Vampyrellidae
The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Aconchulinida (formerly Vampyrellida) within the phylum Cercozoa.[1][2] Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus Vampyrella, and maybe several other vampyrellid amoebae (e.g. Gobiella).[2] The cells are naked and characterised by radiating, filose pseudopodia (also referred to as filopodia) and an orange colouration of the main cell body.[3][4]
| Vampyrellidae | |
|---|---|
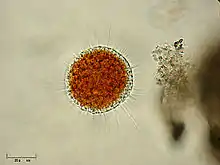 | |
| Vampyrella lateritia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Chromista |
| Phylum: | Cercozoa |
| Class: | Proteomyxidea |
| Order: | Aconchulinida |
| Family: | Vampyrellidae Zopf, 1885 |
| Genera | |
| |
In former times the family Vampyrellidae contained several genera (e.g. Vampyrella, Gobiella, Leptophrys, Platyreta, Theratromyxa) and was identical with the order Vampyrellida West, 1901, also known under the name "Aconchulinida".[5] However, based on molecular sequence data it seemed reasonable to restrict the family Vampyrellidae to a subgroup (containing the genus Vampyrella) and to establish another family for the genera Leptophrys, Platyreta and Theratromyxa, namely the Leptophryidae Hess et al., 2012.[2]
Characteristics
_(14596233838).jpg.webp)
When free-floating, the cell is spherical and around 30 μm across, with long radially directed filose pseudopods as well as distinctive shorter club-shaped ones, so that it resembles a heliozoan. Moving, the cell stretches out and takes a more typical amoeboid form, with an obvious distinction between the clear periphery and pseudopods and the greenish interior. In this form it finds its way into algae cells and feeds on their interiors. At least one genus, Theratromyxa, also feeds on soil nematodes.[6] A few other vampyrellids are parasitic on fungi. As such, these vampyrellids can be an important control of parasitic rust fungus of wheat and other crops.
Vampyrellids characteristically have mitochondria with tubular cristae. Together with the nucleariids they include the majority of the naked filose amoebae.
Systematics and Phylogeny
Clades and Genera
There are at least 45 credibly described species that are either proved or likely to belong to the order Vampyrellida, falling into 14 genera, which can be grouped into 5 clades:[7]
- Leptophryidae Hess, Sausen & Melkonian, 2012
- Arachnomyxa Hess, 2017
- Leptophrys Hertwig & Lesser, 1874
- Planctomyxa Hess, 2017
- Platyreta Cavalier-Smith & Bass, 2008
- Theratromyxa Zwillenberg, 1952
- Vernalophrys Gong et al. 2015
- Placopodidae Jahn, 1928 = Hyalodiscidae Poche, 1913
- Placopus Schulze, 1875 = Hyalodiscus Hertwig & Lesser, 1874[8]
- Sericomyxidae More, Simpson & Hess, 2021
- Sericomyxa More et al. 2021
- Thalassomyxa clade
- Thalassomyxa Grell, 1985
- Vampyrellidae Zopf, 1885
- Vampyrella Cienkowski, 1865
- Vampyrellida incertae sedis
- Arachnula Cienkowski, 1876 (potential synonym with Thalassomyxa, Leptophryidae)
- Asterocaelum Canter, 1973 (? Leptophryidae)
- Lateromyxa Hülsmann, 1993
- Monadopsis Klein, 1882
- Genera with uncertain phylogenetic affinity
- Gobiella Cienkowski, 1881 (putative amoeboid heterokont alga, ≈Chlamydomyxa)
- Vampyrellidium Zopf, 1885 (putative nucleariid amoebae)
- Vampyrelloides Schepotieff, 1912 = Protogenes Trichense, 1885
- Vampyrina Frenzel, 1893
Phylogenetic Tree[7]
| Vampyrellidae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- "Vampyrellidae". Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- Hess, Sebastian; Sausen, Nicole; Melkonian, Michael (2012-02-15). "Shedding Light on Vampires: The Phylogeny of Vampyrellid Amoebae Revisited". PLOS ONE. 7 (2): e31165. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...731165H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031165. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3280292. PMID 22355342.
- Cienkowski, L. (1865-12-01). "Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Monaden". Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie (in German). 1 (1): 203–232. doi:10.1007/BF02961414. ISSN 0176-7364. S2CID 84323025.
- Zopf, Wilhelm (1885). Die Pilzthiere oder Schleimpilze. Breslau: Trewendt.
- David Bass; Ema E.-Y. Chao; Sergey Nikolaev; Akinori Yabuki; Ken-ichiro Ishida; Cédric Berney; Ursula Pakzad; Claudia Wylezich & Thomas Cavalier-Smith (2009). "Phylogeny of novel naked filose and reticulose Cercozoa: Granofilosea cl. n. and Proteomyxidea revised". Protist. 160 (1): 75–109. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2008.07.002. PMID 18952499.
- Morphology and fine structure of the trophozoites of Theratromyxa weberi (Protozoa: Vampyrellidae) predacious on soil nematodes
- Hess, Sebastian; Suthaus, Andreas. "The Vampyrellid Amoebae (Vampyrellida, Rhizaria)". Protist. 173 (1: 125854). doi:10.1016/j.protis.2021.125854.
- The homonymy of Hyalodiscus Hertwig & Lesser, 1874 with the diatom genus Hyalodiscus Ehrenberg, 1845 (first described as a zoological taxon) in conflict with the code of the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) resulted in the adoption of the valid junior synonym Placopus
External links
- Röpstorf, Peter; Hülsmann, Norbert; Hausmann, Klaus (1994). "Comparative fine structural investigations of interphase and mitotic nuclei of vampyrellid filose amoebae". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 41 (1): 18–30. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1994.tb05930.x. S2CID 84357480.
- http://starcentral.mbl.edu/microscope/portal.php?pagetitle=assetfactsheet&imageid=932
- http://tolweb.org/tree?group=The_other_protists&contgroup=Eukaryotes