Articular disk
The articular disk (or disc) is a thin, oval plate of fibrocartilage present in several joints which separates synovial cavities. This separation of the cavity space allows for separate movements to occur in each space.
| Articular disk | |
|---|---|
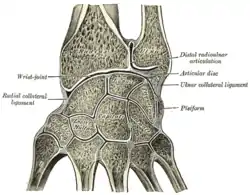 Vertical section through the articulations at the wrist, showing the synovial cavities. (Articular disk labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | discus articularis |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.032 A03.5.03.003 A03.5.04.002 A03.5.10.002 |
| TA2 | 1543 |
| FMA | 76690 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The presence of an articular disk also permits a more even distribution of forces between the articulating surfaces of bones, increases the stability of the joint, and aids in directing the flow of synovial fluid to areas of the articular cartilage that experience the most friction.
Additional images
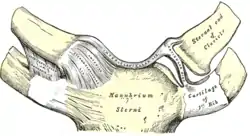 Sternoclavicular articulation. Anterior view.
Sternoclavicular articulation. Anterior view. Diagrammatic section of a diarthrodial joint, with an articular disk.
Diagrammatic section of a diarthrodial joint, with an articular disk.
See also
- Triangular fibrocartilage ("articular disk of the distal radioulnar articulation")
- Articular disk of the temporomandibular joint
- Articular disk of sternoclavicular articulation
References
External links
- Anatomy figure: 10:06-15 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Hand kinesiology at the University of Kansas Medical Center
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.