Sialidosis
Mucolipidosis type I (ML I) is an inherited lysosomal storage disease that results from a deficiency of the enzyme alpha-N -acetyl neuraminidase (sialidase).[1] The lack of this enzyme results in an abnormal accumulation of complex carbohydrates known as mucopolysaccharides, and of fatty substances known as mucolipids. Both of these substances accumulate in bodily tissues.
| Sialidosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Sialidosis |
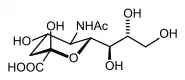 | |
| Sialic acid | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Presentation
Symptoms of ML I are either present at birth or develop within the first year of life. In many infants with ML I, excessive swelling throughout the body is noted at birth. These infants are often born with coarse facial features, such as a flat nasal bridge, puffy eyelids, enlargement of the gums, and excessive tongue size (macroglossia). Many infants with ML I are also born with skeletal malformations such as hip dislocation. Infants often develop sudden involuntary muscle contractions (called myoclonus) and have red spots in their eyes (cherry red spots). They are often unable to coordinate voluntary movement (called ataxia). Tremors, impaired vision, and seizures also occur in children with ML I. Tests reveal abnormal enlargement of the liver (hepatomegaly) and spleen (splenomegaly) and extreme abdominal swelling. Infants with ML I generally lack muscle tone (hypotonia) and have mental retardation that is either initially or progressively severe. Many patients suffer from failure to thrive and from recurrent respiratory infections. Most infants with ML I die before the age of 1 year.
Related conditions
Other diseases that result from a deficiency in the sialidase enzyme are categorized in a broader group known as sialidoses. Because ML I is classified as a sialidosis, it is sometimes referred to as sialidosis type II.
A rarer form of sialidosis – sialidosis type 1– occurs in children and adolescents and is often referred to as the juvenile form of the disorder. Children usually begin to show symptoms during the second decade of life, and myoclonus and cherry-red macules are often the initial symptoms. Patients usually develop seizures and progressive deterioration of coordinated muscular and mental activities.
Pathophysiology
The role of sialidase is to remove a particular form of sialic acid (a sugar molecule) from sugar-protein complexes (referred to as glycoproteins), which allows the cell to function properly. Because the enzyme is deficient, small chains containing the sugar-like material accumulate in neurons, bone marrow, and various cells that defend the body against infection.
Diagnosis
The detection of high urinary sialyl oligosaccharides and the confirmation of lysosomal enzyme deficiency in leukocytes or cultured fibroblasts make the diagnosis.[2]
Management
Treatment of sialidosis is similar to the other progressive myoclonic epilepsy disorders, which consists of managing seizures and myoclonus along with palliative, supportive, and rehabilitative care.[2]
See also
- Fucosidosis
- Sialic acid
- Neuraminidase
- Mucolipidosis
- Lysosomal storage disease
Notes
- James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. p. 538. ISBN 978-0808923510.
- Shahwan, Amre; Farrell, Michael; Delanty, Norman (2005-04-01). "Progressive myoclonic epilepsies: a review of genetic and therapeutic aspects". The Lancet Neurology. 4 (4): 239–248. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(05)70043-0. ISSN 1474-4422. PMID 15778103. S2CID 2304164.
References
- mucolipidoses at NINDS - article derived from detail sheet available here
External links
- Sialidosis type 1 and 3 at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
- Sialidosis at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases