Business plan
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it intends to implement to achieve the stated targets. In its entirety, this document serves as a road-map (a plan) that provides direction to the business.[1][2]
| Corporate finance |
|---|
 |
| Working capital |
|
| Sections |
|
| Social components |
|
Written business plans are often required to obtain a bank loan or other kind of financing. Templates [3] and guides, such as the ones offered in the United States by the Small Business Administration[4] can be used to facilitate producing a business plan.
Audience
Business plans may be internally or externally focused. Externally-focused plans draft goals that are important to outside stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. These plans typically have detailed information about the organization or the team making effort to reach its goals. With for-profit entities, external stakeholders include investors and customers,[5] for non-profits, external stakeholders refer to donors and clients,[6] for government agencies, external stakeholders are the tax-payers, higher-level government agencies, and international lending bodies such as the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, various economic agencies of the United Nations, and development banks.
Internally-focused business plans target intermediate goals required to reach the external goals. They may cover the development of a new product, a new service, a new IT system, a restructuring of finance, the refurbishing of a factory or the restructuring of an organization. An internally-focused business plan is often developed in conjunction with a balanced scorecard or OGSM or a list of critical success factors. This allows the success of the plan to be measured using non-financial measures.
Business plans that identify and target internal goals, but provide only general guidance on how they will be met are called strategic plans.
Operational plans describe the goals of an internal organization, working group or department.[7] Project plans, sometimes known as project frameworks, describe the goals of a particular project. They may also address the project's place within the organization's larger strategic goals.[8]
Content
Business plans are decision-making tools. The content and format of the business plan are determined by the goals and audience. For example, a business plan for a non-profit might discuss the fit between the business plan and the organization's mission. Banks are quite concerned about defaults, so a business plan for a bank loan will build a convincing case for the organization's ability to repay the loan. Venture capitalists are primarily concerned about initial investment, feasibility, and exit valuation. A business plan for a project requiring equity financing will need to explain why current resources, upcoming growth opportunities, and sustainable competitive advantage will lead to a high exit valuation.[9]
Preparing a business plan draws on a wide range of knowledge from many different business disciplines: finance, human resource management, intellectual property management, supply chain management, operations management, and marketing, among others.[10] It can be helpful to view the business plan as a collection of sub-plans, one for each of the main business disciplines.[11]
"... a good business plan can help to make a good business credible, understandable, and attractive to someone who is unfamiliar with the business. Writing a good business plan can't guarantee success, but it can go a long way toward reducing the odds of failure."[11]
Presentation
The format of a business plan depends on its presentation context. It is common for businesses, especially start-ups, to have three or four formats for the same business plan.
An "elevator pitch" is a short summary of the plan's executive summary. This is often used as a teaser to awaken the interest of potential investors, customers, or strategic partners. It is called an elevator pitch as it is supposed to be content that can be explained to someone else quickly in an elevator. The elevator pitch should be between 30 and 60 seconds.[12]
A pitch deck is a slide show and oral presentation that is meant to trigger discussion and interest potential investors in reading the written presentation. The content of the presentation is usually limited to the executive summary and a few key graphs showing financial trends and key decision-making benchmarks. If a new product is being proposed and time permits, a demonstration of the product may be included.[13]
A written presentation for external stakeholders is a detailed, well written, and pleasingly formatted plan targeted at external stakeholders.
An internal operational plan is a detailed plan describing planning details that are needed by management but may not be of interest to external stakeholders. Such plans have a somewhat higher degree of candor and informality than the version targeted at external stakeholders and others.
Business plans for start-ups
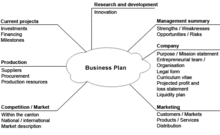
Typical structure for a business plan for a start-up venture [14]
- cover page and table of contents
- executive summary
- mission statement
- business description
- business environment analysis
- SWOT analysis
- industry background
- competitor analysis
- market analysis
- marketing plan
- operations plan
- management summary
- financial plan
- achievements and milestones
Typical questions addressed by a business plan for a start-up venture [15]
- What problem does the company's product or service solve? What niche will it fill?
- What is the company's solution to the problem?
- Who are the company's customers, and how will the company market and sell its products to them?
- What is the size of the market for this solution?
- What is the business model for the business (how will it make money)?
- Who are the competitors and how will the company maintain a competitive advantage?
- How does the company plan to manage its operations as it grows?
- Who will run the company and what makes them qualified to do so?
- What are the risks and threats confronting the business, and what can be done to mitigate them?
- What are the company's capital and resource requirements?
- What are the company's historical and projected financial statements?
Revising the business plan
Cost overruns and revenue shortfalls
Cost and revenue estimates are central to any business plan for deciding the viability of the planned venture. But costs are often underestimated and revenues overestimated resulting in later cost overruns, revenue shortfalls, and possibly non-viability. During the dot-com bubble 1997-2001 this was a problem for many technology start-ups. Reference class forecasting has been developed to reduce the risks of cost overruns and revenue shortfalls and thus generate more accurate business plans.
Legal and liability issues
Disclosure requirements
An externally targeted business plan should list all legal concerns and financial liabilities that might negatively affect investors. Depending on the number of funds being raised and the audience to whom the plan is presented, failure to do this may have severe legal consequences.
Limitations on content and audience
Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with third parties, non-compete agreements, conflicts of interest, privacy concerns, and the protection of one's trade secrets may severely limit the audience to which one might show the business plan. Alternatively, they may require each party to receive the business plan to sign a contract accepting special clauses and conditions.
This situation is complicated by the fact that many venture capitalists will refuse to sign an NDA before looking at a business plan, lest it put them in the untenable position of looking at two independently developed look-alike business plans, both claiming originality. In such situations, one may need to develop two versions of the business plan: a stripped-down plan that can be used to develop a relationship and a detailed plan that is only shown when investors have sufficient interest and trust to sign a Non-disclosure agreement.
Open business plans
Traditionally business plans have been highly confidential and quite limited in the audience. The business plan itself is generally regarded as a secret.
An open business plan is a business plan with an unlimited audience. The business plan is typically web published and made available to all.
In the free software and open source business model, trade secrets, copyright and patents can no longer be used as effective locking mechanisms to provide sustainable advantages to a particular business and therefore a secret business plan is less relevant in those models.
Uses
- Education
- Business plans are used in some primary and secondary programs to teach economic principles.
- Wikiversity has a Lunar Boom Town project where students of all ages can collaborate with designing and revising business models and practice evaluating them to learn practical business planning techniques and methodology
- Fundraising
Fundraising is the primary purpose of many business plans since they are related to the inherent probable success/failure of the company risk.
- Angel investors
- Business loans
- Grants
- Startup company funding
- Venture capital
- Internal use
- Management by objectives (MBO) is a process of agreeing upon objectives (as can be detailed within business plans) within an organization so that management and employees agree to the objectives and understand what they are in the organization.
- Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy, including its capital and people. Business plans can help decision-makers see how specific projects relate to the organization's strategic plan.
- Total quality management (TQM) is a business management strategy aimed at embedding awareness of quality in all organizational processes. TQM has been widely used in manufacturing, education, call centers, government, and service industries, as well as NASA space and science programs.
Not for-profit businesses
The business goals may be defined both for non-profit or for-profit organizations. For-profit business plans typically focus on financial goals, such as profit or creation of wealth. Non-profit, as well as government agency business plans tend to focus on the "organizational mission" which is the basis for their governmental status or their non-profit, tax-exempt status, respectively—although non-profits may also focus on optimizing revenue.
The primary difference between profit and non-profit organizations is that "for-profit" organizations look to maximize wealth versus non-profit organizations, which look to provide a greater good to society. In non-profit organizations, creative tensions may develop in the effort to balance mission with "margin" (or revenue).
Satires
The business plan is the subject of many satires. Satires are used both to express cynicism about business plans and as an educational tool to improve the quality of business plans. For example,
- In his presentation, Five Criteria For a Successful Business Plan in Biotech, Dr. Roger Bernier, uses Dilbert comic strips to remind people what not to do when researching and writing a business plan for a biotech start-up.[16]
- Selena Maranjian's "Fool on the Hill" article in The Motley Fool, "'South Park's' Investing Lesson" (November 8, 2001), references the "Underpants Gnomes" to illustrate the fallacy of focusing on goals without a clear implementation strategy. That "Gnomes" episode satirizes the business plans of the Dot-com era.[17]
- Chapter 26 of Neal Stephenson's 1999 novel Cryptonomicon begins with the business plan of a fictional high tech company, satirizing both the writing style and the physical form of slickly produced business publications like business plans and annual reports.
See also
- Business case
- Business model
- Business Motivation Model
- Corporate finance
- Cost overrun
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Marketing plan
- Optimism bias
- Parkinson's Law of Triviality
- Reference class forecasting
- Revenue shortfall
- Strategic plan
- Entrepreneurship
References
- "Business Plan Definition - Entrepreneur Small Business Encyclopedia". Entrepreneur. Retrieved 2018-10-29.
Business Plan - Definition: A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement[.] A business plan is also a road map that provides directions so a business can plan its future [...].
-
Bida Journal of Management and Technology. Bida: School of Business and Management, Federal Polytechnic. 1 (1): 113. 2008 https://books.google.com/books?id=qWYnAQAAIAAJ. Retrieved 21 December 2020.
[...] business plan [...] a guide or roadmap for any business activity. A business plan can also be referred to as a blue-print or scheme of a business enterprise.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - U.S. Small Business Administration, "Business Plan Template", accessed 28 December 2020
- U.S. Small Business Administration "Business Plan" (n.d.) Retrieved 2020 December 28.
- Small Business Notes Archived 2010-11-26 at the Wayback Machine business plan outline for small business start-up
- Tufts University non-profit business plan
- State of Louisiana, USA Archived 2012-09-15 at the Wayback Machine government agency operational plan
- Tasmanian government project management knowledge base government project plan Archived June 22, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- M&M Consultants Archived 2020-11-13 at the Wayback Machine You might know where we’re going with this – "potential investors, banks, private equity, and funding. People and institutions you want money from. If that’s the case, your business plan, and the way you present it, might be crucial to your success. If it’s not convincing, your business won’t be convincing either." Thus resulting in you not getting an investment.
- Boston College, Carroll School of Management, Business Plan Project Archived 2008-01-16 at the Wayback Machine The business school advises students that "To create a robust business plan, teams must take a comprehensive view of the enterprise and incorporate management-practice knowledge from every first-semester course." It is increasingly common for business schools to use business plan projects to provide an opportunity for students to integrate knowledge learned through their courses.
- Eric S. Siegel, Brian R. Ford, Jay M. Bornstein (1993), 'The Ernst & Young Business Plan Guide' (New York: John Wiley and Sons) ISBN 0-471-57826-6
- "How to Master Your Elevator Pitch". 24 May 2010. Retrieved 2014-10-14.
- Contributor. "How To Create An Early-Stage Pitch Deck For Investors".
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - Creating a Business Plan: Expert Solutions to Everyday Challenges. United States: Harvard Business School. 2007. pp. 7. ISBN 978-1422118856.
- "Cayenne Consultng LLC Ten Big Questions" (PDF). Cayenne Consultng LLC. Cayenne Consultng LLC. 2015-03-28. Retrieved 2015-03-28.
- Bernier, Roger Laurent. Five Criteria For a Successful Business Plan in Biotech. Archived from the original on January 6, 2012.
- Maranjian, Selena (November 8, 2001). "'South Park's' Investing Lesson". The Motley Fool. Archived from the original on 2012-03-13. Retrieved 2007-10-16.