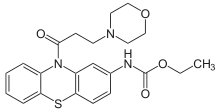
Moracizine
Moracizine[1] or moricizine, sold under the trade name Ethmozine, is an antiarrhythmic of class IC.[2] It was used for the prophylaxis and treatment of serious and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias,[3] but was withdrawn in 2007 for commercial reasons.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ethmozine |
| Other names | Moricizine (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601214 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 34–38% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Elimination half-life | 3–4 hours (healthy volunteers), 6–13 hours (cardiac disease) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.216 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 427.52 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Pharmacology
Moracizine, a phenothiazine derivative, undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism and is also extensively metabolized after it has entered the circulation. It may have pharmacologically active metabolites. A clinical study has shown that moracizine is slightly less effective than encainide or flecainide in suppressing ventricular premature depolarizations. Compared with disopyramide and quinidine, moracizine was equally or more effective in suppressing premature ventricular contractions, couplets, and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia.
In the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST), a large study testing the influence of antiarrhythmics on mortality, showed a statistically non-significant increase of mortality from 5.4 to 7.2% under moracizine. This is in line with other class IC antiarrhythmics.[5]
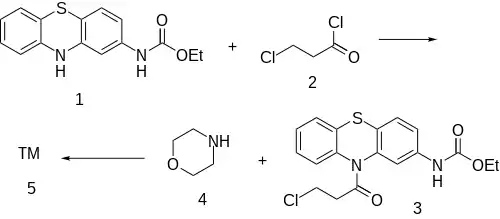
Synthesis
Note: The carbamate structure reminds the reader of Gastrophenzine or particularly Ethacizine.
The amide formation between Phenothiazine-2-ethylcarbamate [37711-29-8] (1) and 3-Chloropropionyl chloride [625-36-5] (2) gives ethyl N-[10-(3-chloropropanoyl)phenothiazin-2-yl]carbamate [119407-03-3] [34749-22-9] (3). Displacement of the remaining ω-halogen by morpholine (4) then completes the synthesis of Moricizine (5).
References
- "The use of stems in the selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. p. 103.
- Ahmmed GU, Hisatome I, Kurata Y, Makita N, Tanaka Y, Tanaka H, et al. (March 2002). "Analysis of moricizine block of sodium current in isolated guinea-pig atrial myocytes. Atrioventricular difference of moricizine block". Vascular Pharmacology. 38 (3): 131–41. doi:10.1016/S1537-1891(02)00213-6. PMID 12402511.
- British National Formulary (59th ed.). British Medical Journal Publishing Group, Pharmaceutical Press. 2010.
- "Shire Announces Ethmozine will be Available until December 31, 2007". Heart Rhythm Society. Archived from the original on December 10, 2011. Retrieved January 12, 2012.
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial II Investigators (July 1992). "Effect of the antiarrhythmic agent moricizine on survival after myocardial infarction". The New England Journal of Medicine. 327 (4): 227–33. doi:10.1056/NEJM199207233270403. PMID 1377359.
- Gritsenko, A.N., Ermakova, Z.I. & Zhuravlev, S.V. Pharm Chem J (1972) 6: 575.
- Anna Nikitichna Gritsenko, 5 More », U.S. Patent 3,740,395 (1973).
- Gary O. Page, U.S. Patent 5,202,435 (1993 to Roberts Laboratories Inc, Bristol Myers Squibb Pharma Co).
- L.P. Nikitenkov, et al. RU 2159771 (2000 to).