Naxos syndrome
Naxos disease[1] (also known as "diffuse non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and cardiomyopathy"[1] or "diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy", first described on the island of Naxos by Nikos Protonotarios[1]) is a cutaneous condition characterized by a palmoplantar keratoderma.[1] The prevalence of the syndrome is up to 1 in every 1000 people in the Greek islands.[2]
| Naxos disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Diffuse non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and cardiomyopathy |
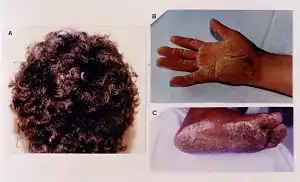 | |
| Cutaneous phenotype of Naxos disease: woolly hair (A), palmar (B) and plantar (C) keratoses. | |
It has been associated with mutations in the genes encoding the proteins desmoplakin, plakoglobin, desmocollin-2, and SRC-interacting protein (SIP).[3][4] Naxos disease has the same cutaneous phenotype as the Carvajal syndrome.[2]
Symptoms
Between 80 and 99% of those with Naxos disease will display some of the following symptoms:
- Disease of the heart muscle
- Thickening of palms and soles
- Sudden increased heart rate
- Dizzy spells
- Kinked hair[5]
See also
References
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- Protonotarios, Nikos; Tsatsopoulou, Adalena (2006). "Naxos disease: Cardiocutaneous syndrome due to cell adhesion defect". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 1 (1): 4. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-1-4. PMC 1435994. PMID 16722579.
- McKoy G, Protonotarios N, Crosby A, et al. (June 2000). "Identification of a deletion in plakoglobin in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy with palmoplantar keratoderma and woolly hair (Naxos disease)". Lancet. 355 (9221): 2119–24. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02379-5. PMID 10902626. S2CID 39821701.
- "Keratoderma with woolly hair". Genetics Home Reference. 17 April 2018. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- "Naxos disease | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
External links