Common hepatic artery
The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder.[1]
| Common hepatic artery | |
|---|---|
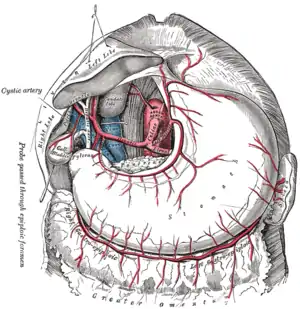 Branches of the celiac artery - stomach in situ. (Hepatic artery is visible at upper left.) | |
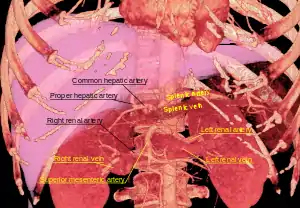 3D-rendered computed tomography, showing common hepatic artery in center | |
| Details | |
| Source | celiac artery |
| Branches | hepatic artery proper gastroduodenal artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria hepatica communis |
| MeSH | D006499 |
| TA98 | A12.2.12.015 |
| TA2 | 4214 |
| FMA | 14771 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
It arises from the celiac artery[2] and has the following branches:[3]
| Branch | Details |
| hepatic artery proper | supplies the gallbladder via the cystic artery and the liver via the left and right hepatic arteries |
| gastroduodenal artery | branches into the right gastroepiploic artery and superior pancreaticoduodenal artery |
| right gastric artery | branches to supply the lesser curvature of the stomach inferiorly |
Additional images
 Common hepatic artery and its branches including hepatic artery proper and right gastric artery (pyloric artery)
Common hepatic artery and its branches including hepatic artery proper and right gastric artery (pyloric artery)
References
- "Common Hepatic Artery - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2022-03-27.
- "Common hepatic artery". Kenhub. Retrieved 2022-03-27.
- D'Souza, Donna. "Common hepatic artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2022-03-27.
External links
- Anatomy photo:38:03-0204 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Stomach, Spleen and Liver: Contents of the Hepatoduodenal ligament"
- celiactrunk at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.