Wisconsin's 66th Assembly district
The 66th Assembly District of Wisconsin is one of 99 districts in the Wisconsin State Assembly.[2] Located in southeast Wisconsin, the district covers most of the city of Racine, Wisconsin, including downtown Racine and Racine Harbor and landmarks such as the Racine Art Museum, Old Main Street Historic District, Historic Sixth Street Business District, the Racine Zoo, Memorial Hall, and Johnson Wax Headquarters.[3] The district is represented by Democratic minority leader Greta Neubauer, since January 2018.[4]

| Wisconsin's 66th State Assembly district | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
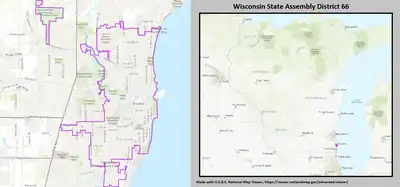 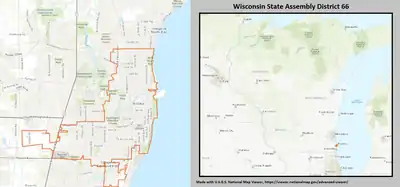 2022 map defined in Johnson v. Wisconsin Elections Commission 2011 map was defined in 2011 Wisc. Act 43 | |||||
| Assemblymember |
| ||||
| Demographics | 43.2% White 26.6% Black 26.6% Hispanic 0.9% Asian 1.1% Native American 0.0% Hawaiian/Pacific Islander 1.0% Other | ||||
| Population (2020) • Voting age | 59,365[1] 43,487 | ||||
| Notes | Southeast Wisconsin | ||||
The 66th Assembly District is located within Wisconsin's 22nd Senate district, along with the 64th and 65th Assembly districts.
History
The district was created in the 1972 redistricting act (1971 Wisc. Act 304) which first established the numbered district system, replacing the previous system which allocated districts to specific counties.[5] The 66th district was drawn somewhat in line with the former Kenosha County 2nd district (Kenosha County excluding most of the city of Kenosha), but removed southeastern Kenosha County and replaced it with a number of neighboring towns in central Racine County and eastern Walworth County.
After the 1983 redistricting, which undid the 1982 redistricting that had temporarily scrambled State Assembly districts, the boundaries of the 66th district remained relatively consistent for the next 28 years, based in Kenosha County with a varying set of rural towns from Racine and Walworth counties. That changed in the controversial 2011 redistricting plan (2011 Wisc. Act 43) which moved the district entirely into the city of Racine in Racine County in area previously represented by the 61st and 62nd Assembly districts. The previous territory covered by the 66th district is now split between the 61st, 63rd, and 64th Assembly districts.[6][7] This was part of a larger gerrymandering plan for the Racine and Kenosha County districts to convert one Assembly seat and one Senate seat from tossups to safely Republican.
List of past representatives
| Member | Party | Residence | Counties represented | Term start | Term end | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District created | ||||||
| Russell Olson | Rep. | Bassett | Kenosha, Racine, Walworth | January 1, 1973 | January 1, 1979 | |
| Mary Wagner | Dem. | Brighton | January 1, 1979 | January 3, 1983 | ||
| Steven Foti | Rep. | Oconomowoc | Washington, Waukesha | January 3, 1983 | January 7, 1985 | |
| Cloyd A. Porter | Rep. | Burlington | Kenosha, Racine, Walworth | January 7, 1985 | January 1, 2001 | |
| Samantha Kerkman | Rep. | Randall | Kenosha, Racine | January 1, 2001 | January 7, 2013 | [6] |
| Cory Mason | Dem. | Racine | Racine | January 7, 2013 | January 15, 2018 | [7] |
| --Vacant-- | January 15, 2018 | January 27, 2018 | ||||
| Greta Neubauer | Dem. | Racine | January 27, 2018 | Current | [4] | |
References
- "LTSB Open Data: Wisconsin Assembly Districts (2022)". Wisconsin Legislative Technology Services Bureau. Retrieved November 20, 2022.
- "Assembly District 66". Wisconsin Legislature. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- "Wisconsin Legislative Districts - Assembly District 66 Boundaries". Wisconsin Legislature. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- "Representative Greta Neubauer". Wisconsin Legislature. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau (1973). "Legislature" (PDF). In Theobald, H. Rupert; Robbins, Patricia V. (eds.). The state of Wisconsin 1973 Blue Book (Report). Madison, Wisconsin: State of Wisconsin. pp. 227–230. Retrieved January 22, 2021.
- Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau (2009). "Biographies" (PDF). In Barish, Lawrence S.; Lemanski, Lynn (eds.). State of Wisconsin 2009-2010 Blue Book (Report). State of Wisconsin. pp. 60–63. ISBN 978-0-9752820-3-8. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau (2017). "State Legislature" (PDF). State of Wisconsin Blue Book 2017-2018 (Report). State of Wisconsin. pp. 84–89. ISBN 978-0-9752820-9-0. Retrieved January 29, 2021.

