "Street of Pottery".
The historical center of the city is the Place du Marchix or Market Square near the Convent of the Benedictines. The current Place of the Castle was the forecourt of the castle. The Place de Notre-Dame formerly hosted a "Market of Fabrics." Vitré, a prosperous city since the 15th century, had a brotherhood for promoting the international trade of textiles, founded in 1472.
Renaissance
Vitré's economy flourished during the Renaissance as much as any city in the Duchy of Brittany. Its peak came in the 16th century when the "Confrérie des Marchands d'Outre-Mer" - merchant venturers - sold the hemp produced locally throughout Europe. The merchants built large private mansions with ornate Renaissance decorations that are still visible today with the city walls. Henry IV passed through Vitré in 1598. He was struck by the opulence of the town and exclaimed: "If I were not King of France, I would be a burgher of Vitré! ".
During the French Wars of Religion, at the end of the 16th century, the Protestant city was besieged for five months by the troops of the League under the command of the duke of Mercœur, governor of Brittany. The siege was unsuccessful and the city remained one of the few bastions to resist the Leaguers in western France.
At the beginning of the 17th century, the family of Laval, who were barons of Vitré, petered out with the death of Guy XX in Hungary.[7] The new lords from the family of La Trémoïlle soon deserted the town for the Court of Versailles. Over this period, the city lost much of its vitality, becoming a town of secondary importance.
With 14,000 inhabitants in 1762, one of the largest cities of Brittany, Vitré begins are slow demographic decline until the interwar period with a population of 8,212 people in 1931. This situation lasted through 18th century and until the arrival of the railroad in the middle of the 19th century. In addition, the end of the 18th century was marked by the Chouannerie, the French Revolution and the beginning of a new and important period for the city, its role as a sub-prefecture.
The 19th and 20th centuries

To prepare for the arrival of the railroads, the city decided to destroy the southern fortifications of the city to open up the closed city and to improve visibility. The Door "d'En-Haut" (1835), "Gâtesel" (1839) and "d'En-Bas" were destroyed to make way for developments in the south of the closed city.
Vitré has been a railway hub since the first lines were opened on 15 April 1857 on the Paris-Brest line. The construction of the station was carried out in 1855 in the form of a small neo-gothic manor house in the downtown area, just south of the closed city. The arrival of the barracks in 1874 with the military and their families accounted for up to 2,000 people, which has grown the population of Vitré as much.
The city was literally cut in two by this important railway influence. However, in spite of these industrial developments, the city developed little and remained a small market town within an agricultural area. Moreover, it lost its statute of sub-prefecture in 1926.
Vitré did not suffer massive destruction during the two World Wars, and preserved its historical inheritance, with the exception of Fougères, which underwent a terrible bombardment in June 1944, destroying a good part of it. In the aftermath of the Second World War, Vitré experienced an economic boom along with the rest of France.
From 1950 on, Vitré grew extensively. During "the thirty glorious years", Vitré experienced massive rural migration, like many other towns of France.
This migration triggered new building developments, including modern six-story buildings in the "Maison Rouge" district. The city has considerably developed and extended with industrial areas and suburbs. The population of Vitré expanded from 8,212 inhabitants in 1931 to around 19,000 in 2018, a population multiplied by two. Inner-city areas are protected to conserve the town's rich heritage of art and architecture. In 1999, Vitré obtained the label "Town of Art and History" because of its rich cultural inheritance. The town's monuments attract many tourists each year.
Sights
The heritage of the town of Vitré is a tremendous wealth. This is one of the cities of Brittany that has best preserved its original appearance with its houses with porch or timber-framed (the third city after of Rennes and Vannes in Brittany), its ramparts, its religious heritage, old streets, etc. Vitré is a perfect example of a town of 500 years ago.
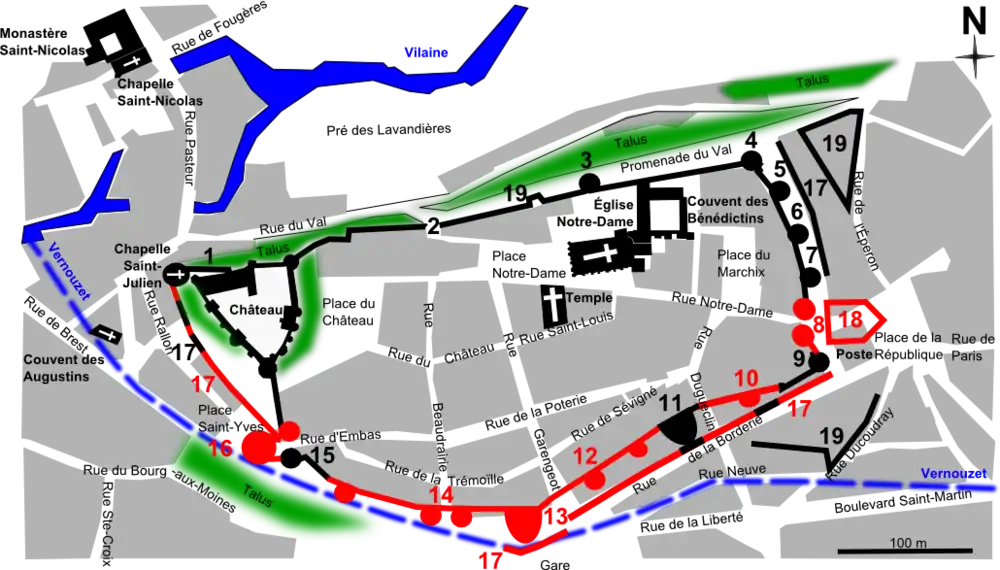
Castles
- Château de Vitré (11th-20th century)
- Intramuros
- Fortifications of Vitré at north and east of intramuros (Tour des Claviers, Tour de la Bridole, Gates tower of Embas, Postern St. Pierre)
- Rochers-Sévigné Castle
- Château-Marie (17th century)
- Hôtel Ringues de la Troussanais (Renaissance)
- Medieval streets (Beaudrairie, Poterie, d'Embas, etc.) and places (Marchix, Station, Château, Notre-Dame, etc.)
Religious heritage

- Saint-Nicolas Chapel (near Castle of Vitré)
- Notre-Dame Church (14th century) gothic
- Tower of the ancient Saint-Martin's Church (15th century)
- Saint-Martin Church (19th century)
- Sainte-Croix Church (17th-19th century)
- Protestant Church
- Convent of Bénédictins (Tribunal)
- Convent of Augustins (17th century)
- Chapels, calvaries situated in the city and countryside
Other sights
- Menhir "La Pierre Blanche" (Beauvais Road to Pocé-les-Bois)
- Hôtel Sévigné-Nétumières (18th Century)
- The Station (19th century)
- Old barracks of 70e régiment d'infanterie
- The Grand Park

Personalities
The following personalities are associated with Vitré:
- François Dollier de Casson second founder of Montreal
- Pierre Landais, Breton politician (15th century)
- Jacques Collebaut, composer
- fr:Tancrède Abraham, painter
- fr:Édouard Frain de la Gaulayrie, curator of Vitré and historian, born in Rennes, died in Vitré
- Bertrand d'Argentré, historian of Brittany
- Jacquet of Mantua or Jacques Colebault, Renaissance composer
- Pierre-Olivier Malherbe, European explorer
- Claude-Étienne Savary, translator of the Koran
- Arthur Le Moyne de La Borderie, historian of Brittany
- Auguste Pavie et Charles Rabot, explorers, the first: Laos and Cambodia, the second: Kola and Svalbard
- Morvan Marchal, Breton nationalist, creator of the modern flag of Brittany
- René Alexandre
- Pierre Méhaignerie, deputy-mayor of Vitré, former minister and European deputy
The 18th-century mathematician and contributor to the Encyclopédie Jean-Joseph Rallier des Ourmes (1701–1771) died in Vitré
Events
- Monsters of Death, 28 September 1991
- Vitre Jazz Festival, March 2006
Transportation
Located east of Brittany, the city of Vitré is crossed by the expressway which prolongs motorway A 11, while the motorway of the Estuaries. As in the whole of the Ille-et-Vilaine département, the communes of the country of Vitré are accessible by these expressways. Vitré is unusual in that urban transportation is zero-fare for all routes. Vitré station has rail connections to Rennes, Laval, Nantes and Paris.
Twin towns – sister cities
 Helmstedt, Germany (1979)
Helmstedt, Germany (1979) Lymington, United Kingdom (1981)
Lymington, United Kingdom (1981).svg.png.webp) Terrebonne, Canada (1983)
Terrebonne, Canada (1983) Djenné, Mali (1987)
Djenné, Mali (1987) Villajoyosa, Spain (1989)
Villajoyosa, Spain (1989) Greece, United States (1990)
Greece, United States (1990) Środa Wielkopolska, Poland (1994)
Środa Wielkopolska, Poland (1994) Tălmaciu, Romania (1999)
Tălmaciu, Romania (1999)
References
- "Répertoire national des élus: les maires" (in French). data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises. 13 September 2022.
- "Populations légales 2020". The National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies. 29 December 2022.
- Des villages de Cassini aux communes d'aujourd'hui: Commune data sheet Vitré, EHESS (in French).
- Population en historique depuis 1968, INSEE
- (in French) Ofis ar Brezhoneg: Office Public de la Langue Bretonne
- One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Vitré". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 149.
- Malcolm Walsby, The Counts of Laval: Culture, Patronage and Religion in Fifteenth and Sixteenth-Century France (Ashgate, Aldershot, 2007)
- "Les Villes Jumelles de Vitré". jumelage-vitre.com (in French). Vitré. Retrieved 10 April 2021.
External links
- Town Hall and informations to Vitré
- Tourists
- news of Vitré
- Country of Vitré
- news of Vitré
- Golf des Rochers Vitré
- Base Mérimée: Search for heritage in the commune, Ministère français de la Culture. (in French)