Lateral circumflex femoral artery
The lateral circumflex femoral artery, also known as the lateral femoral circumflex artery, or the external circumflex artery,[1] is an artery in the upper thigh.
| circumflex femoral artery | |
|---|---|
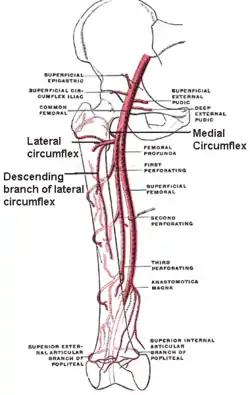 The profunda femoris artery, femoral artery and their major branches - right thigh, anterior view. Circumflex femoral arteries labeled. | |
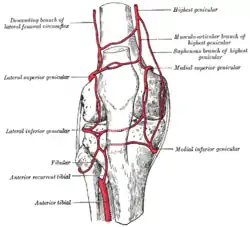 Circumpatellar anastomosis. (Descending branch of lateral femoral circumflex visible at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | deep femoral artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria circumflexa femoris lateralis |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.027 |
| TA2 | 4692 |
| FMA | 20798 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The lateral femoral circumflex artery usually arises from the lateral side of the profunda femoris artery, but may occasionally arise directly from the femoral artery.[2] It is the largest branch of the profunda femoris artery.[2] It passes horizontally between the divisions of the femoral nerve. It also passes behind the sartorius muscle and rectus femoris muscle.[3] It divides into ascending, transverse, and descending branches.[2] The artery usually courses anterior to the femoral neck.[3]
Branches
The lateral circumflex femoral artery has three branches:
- The ascending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery passes upward, beneath the tensor fasciae latae muscle, to the lateral aspect of the hip, and anastomoses with the terminal branches of the superior gluteal and deep circumflex iliac artery.
- The descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery runs downward, behind the rectus femoris, upon the vastus lateralis, to which it gives offsets; one long branch descends in the muscle as far as the knee, and anastomoses with the superior lateral genicular artery. It is accompanied by the branch of the femoral nerve to the vastus lateralis muscle.
- The transverse branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery is a small artery in the thigh. It is the smallest branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery and passes lateralward over the vastus intermedius, pierces the vastus lateralis, and winds around the femur, just below the greater trochanter, anastomosing on the back of the thigh with the medial femoral circumflex artery, the inferior gluteal artery, and the perforating arteries of the profunda femoris artery.
Variation
The lateral femoral circumflex artery has a variable origin.[2][4] In 67% of people, it arises 1.5 cm below the origin of the profunda femoris artery, and in others it arises at different distances from the origin.[2] In up to 20% of people, it arises directly from the femoral artery.
A rare variant, where the lateral circumflex femoral artery passes posterior to the femoral nerve, has also been reported.[5] This is significant in orthopaedic surgery.[5]
See also
Additional images
 The femoral artery.
The femoral artery.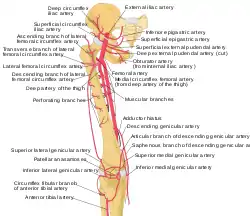 Labeled arteries of the thigh.
Labeled arteries of the thigh. Arteries of the thigh labeled with numbers. The lateral circumflex femoral is labeled as #5.
Arteries of the thigh labeled with numbers. The lateral circumflex femoral is labeled as #5.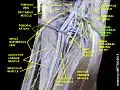 Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Lateral circumflex femoral artery
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 630 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 630 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Power, John Hatch (5 March 2010). Anatomy of the Arteries of the Human Body, with the Descriptive Anatomy of the Heart Paperback. Nabu Press. ISBN 978-1146643283.
- Scott Levin, L.; Baumeister, Steffen (2009-01-01), Wei, Fu-Chan; Mardini, Samir (eds.), "CHAPTER 7 - Lower extremity", Flaps and Reconstructive Surgery, Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders, pp. 63–70, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-0519-7.00007-1, ISBN 978-0-7216-0519-7, retrieved 2021-02-23
- Manaster, B. J.; Crim, Julia, eds. (2016-01-01), "Thigh Radiographic Anatomy and MR Atlas", Imaging Anatomy: Musculoskeletal (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Elsevier, pp. 606–659, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-37756-0.50046-6, ISBN 978-0-323-37756-0, retrieved 2021-02-23
- Yang, Guang; Chung, Kevin C. (2018-01-01), Chung, Kevin C. (ed.), "Procedure 78 - Free Anterolateral Thigh Flap", Operative Techniques: Hand and Wrist Surgery (Third Edition), Elsevier, pp. 713–719, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-40191-3.00078-0, ISBN 978-0-323-40191-3, retrieved 2021-02-23
- Goel, Shivi; Arora, Jyoti; Mehta, Vandana; Sharma, Mona; Suri, RK; Rath, Gayatri (Jan 16, 2015). "Unusual disposition of lateral circumflex femoral artery: Anatomical description and clinical implications". World Journal of Clinical Cases. 3 (1): 85–88. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v3.i1.85. PMC 4295224. PMID 25610855.
External links
- Lateral circumflex femoral artery at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- Anatomy figure: 12:04-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Arteries of the lower extremity shown in association with major landmarks."
- Cross section image: pelvis/pelvis-e12-15—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna