Administrative divisions of Mexico
The United Mexican States (Spanish: Estados Unidos Mexicanos) is a federal republic composed of 32 federal entities: 31 states[1] and Mexico City, an autonomous entity. According to the Constitution of 1917, the states of the federation are free and sovereign in all matters concerning their internal affairs.[2] Each state has its own congress and constitution.
| Mexican States Estados Mexicanos (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
| |
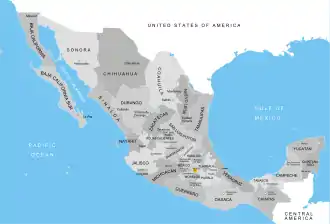 | |
| Category | Federated state |
| Location | United Mexican States |
| Number | 32 (31 states and Mexico City) |
| Populations | Smallest:
|
| Areas | Smallest:
|
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions |
|
Politics of Mexico |
|---|
 |
|
Federal entities of Mexico
Roles and powers of the states

The states of the Mexican Federation are free, sovereign, autonomous and independent of each other. They are free to govern themselves according to their own laws; each state has a constitution that cannot contradict the federal constitution, which covers issues of national competence. The states cannot make alliances with other states or any independent nation without the consent of the whole federation, except those related to defense and security arrangements necessary to keep the border states secure in the event of an invasion. The political organization of each state is based on a separation of powers in a congressional system: legislative power is vested in a unicameral congress (the federal congress has two chambers), executive power is independent of the legislature and vested in a governor elected by universal suffrage, and judicial power is vested in a Superior Court of Justice. Since the states have legal autonomy, each has its own civil and penal codes and judicial body.
In the Congress of the Union, the federative entities (the states) are each represented by three senators. Two are elected by universal suffrage on the principle of relative majority and one is assigned to the party that obtains the largest minority. In addition, the federation makes up a constituency in which 32 senators are elected by the method of proportional representation. Federal Deputies, however, do not represent the states, but rather the citizens themselves. The Chamber of Deputies and the Senate together comprise the Congress of the Union.
Internal organization of states
The states are internally divided into municipalities. Each municipality is autonomous in its ability to elect its own council. A council is headed by a mayor who is elected every three years. Each municipality has a council composed of councilors in terms of population size. In most cases, the council is responsible for providing all utilities required for its population. This concept, which arises from the Mexican Revolution, is known as a "free municipality".
As of January 2021, there are 2,454 municipalities in Mexico. The state with the highest number of municipalities is Oaxaca, with 570, and the state with the lowest number is Baja California Sur, with only five.[3]
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital of the United Mexican States. It had special status as a federal district until January 2016 and was originally called Distrito Federal.
Mexico City was separated from the State of Mexico, of which it was the capital, on November 18, 1824, to become the capital of the federation. As such, it belonged not to any state in particular but to all of them and to the federation. Therefore, the president of Mexico, who represented the federation, designated its head of government, previously referred to as the regent (regente) or head of department (jefe del departamento). However, the Federal District received more autonomy in 1997, and its citizens were then able to elect their chief of government for the first time.
In 2016, the Mexican Congress approved a constitutional reform eliminating the federal district and establishing Mexico City as a fully autonomous entity on par with the states.[4][5] However, unlike the other states of the Union, it would receive funds for education and health. When full autonomy was granted, Mexico City adopted its own constitution (it previously had only an organic law, the Statute of Autonomy) and its boroughs expanded their local government powers.[6]
Self-determination of indigenous peoples
The second article of the constitution recognizes the multicultural composition of the nation, which is founded upon the indigenous peoples. The government grants them the right of self-determination and autonomy. According to this article, the indigenous peoples are granted
- The right to decide their internal forms of social, economic, political and cultural organization;
- The right to apply their own normative systems of regulation as long as human rights and rights of women (gender equality) are granted;
- The right to preserve and enrich their languages and culture; and
- The right to elect representatives to the municipal council in which their territories are located, among other rights
The nation commits to and demands the constituent states and municipalities to promote the economic and social development of the indigenous communities, as well as an intercultural and bilingual education. According to the General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples, the nation recognizes 68 indigenous languages as "national languages", with the same validity as Spanish in the territories in which they are spoken. The indigenous peoples are entitled to request public services in their languages.
Postal abbreviations and ISO 3166-2 codes
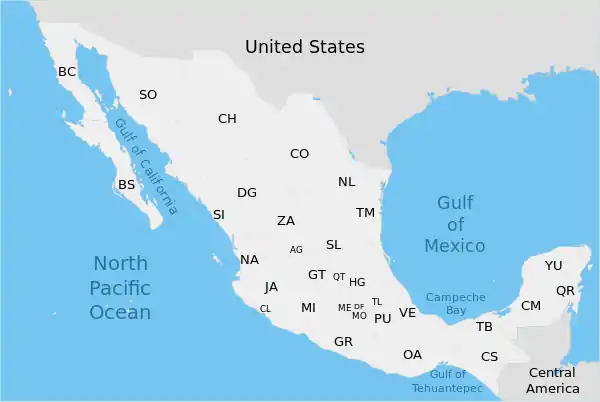
| Name of federative entity | Conventional abbreviation |
2-letter code* | 3-letter code (ISO 3166-2:MX) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ags. | MX - AG | MX-AGU | |
| B.C. | MX - BC | MX-BCN | |
| B.C.S. | MX - BS | MX-BCS | |
| Camp. | MX - CM | MX-CAM | |
| Chis. | MX - CS | MX-CHP | |
| Chih. | MX - CH | MX-CHH | |
| Coah. | MX - CO | MX-COA | |
| Col. | MX - CL | MX-COL | |
| CDMX | MX - DF | MX-CMX | |
| Dgo. | MX - DG | MX-DUR | |
| Gto. | MX - GT | MX-GUA | |
| Gro. | MX - GR | MX-GRO | |
| Hgo. | MX - HG | MX-HID | |
| Jal. | MX - JA | MX-JAL | |
| Edomex. or Méx. | MX - EM | MX-MEX | |
| Mich. | MX - MI | MX-MIC | |
| Mor. | MX - MO | MX-MOR | |
| Nay. | MX - NA | MX-NAY | |
| N.L. | MX - NL | MX-NLE | |
| Oax. | MX - OA | MX-OAX | |
| Pue. | MX - PU | MX-PUE | |
| Qro. | MX - QT | MX-QUE | |
| Q. Roo. or Q.R. | MX - QR | MX-ROO | |
| S.L.P. | MX - SL | MX-SLP | |
| Sin. | MX - SI | MX-SIN | |
| Son. | MX - SO | MX-SON | |
| Tab. | MX - TB | MX-TAB | |
| Tamps. | MX - TM | MX-TAM | |
| Tlax. | MX - TL | MX-TLA | |
| Ver. | MX - VE | MX-VER | |
| Yuc. | MX - YU | MX-YUC | |
| Zac. | MX - ZA | MX-ZAC |
*Mexico's post agency, Correos de México, does not offer an official list. Various competing commercially devised lists exist. The list here reflects choices among them according to these sources.
History
Constitutional empire
.svg.png.webp)
On September 27, 1821, after three centuries of Spanish rule, Mexico gained independence. The Treaty of Córdoba recognized part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain as an Independent Empire – "monarchist, constitutional and moderate".[8] The new country named itself the Mexican Empire. The morning after the Army of the Three Guarantees entered Mexico City on September 28, 1821, Agustín de Iturbide ordered the Supreme Provisional Governmental Junta (September 1821 – February 1822) to meet to elect a president of the Imperial Regency and to issue a declaration of independence for the new nation. Iturbide was elected president of the Regency, and that afternoon the members of the Regency and the Supreme Junta signed the Declaration.
A minority of the Constituent Congress, looking for stability, elected Agustín de Iturbide as emperor. On July 21, 1822, Iturbide was crowned Emperor of Mexico.[9] However, the Constitutional Empire quickly demonstrated the incompatibility of its two main parts: the Emperor and the Constituent Congress. The deputies were imprisoned just for expressing their opinions, and eventually Iturbide decided to dissolve the Congress and instead establish a National Board.[10]
The lack of a legitimate legislature, the illegitimacy of the Emperor, and the absence of real solutions to the nation's problems increased revolutionary activity.[11] Antonio López de Santa Anna proclaimed the Plan of Casa Mata, to which later joined Vicente Guerrero and Nicolás Bravo. Iturbide was forced to reestablish the Congress and, in a vain attempt to save the order and keep the situation favorable to his supporters, he abdicated the crown of the empire on March 19, 1823.[12]
Congress nullified the designation of Iturbide and therefore the recognition of the abdication. It deemed the coronation of Iturbide to have been a logical mistake in consummation of Independence.[12] The dissolution of the Empire was the first political realignment of independent Mexico.
Federal republic
.svg.png.webp)
After the fall of the Empire, a triumvirate called the Supreme Executive Power was created. The provisional government created the Federal Republic, and it was in effect from April 1, 1823, to October 10, 1824.[13]
Unrest in the provinces was widespread. On May 21, 1823, The Founding Plan of the Federal Republic was enacted. Its sixth article stated, "The component parts of the Republic are free, sovereign and independent States in that which touches internal administration and government".[14] Most of the Free States, which were invited to form the Federal Republic, joined the Union, except for the five Central American provinces, the former Captaincy General of Guatemala, which formed their own Federal Republic.[15]
On January 31, 1824, the decree to create a Constitutive Act of the Mexican Federation was issued, which incorporated the basic structure of the Federal Republic. It was determined that the criteria for inviting states to the federation should be that they "...not be so few that through expansion and wealth in a few years they be able to aspire to constitute themselves as independent nations, breaking the federal bond, nor so many that through lack of manpower and resources the system should come to be unworkable."[16]
Between 1823 and 1824, some of the Free States created their own constitutions, and others had already installed a Constituent Congress. Special cases were those of Yucatán, which on December 23, 1823, decided to join the federation but as a Federated Republic, and Chiapas, which decided by referendum to join the federation on September 14, 1824.[17]
On October 4, 1824, the Federal Constitution of the United Mexican States of 1824 was enacted. The constitution officially created the United Mexican States. The country was composed of 19 states and 4 federal territories.[18] After the publication of the constitution, on November 18, the Federal District was created.[19] On November 24, Tlaxcala, which had retained a special status since the colonial era, was incorporated as a territory.[20]
On October 10, 1824, Guadalupe Victoria took office as the first President of Mexico.[21]
Centralist republic
.svg.png.webp)
The political structure of the Republic was amended by a decree on October 3, 1835, when the centralist system was established.
The constituent states of the Republic lost their freedom, autonomy, independence, and sovereignty by being totally subordinated to the central government. However, the territorial division itself was the same, as the text of Article 8 of the Law determined: The national territory is divided into departments, on the basis of population, location and other leading circumstances: its number, extension and subdivisions, would be detailed by constitutional law.[22]
The Seven Constitutional Laws (Spanish: Siete Leyes Constitucionales) were promulgated on December 30, 1836.[23] The 1st article confirmed the decree of the law October 3, 1835; the Republic would be divided into departments, these in districts and the districts in parties. The 2nd article posited that the division of the Republic into departments would be under a special law with constitutional character.[24] On December 30, 1835, a transitory decree was added to the Seven Laws. The decree stated that the territory of Tlaxcala and the Federal District would become a part of the Department of Mexico. The territories of Alta and Baja California would form the department of the Californias. Coahuila y Tejas would be divided into two departments. Colima would form part of Michoacán, and Aguascalientes would be declared a department.
This period of political instability caused several conflicts between the central government and the entities of the country, and there were rebellions in several states:[25]
- Yucatán, due to being a Federated Republic, declared itself independent in 1840 (officially in 1841). The República de Yucatán (English: Republic of Yucatán) rejoined Mexico in 1848.
- Texas declared its independence and declared war against the central government of Mexico. The Republic of Texas was created. Texas remained independent until 1845, when it joined the United States of America. From 1861 to 1865, Texas was part of the Confederate States of America. After the defeat of the Confederacy in the American Civil War (1861–65) and Reconstruction, Texas rejoined the United States of America in 1870.
- In 1840, the states of Nuevo León, Tamaulipas and Coahuila declared themselves independent from Mexico for just under 250 days; the República del Río Grande never consolidated because independent forces were defeated by the centralist forces.
- Tabasco declared its separation from Mexico in February 1841, in protest against centralism and the imposed sanctions by centralist president Anastasio Bustamante. It rejoined in December 1842.
On September 11, 1842, the region of Soconusco joined Mexico as part of the department of Chiapas.
Restoration of the Republic and Second Empire
The Federal Republic was restored by the interim president José Mariano Salas on August 22, 1846. The state of Guerrero was provisionally erected in 1849, on the condition that it be approved by the legislatures of the states of México, Puebla and Michoacán, whose territories would be affected.
On February 5, 1857, the Federal Constitution of the United Mexican States of 1857 was enacted. In 1864, however, after the French intervention, the conservative Mexicans restored the constitutional monarchy, known as the Second Mexican Empire, led by the emperor Maximilian of Habsburg and supported by the French army of Napoleon III. The Empire was deposed in 1867 by the republican forces of Benito Juárez and the Federal Republic was restored again under the Constitution of 1857.
The Political Constitution of the United Mexican States of 1917 was the result of the Mexican Revolution. The third Constitution of Mexico confirmed the federal system of government that is currently in effect.[26]
See also
- Administrative division
- List of Latin American countries by Human Development Index
- Territorial evolution of Mexico
Notes
- ^a Some of these flags are used in states like Civil or Historic Flags (Yucatán, Hidalgo, Baja California, Michoacán) and are even more recognized by people as the official state flags assigned by President Ernesto Zedillo in 1999 and can be found waving in homes of the people. The others are proposed by citizen or groups to state legislatures, but have not yet been approved. Only two states in Mexico have changed the flags and have formalized their own, Jalisco and Tlaxcala.
References
- INEGI (January 1, 2016). "México en Cifras". en.www.inegi.org.mx (in Spanish). Retrieved January 6, 2020.
- Article 40 of "Federal Constitution of the United Mexican States" (PDF). Supreme Court of Mexico. p. 105. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 11, 2011. Retrieved April 5, 2011.
- "Censo de Población y Vivienda 2020 - SCITEL" (in Spanish). INEGI. Retrieved January 27, 2021.
- Mendez, Jose Luis; Dussauge-Laguna, Mauricio (2017). "Policy analysis in Mexico". International Library of Policy Analysis. Policy Press. 9th: 336. ISBN 9781447329169.
- "Mexico City Will Become A State". Wilson Center. June 2, 2016. Retrieved January 6, 2020.
- "Ponen fin al DF tras 191 años; Senado aprueba Reforma Política". December 16, 2015.
- "Constitution of Mexico City" (PDF) (in Spanish). Gobierno de la Ciudad de México. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- "24 de agosto de 1821. Se firman los tratados de Córdoba". Gobierno Federal. Archived from the original on September 21, 2010. Retrieved October 5, 2010.
- "21 de julio de 1822. Agustín de Iturbide es coronado emperador de México". Gobierno Federal. Archived from the original on October 6, 2010. Retrieved October 5, 2010.
- "La Transición del Imperio a la Republica (1821–1823)". Estudios de Historia Moderna y Contemporánea de México. Archived from the original on January 17, 2011. Retrieved October 5, 2010.
- Suárez y Navarro, Juan (1850). Historia de México y del general Antonio López de Santa Anna. México. p. 23.
- "La Transicion del Imperio a la Republica o la Participacion Indiscriminada" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on January 17, 2011. Retrieved May 6, 2010.
- "El Viajero en México (Pág. 30)" (PDF). CDigital. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved October 5, 2010.
- "División Territorial de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos (1810–1995) Pag.21" (PDF). INEGI. Retrieved October 5, 2010.
- "01 de julio de 1823. Las Provincias Unidas del Centro de América se independizan de México". Gobierno Federal. Archived from the original on September 20, 2010. Retrieved October 5, 2010.
- "Acta constitucional presentada al soberano Congreso Constituyente por su comisión" (in Spanish).
- "Aniversario de la Federación de Chiapas a México" (in Spanish).
- "Decreto. Constitución federal de los Estados-Unidos Mexicanos" (in Spanish).
- "Decreto. Se señala á México con el distrito que se expresa para la residencia de los supremos poderes de la federación" (in Spanish).
- "Decreto. Se declara á Tlaxcala territorio de la federación" (in Spanish).
- Tuck, Jim. "Guadalupe Victoria: Mexico's unknown first president".
- "Bases Constitucionales Expedidas por el Congreso Constituyente", en Felipe Tena Ramírez", Op.cit. p. 203
- "La Suprema Corte en las Constituciones Centralistas" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 12, 2007. Retrieved April 25, 2010.
- "Division Territorial de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos de 1810 a 1995 (Page 27)" (PDF) (in Spanish).
- "Division Territorial de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos de 1810 a 1995 (Page 28)" (PDF) (in Spanish).
- "Division Territorial de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos de 1810 a 1995 (Page 29)" (PDF) (in Spanish).
- Political Constitution of the United Mexican States; articles 2, and 42 through 48
- Law of Linguistic Rights or "Ley de los Derechos Lingüísticos" approved in 2001.juihu b
.svg.png.webp)