ST8:USA300
ST8:USA300 is a strain of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) that has emerged as a particularly antibiotic resistant epidemic that is responsible for rapidly progressive, fatal diseases including necrotizing pneumonia, severe sepsis and necrotizing fasciitis.[1] The epidemiology of infections caused by MRSA is rapidly changing: in the past 10 years, infections caused by this organism have emerged in the community (whereas previously MRSA infections were almost exclusively hospital-acquired). The 2 MRSA clones in the United States most closely associated with community outbreaks, USA400 (MW2 strain, ST1 lineage) and USA300, often contain Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) genes and, more frequently, have been associated with skin and soft tissue infections. Outbreaks of community-associated (CA)-MRSA infections have been reported in correctional facilities, among athletic teams, among military recruits, in newborn nurseries, and among sexually active men who have sex with men, CA-MRSA infections now appear to be endemic in many urban regions and cause most MRSA infections.[2][3]
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | |
|---|---|
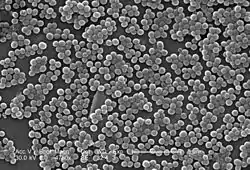 | |
| Electron micrograph of MRSA | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | S. aureus |
| Binomial name | |
| Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach 1884 | |
| Type strain | |
| "ST8:USA300" | |
References
- Boyle-Vavra S, Daum RS (2007). "Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: the role of Panton-Valentine leukocidin". Lab. Invest. 87 (1): 3–9. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700501. PMID 17146447.
- Maree CL, Daum RS, Boyle-Vavra S, Matayoshi K, Miller LG (2007). "Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates causing healthcare-associated infections". Emerging Infect. Dis. 13 (2): 236–42. doi:10.3201/eid1302.060781. PMC 2725868. PMID 17479885.
- Diep BA, Chambers HF, Graber CJ, et al. (February 2008). "Emergence of multidrug-resistant, community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone USA300 in men who have sex with men". Ann. Intern. Med. 148 (4): 249–57. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-148-4-200802190-00204. PMID 18283202.