Inferior mesenteric artery
In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery, often abbreviated as IMA, is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.[1]
| Inferior mesenteric artery | |
|---|---|
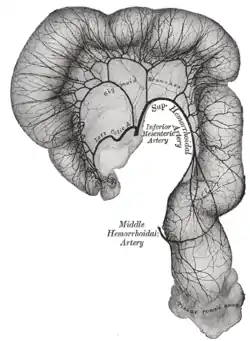 Sigmoid colon and rectum, showing distribution of branches of inferior mesenteric artery and their anastomoses. (Inferior mesenteric artery labeled at center.) | |
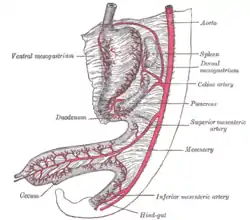 Abdominal part of digestive tube and its attachment to the primitive or common mesentery. Human embryo of six weeks. (Inferior mesenteric artery labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | vitelline arteries |
| Source | abdominal aorta |
| Branches | left colic artery, sigmoid branches, superior rectal artery |
| Vein | inferior mesenteric vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria mesenterica inferior |
| MeSH | D017537 |
| TA98 | A12.2.12.069 |
| TA2 | 4291 |
| FMA | 14750 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
Proximally, its territory of distribution overlaps (forms a watershed) with the middle colic artery, and therefore the superior mesenteric artery. The SMA and IMA anastomose via the marginal artery of the colon (artery of Drummond) and via Riolan's arcade (also called the "meandering artery", an arterial connection between the left colic artery and the middle colic artery). The territory of distribution of the IMA is more or less equivalent to the embryonic hindgut.[1][2]
Branches
The IMA branches off the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta below the renal artery branch points, 3-4 cm above the aortic bifurcation (into the common iliac arteries) at the L3 vertebral level.[3]
Along its course, the IMA has the following branches:[1][2][3]
| Branch | notes |
| left colic artery | supplies descending colon |
| sigmoid branches | the most superior being described as 'the superior sigmoid artery' |
| superior rectal artery | effectively the terminal branch of the IMA (the continuation of the IMA after all other branches) |
All these arterial branches further divide into arcades which then supply the colon at regular intervals.
Associated veins
The IMA is accompanied along its course by a similarly named vein, the inferior mesenteric vein, which drains into the splenic vein.[1]
The IMV therefore drains to the portal vein and does not fully mirror the course of the IMA.[1][2][3]
Clinical significance
The IMA and/or its branches must be resected for a left hemicolectomy.[4]
A horseshoe kidney, a common (1 in 500) anomaly of the kidneys, will be positioned below the IMA.[5][6]
Additional images
 The abdominal aorta and its branches.
The abdominal aorta and its branches. The inferior mesenteric artery and its branches.
The inferior mesenteric artery and its branches.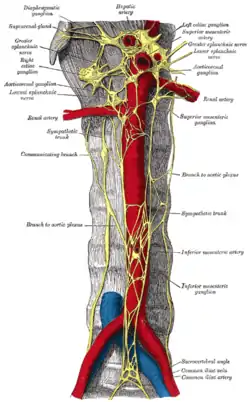 Abdominal portion of the sympathetic trunk, with the celiac plexus and hypogastric plexus.
Abdominal portion of the sympathetic trunk, with the celiac plexus and hypogastric plexus. Duodenojejunal fossa.
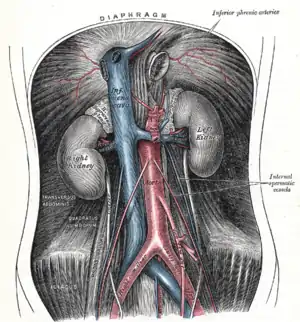
Duodenojejunal fossa.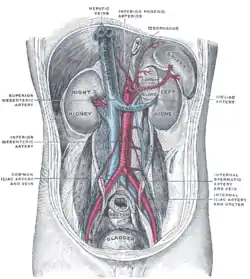 Posterior abdominal wall, after removal of the peritoneum, showing kidneys, suprarenal capsules, and great vessels.
Posterior abdominal wall, after removal of the peritoneum, showing kidneys, suprarenal capsules, and great vessels.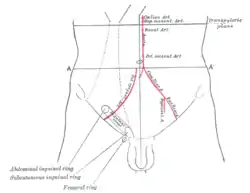 Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal.
Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal. Inferior mesenteric artery
Inferior mesenteric artery Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection.Anterior view.
Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection.Anterior view. Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection.Anterior view.
Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection.Anterior view. Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection.Anterior view.
Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection.Anterior view.
References
- Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41st ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Limited. ISBN 9780702052309. OCLC 920806541.
- Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F., II; Agur, A. M. R. (13 February 2013). Clinically oriented anatomy (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1451119459. OCLC 813301028.
- Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Mitchell, Adam W. M.; Gray, Henry (15 November 2015). Gray's anatomy for students (3rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. ISBN 9780702051319. OCLC 881508489.
- Charan, Ishwar; Kapoor, Akhil; Singhal, Mukesh Kumar; Jagawat, Namrata; Bhavsar, Deepak; Jain, Vikas; Kumar, Vanita; Kumar, Harvindra Singh (December 2015). "High Ligation of Inferior Mesenteric Artery in Left Colonic and Rectal Cancers: Lymph Node Yield and Survival Benefit". The Indian Journal of Surgery. 77 (Suppl 3): 1103–1108. doi:10.1007/s12262-014-1179-2. ISSN 0972-2068. PMC 4775673. PMID 27011519.
- Schiappacasse, G; Aguirre, J; Soffia, P; Silva, C S; Zilleruelo, N (January 2015). "CT findings of the main pathological conditions associated with horseshoe kidneys". The British Journal of Radiology. 88 (1045). doi:10.1259/bjr.20140456. ISSN 0007-1285. PMC 4277381. PMID 25375751.
- "Clinical case: Horseshoe kidney transplantation". Kenhub. Retrieved 2019-09-28.
External links
- Lotti M. Anatomy in relation to left colectomy
- Anatomy figure: 39:02-05 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Branches of the inferior mesenteric artery."
- Anatomy photo:40:11-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Branches of the Abdominal Aorta"
- Anatomy image:7924 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:7997 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:8407 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:8659 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Atlas image: abdo_wall70 at the University of Michigan Health System - "Posterior Abdominal Wall, Dissection, Anterior View"
- sup&infmesentericart at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)