Incretin
Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans by a blood-glucose–dependent mechanism.
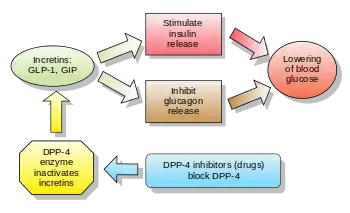
Some incretins (GLP-1) also inhibit glucagon release from the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans. In addition, they slow the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood stream by reducing gastric emptying and may directly reduce food intake. The two main candidate molecules that fulfill criteria for an incretin are the intestinal peptides glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP, also known as: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). Both GLP-1 and GIP are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Both GLP-1 and GIP are members of the glucagon peptide superfamily.[1][2][3]
Medical uses
Medications based on incretins are used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2.
Several long-lasting GLP-1 analogs having insulinotropic activity have been developed, and several, including dulaglutide (Trulicity), exenatide (Byetta), liraglutide (Victoza), semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy and Rybelsus) and exenatide extended-release (Bydureon), have been approved for use in the U.S.
Another approach is to inhibit DPP-4, the enzyme that inactivates GLP-1 and GIP. Several DPP-4 inhibitors that can be taken orally as tablets have been developed.
Incretin effect
The incretin effect describes the phenomenon whereby oral glucose intake elicits a higher insulin response compared to intravenously introduced glucose that produces the same levels of serum glucose levels.[4]
History
In 1932, Belgian physiologist Jean La Barre used the word "incretin" for a gut hormone, which stimulates the endocrine pancreas including insulin release.[5] He also proposed that such incretins could be used as a treatment for diabetes mellitus.[5]
See also
- Secretin family
References
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA (November 2006). "The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes". Lancet. 368 (9548): 1696–705. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69705-5. PMID 17098089. S2CID 25748028.
- Amori RE, Lau J, Pittas AG (July 2007). "Efficacy and safety of incretin therapy in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis". JAMA. 298 (2): 194–206. doi:10.1001/jama.298.2.194. PMID 17622601.
- Rang HP, Ritter JM, Flower R, Henderson G (2016). Rang and Dale's Pharmacology (8th ed.). United Kingdom: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. p. 385. ISBN 9780702053627. OCLC 903083639.
- Nauck, Michael A; Meier, Juris J (June 2016). "The incretin effect in healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes: physiology, pathophysiology, and response to therapeutic interventions". The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 4 (6): 525–536. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(15)00482-9. ISSN 2213-8587. PMID 26876794.
- Rehfeld JF (2018-07-16). "The Origin and Understanding of the Incretin Concept". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 9: 387. doi:10.3389/fendo.2018.00387. PMC 6054964. PMID 30061863.