Retropharyngeal lymph nodes
The retropharyngeal lymph nodes, from one to three in number, lie in the buccopharyngeal fascia, behind the upper part of the pharynx and in front of the arch of the atlas, being separated, however, from the latter by the Longus capitis.
| Retropharyngeal lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
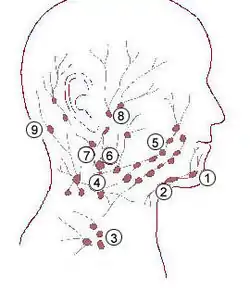 1: Submental lymph nodes 2: Submandibular lymph nodes 3: Supraclavicular lymph nodes 4: Retropharyngeal lymph nodes 5: Buccal lymph nodes 6: Superficial cervical lymph nodes 7: Jugular lymph nodes 8: Parotid lymph nodes 9: Retroauricular lymph nodes & occipital lymph nodes | |
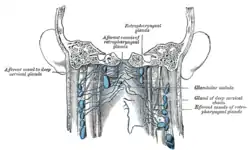 Lymphatics of pharynx. (Retropharyngeal lymph nodes labeled at center top.) | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Drains to | superior deep cervical lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nodi lymphoidei retropharyngei |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Their afferents drain the nasal cavities, the nasal part of the pharynx, and the auditory tubes.
Their efferents pass to the superior deep cervical lymph nodes.
They are in the retropharyngeal space.[1]
They frequently disappear by age 4-5.[2] (This is why retropharyngeal abscess is rare in older children.)
See also
- Rouvière node
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 694 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 694 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Chong VF, Fan YF (October 2000). "Radiology of the retropharyngeal space". Clin Radiol. 55 (10): 740–8. doi:10.1053/crad.2000.0510. PMID 11052873.
- Jill M. Baren; Steven G. Rothrock (15 October 2007). Pediatric emergency medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 306–. ISBN 978-1-4160-0087-7. Retrieved 26 May 2010.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.