Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. [lower-alpha 1]
| Part of a series on |
| Finance |
|---|
 |
|
In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities.
A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitability assessment of an action or entity. In some cases, theories in finance can be tested using the scientific method, covered by experimental finance.
Some fields are multidisciplinary, such as mathematical finance, financial law, financial economics, financial engineering and financial technology. These fields are the foundation of business and accounting.
The early history of finance parallels the early history of money, which is prehistoric. Ancient and medieval civilizations incorporated basic functions of finance, such as banking, trading and accounting, into their economies. In the late 19th century, the global financial system was formed.
It was in the middle of the 20th century that finance emerged as a distinct academic discipline, separate from economics.[1] (The first academic journal, The Journal of Finance, began publication in 1946.) The earliest doctoral programs in finance were established in the 1960s and 1970s.[2]
The financial system







As above, the financial system consists of the flows of capital that take place between individuals and households (personal finance), governments (public finance), and businesses (corporate finance). "Finance" thus studies the process of channeling money from savers and investors to entities that need it. [lower-alpha 2] Savers and investors have money available which could earn interest or dividends if put to productive use. Individuals, companies and governments must obtain money from some external source, such as loans or credit, when they lack sufficient funds to operate.
In general, an entity whose income exceeds its expenditure can lend or invest the excess, intending to earn a fair return. Correspondingly, an entity where income is less than expenditure can raise capital usually in one of two ways: (i) by borrowing in the form of a loan (private individuals), or by selling government or corporate bonds; (ii) by a corporation selling equity, also called stock or shares (which may take various forms: preferred stock or common stock). The owners of both bonds and stock may be institutional investors – financial institutions such as investment banks and pension funds – or private individuals, called private investors or retail investors.
The lending is often indirect, through a financial intermediary such as a bank, or via the purchase of notes or bonds (corporate bonds, government bonds, or mutual bonds) in the bond market. The lender receives interest, the borrower pays a higher interest than the lender receives, and the financial intermediary earns the difference for arranging the loan.[4][5][6] A bank aggregates the activities of many borrowers and lenders. A bank accepts deposits from lenders, on which it pays interest. The bank then lends these deposits to borrowers. Banks allow borrowers and lenders, of different sizes, to coordinate their activity.
Investing typically entails the purchase of stock, either individual securities, or via a mutual fund for example. Stocks are usually sold by corporations to investors so as to raise required capital in the form of "equity financing", as distinct from the debt financing described above. The financial intermediaries here are the investment banks. The investment banks find the initial investors and facilitate the listing of the securities, typically shares and bonds. Additionally, they facilitate the securities exchanges, which allow their trade thereafter, as well as the various service providers which manage the performance or risk of these investments. These latter include mutual funds, pension funds, wealth managers, and stock brokers, typically servicing retail investors (private individuals).
Inter-institutional trade and investment, and fund-management at this scale, is referred to as "wholesale finance". Institutions here extend the products offered, with related trading, to include bespoke options, swaps, and structured products, as well as specialized financing; this "financial engineering" is inherently mathematical, and these institutions are then the major employers of "quants" (see below). In these institutions, risk management, regulatory capital, and compliance play major roles.
Areas of finance
As outlined, finance comprises, broadly, the three areas of personal finance, corporate finance, and public finance. These, in turn, overlap and employ various activities and sub-disciplines – chiefly investments, risk management, and quantitative finance.
Personal finance

Personal finance is defined as "the mindful planning of monetary spending and saving, while also considering the possibility of future risk".[7] Personal finance may involve paying for education, financing durable goods such as real estate and cars, buying insurance, investing, and saving for retirement.[8] Personal finance may also involve paying for a loan or other debt obligations. The main areas of personal finance are considered to be income, spending, saving, investing, and protection.[9] The following steps, as outlined by the Financial Planning Standards Board,[10] suggest that an individual will understand a potentially secure personal finance plan after:
- Purchasing insurance to ensure protection against unforeseen personal events;
- Understanding the effects of tax policies, subsidies, or penalties on the management of personal finances;
- Understanding the effects of credit on individual financial standing;
- Developing a savings plan or financing for large purchases (auto, education, home);
- Planning a secure financial future in an environment of economic instability;
- Pursuing a checking and/or a savings account;
- Preparing for retirement or other long term expenses.[11]
Corporate finance

Corporate finance deals with the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, the sources of funding and the capital structure of corporations, and the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources. While corporate finance is in principle different from managerial finance, which studies the financial management of all firms rather than corporations alone, the concepts are applicable to the financial problems of all firms,[12] and this area is then often referred to as "business finance".
Typically "corporate finance" relates to the long term objective of maximizing the value of the entity's assets, its stock, and its return to shareholders, while also balancing risk and profitability. This entails [13] three primary areas:
- Capital budgeting: selecting which projects to invest in – here, accurately determining value is crucial, as judgements about asset values can be "make or break" [14]
- Dividend policy: the use of "excess" funds – are these to be reinvested in the business or returned to shareholders
- Capital structure: deciding on the mix of funding to be used – here attempting to find the optimal capital mix re debt-commitments vs cost of capital
The latter creates the link with investment banking and securities trading, as above, in that the capital raised will generically comprise debt, i.e. corporate bonds, and equity, often listed shares. Re risk management within corporates, see below.
Financial managers – i.e. as opposed to corporate financiers – focus more on the short term elements of profitability, cash flow, and "working capital management" (inventory, credit and debtors), ensuring that the firm can safely and profitably carry out its financial and operational objectives; i.e. that it: (1) can service both maturing short-term debt repayments, and scheduled long-term debt payments , and (2) has sufficient cash flow for ongoing and upcoming operational expenses. See Financial management § Role and Financial analyst § Corporate and other.
Public finance

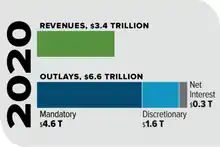
Public finance describes finance as related to sovereign states, sub-national entities, and related public entities or agencies. It generally encompasses a long-term strategic perspective regarding investment decisions that affect public entities.[15] These long-term strategic periods typically encompass five or more years.[16] Public finance is primarily concerned with: [17]
- Identification of required expenditures of a public sector entity;
- Source(s) of that entity's revenue;
- The budgeting process;
- Sovereign debt issuance, or municipal bonds for public works projects.
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve System banks in the United States and the Bank of England in the United Kingdom, are strong players in public finance. They act as lenders of last resort as well as strong influences on monetary and credit conditions in the economy.[18]
Development finance, which is related, concerns investment in economic development projects provided by a (quasi) governmental institution on a non-commercial basis; these projects would otherwise not be able to get financing. See Public utility § Finance. A public–private partnership is primarily used for infrastructure projects: a private sector corporate provides the financing up-front, and then draws profits from taxpayers and/or users.
Investment management


Investment management [19][20][12] is the professional asset management of various securities – typically shares and bonds, but also other assets, such as real estate, commodities and alternative investments – in order to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of investors.
As above, investors may be institutions, such as insurance companies, pension funds, corporations, charities, educational establishments, or private investors, either directly via investment contracts or, more commonly, via collective investment schemes like mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, or REITs.
At the heart of investment management[12] is asset allocation – diversifying the exposure among these asset classes, and among individual securities within each asset class – as appropriate to the client's investment policy, in turn, a function of risk profile, investment goals, and investment horizon (see Investor profile). Here:
- Portfolio optimization is the process of selecting the best portfolio given the client's objectives and constraints.
- Fundamental analysis is the approach typically applied in valuing and evaluating the individual securities.
Overlaid is the portfolio manager's investment style – broadly, active vs passive , value vs growth, and small cap vs. large cap – and investment strategy.
In a well-diversified portfolio, achieved investment performance will, in general, largely be a function of the asset mix selected, while the individual securities are less impactful. The specific approach or philosophy will also be significant, depending on the extent to which it is complementary with the market cycle.
A quantitative fund is managed using computer-based techniques (increasingly, machine learning) instead of human judgment. The actual trading also, is typically automated via sophisticated algorithms.
Risk management
.jpg.webp)

Risk management, in general, is the study of how to control risks and balance the possibility of gains; it is the process of measuring risk and then developing and implementing strategies to manage that risk. Financial risk management [21][22] is the practice of protecting corporate value by using financial instruments to manage exposure to risk, here called "hedging"; the focus is particularly on credit and market risk, and in banks, through regulatory capital, includes operational risk.
- Credit risk is risk of default on a debt that may arise from a borrower failing to make required payments;
- Market risk relates to losses arising from movements in market variables such as prices and exchange rates;
- Operational risk relates to failures in internal processes, people, and systems, or to external events.
Financial risk management is related to corporate finance[12] in two ways. Firstly, firm exposure to market risk is a direct result of previous capital investments and funding decisions; while credit risk arises from the business's credit policy and is often addressed through credit insurance and provisioning. Secondly, both disciplines share the goal of enhancing or at least preserving, the firm's economic value, and in this context[23] overlaps also enterprise risk management, typically the domain of strategic management. Here, businesses devote much time and effort to forecasting, analytics and performance monitoring. See also "ALM" and treasury management.
For banks and other wholesale institutions,[24] risk management focuses on managing, and as necessary hedging, the various positions held by the institution – both trading positions and long term exposures – and on calculating and monitoring the resultant economic capital, and regulatory capital under Basel III. The calculations here are mathematically sophisticated, and within the domain of quantitative finance as below. Credit risk is inherent in the business of banking, but additionally, these institutions are exposed to counterparty credit risk. Banks typically employ Middle office "Risk Groups" here, whereas front office risk teams provide risk "services" / "solutions" to customers.
Additional to diversification – the fundamental risk mitigant here – investment managers will apply various risk management techniques to their portfolios as appropriate:[12] these may relate to the portfolio as a whole or to individual stocks; bond portfolios are typically managed via cash flow matching or immunization. Re derivative portfolios (and positions), "the Greeks" is a vital risk management tool – it measures sensitivity to a small change in a given underlying parameter so that the portfolio can be rebalanced accordingly by including additional derivatives with offsetting characteristics.
Quantitative finance
Quantitative finance – also referred to as "mathematical finance" – includes those finance activities where a sophisticated mathematical model is required,[25] and thus overlaps several of the above.
As a specialized practice area, quantitative finance comprises primarily three sub-disciplines; the underlying theory and techniques are discussed in the next section:
- Quantitative finance is often synonymous with financial engineering. This area generally underpins a bank's customer-driven derivatives business – delivering bespoke OTC-contracts and "exotics", and designing the various structured products and solutions mentioned – and encompasses modeling and programming in support of the initial trade, and its subsequent hedging and management.
- Quantitative finance also significantly overlaps financial risk management in banking, as mentioned, both as regards this hedging, and as regards economic capital as well as compliance with regulations and the Basel capital / liquidity requirements.
- "Quants" are also responsible for building and deploying the investment strategies at the quantitative funds mentioned; they are also involved in quantitative investing more generally, in areas such as trading strategy formulation, and in automated trading, high-frequency trading, algorithmic trading, and program trading.
Financial theory
DCF valuation formula widely applied in business and finance, since articulated in 1938. Here, to get the value of the firm, its forecasted free cash flows are discounted to the present using the weighted average cost of capital for the discount factor. For share valuation investors use the related dividend discount model. |
Financial theory is studied and developed within the disciplines of management, (financial) economics, accountancy and applied mathematics. Abstractly,[12][26] finance is concerned with the investment and deployment of assets and liabilities over "space and time"; i.e., it is about performing valuation and asset allocation today, based on the risk and uncertainty of future outcomes while appropriately incorporating the time value of money. Determining the present value of these future values, "discounting", must be at the risk-appropriate discount rate, in turn, a major focus of finance-theory.[27] Since the debate as to whether finance is an art or a science is still open,[28] there have been recent efforts to organize a list of unsolved problems in finance.
Managerial finance
Managerial finance is the branch of management that concerns itself with the managerial application of finance techniques and theory, emphasizing the financial aspects of managerial decisions; the assessment is per the managerial perspectives of planning, directing, and controlling. The techniques addressed and developed relate in the main to managerial accounting and corporate finance: the former allow management to better understand, and hence act on, financial information relating to profitability and performance; the latter, as above, are about optimizing the overall financial structure, including its impact on working capital. The implementation of these techniques – i.e. financial management – is outlined above. Academics working in this area are typically based in business school finance departments, in accounting, or in management science.
Financial economics
Financial economics [31] is the branch of economics that studies the interrelation of financial variables, such as prices, interest rates and shares, as opposed to real economic variables, i.e. goods and services. It thus centers on pricing, decision making, and risk management in the financial markets, [31] [26] and produces many of the commonly employed financial models. (Financial econometrics is the branch of financial economics that uses econometric techniques to parameterize the relationships suggested.)
The discipline has two main areas of focus: [26] asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital; respectively:
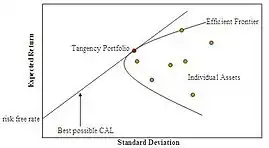
- Asset pricing theory develops the models used in determining the risk-appropriate discount rate, and in pricing derivatives; and includes the portfolio- and investment theory applied in asset management. The analysis essentially explores how rational investors would apply risk and return to the problem of investment under uncertainty; producing the key "Fundamental theorem of asset pricing". Here, the twin assumptions of rationality and market efficiency lead to modern portfolio theory (the CAPM), and to the Black–Scholes theory for option valuation. At more advanced levels – and often in response to financial crises – the study then extends these "Neoclassical" models to incorporate phenomena where their assumptions do not hold, or to more general settings.
- Much of corporate finance theory, by contrast, considers investment under "certainty" (Fisher separation theorem, "theory of investment value", Modigliani–Miller theorem). Here theory and methods are developed for the decisioning about funding, dividends, and capital structure discussed above. A recent development is to incorporate uncertainty and contingency – and thus various elements of asset pricing – into these decisions, employing for example real options analysis.
Financial mathematics
.png.webp)
Financial mathematics [33] is the field of applied mathematics concerned with financial markets; Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered to be the first scholarly work in this area. As above, in terms of practice, the field is referred to as quantitative finance and / or mathematical finance, and comprises primarily the three areas discussed.
The field is largely focused on the modeling of derivatives – with much emphasis on interest rate- and credit risk modeling – while other important areas include insurance mathematics and quantitative portfolio management. Relatedly, the techniques developed are applied to pricing and hedging a wide range of asset-backed, government, and corporate-securities. The main mathematical tools and techniques are:
- for derivatives,[34] Itô's stochastic calculus, simulation, and partial differential equations; see aside boxed discussion re the prototypical Black-Scholes and the various numeric techniques now applied
- for risk management,[24] value at risk, stress testing, "sensitivities" analysis (applying the "greeks"), and xVA; the underlying mathematics comprises mixture models, PCA, volatility clustering and copulas.[35]
- in both of these areas, and particularly for portfolio problems, quants employ sophisticated optimization techniques
Mathematically, these separate into two analytic branches: derivatives pricing uses risk-neutral probability (or arbitrage-pricing probability), denoted by "Q"; while risk and portfolio management generally use physical (or actual or actuarial) probability, denoted by "P". These are interrelated through the above "Fundamental theorem of asset pricing".
The subject has a close relationship with financial economics, which, as above, is concerned with much of the underlying theory that is involved in financial mathematics: generally, financial mathematics will derive and extend the mathematical models suggested. Computational finance is the branch of (applied) computer science that deals with problems of practical interest in finance, and especially [33] emphasizes the numerical methods applied here.
Experimental finance
Experimental finance[36] aims to establish different market settings and environments to experimentally observe and provide a lens through which science can analyze agents' behavior and the resulting characteristics of trading flows, information diffusion, and aggregation, price setting mechanisms, and returns processes. Researchers in experimental finance can study to what extent existing financial economics theory makes valid predictions and therefore prove them, as well as attempt to discover new principles on which such theory can be extended and be applied to future financial decisions. Research may proceed by conducting trading simulations or by establishing and studying the behavior of people in artificial, competitive, market-like settings.
Behavioral finance
Behavioral finance studies how the psychology of investors or managers affects financial decisions and markets[37] and is relevant when making a decision that can impact either negatively or positively on one of their areas. With more in-depth research into behavioral finance, it is possible to bridge what actually happens in financial markets with analysis based on financial theory.[38] Behavioral finance has grown over the last few decades to become an integral aspect of finance.[39]
Behavioral finance includes such topics as:
- Empirical studies that demonstrate significant deviations from classical theories;
- Models of how psychology affects and impacts trading and prices;
- Forecasting based on these methods;
- Studies of experimental asset markets and the use of models to forecast experiments.
A strand of behavioral finance has been dubbed quantitative behavioral finance, which uses mathematical and statistical methodology to understand behavioral biases in conjunction with valuation.
Quantum finance
Quantum finance is an interdisciplinary research field, applying theories and methods developed by quantum physicists and economists in order to solve problems in finance. It is a branch of econophysics. Finance theory is heavily based on financial instrument pricing such as stock option pricing. Many of the problems facing the finance community have no known analytical solution. As a result, numerical methods and computer simulations for solving these problems have proliferated. This research area is known as computational finance. Many computational finance problems have a high degree of computational complexity and are slow to converge to a solution on classical computers. In particular, when it comes to option pricing, there is additional complexity resulting from the need to respond to quickly changing markets. For example, in order to take advantage of inaccurately priced stock options, the computation must complete before the next change in the almost continuously changing stock market. As a result, the finance community is always looking for ways to overcome the resulting performance issues that arise when pricing options. This has led to research that applies alternative computing techniques to finance. Most commonly used quantum financial models are quantum continuous model, quantum binomial model, multi-step quantum binomial model etc.
History of finance
The origin of finance can be traced to the start of civilization. The earliest historical evidence of finance is dated to around 3000 BC. Banking originated in the Babylonian empire, where temples and palaces were used as safe places for the storage of valuables. Initially, the only valuable that could be deposited was grain, but cattle and precious materials were eventually included. During the same period, the Sumerian city of Uruk in Mesopotamia supported trade by lending as well as the use of interest. In Sumerian, "interest" was mas, which translates to "calf". In Greece and Egypt, the words used for interest, tokos and ms respectively, meant "to give birth". In these cultures, interest indicated a valuable increase, and seemed to consider it from the lender's point of view.[40] The Code of Hammurabi (1792-1750 BC) included laws governing banking operations. The Babylonians were accustomed to charging interest at the rate of 20 percent per annum.
Jews were not allowed to take interest from other Jews, but they were allowed to take interest from Gentiles, who had at that time no law forbidding them from practicing usury. As Gentiles took interest from Jews, the Torah considered it equitable that Jews should take interest from Gentiles. In Hebrew, interest is neshek.
By 1200 BC, cowrie shells were used as a form of money in China. By 640 BC, the Lydians had started to use coin money. Lydia was the first place where permanent retail shops opened. (Herodotus mentions the use of crude coins in Lydia in an earlier date, around 687 BC.)[41][42]
The use of coins as a means of representing money began in the years between 600 and 570 BCE. Cities under the Greek empire, such as Aegina (595 BCE), Athens (575 BCE), and Corinth (570 BCE), started to mint their own coins. In the Roman Republic, interest was outlawed altogether by the Lex Genucia reforms. Under Julius Caesar, a ceiling on interest rates of 12% was set, and later under Justinian it was lowered even further to between 4% and 8%.[43]
It's said Belgium is the place where the first exchange happened back in approximately 1531.[44] Since, popular exchanges such as the London Stock Exchange (founded in 1773) and the New York Stock Exchange (founded in 1793) were created.[45][46]
Image gallery

 Courtyard of the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, 1653, the world's first formal stock exchange
Courtyard of the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, 1653, the world's first formal stock exchange Dōjima Rice Exchange, the world's first futures exchange, established in Osaka in 1697
Dōjima Rice Exchange, the world's first futures exchange, established in Osaka in 1697
See also
- Outline of finance
- Financial crisis of 2007–2010
Notes
-
The following are definitions of finance as crafted by the authors indicated:
- Fama and Miller: "The theory of finance is concerned with how individuals and firms allocate resources through time. In particular, it seeks to explain how solutions to the problems faced in allocating resources through time are facilitated by the existence of capital markets (which provide a means for individual economic agents to exchange resources to be available of different points In time) and of firms (which, by their production-investment decisions, provide a means for individuals to transform current resources physically into resources to be available in the future)."
- Guthmann and Dougall: "Finance is concerned with the raising and administering of funds and with the relationships between private profit-seeking enterprise on the one hand and the groups which supply the funds on the other. These groups, which include investors and speculators — that is, capitalists or property owners — as well as those who advance short-term capital, place their money in the field of commerce and industry and in return expect a stream of income."
- Drake and Fabozzi: "Finance is the application of economic principles to decision-making that involves the allocation of money under conditions of uncertainty."
- F.W. Paish: "Finance may be defined as the position of money at the time it is wanted".
- John J. Hampton: "The term finance can be defined as the management of the flows of money through an organisation, whether it will be a corporation, school, or bank or government agency".
- Howard and Upton: "Finance may be defined as that administrative area or set of administrative functions in an organisation which relates with the arrangement of each debt and credit so that the organisation may have the means to carry out the objectives as satisfactorily as possible".
- Pablo Fernandez: “Finance is a profession that requires interdisciplinary training and can help the managers of companies make sound decisions about financing, investment, continuity and other issues that affect the inflows and outflows of money, and the risk of the company. It also helps people and institutions invest and plan money-related issues wisely.”
- Finance thus allows production and consumption in society to operate independently from each other. Without the use of financial allocation, production would have to happen at the same time and space as consumption. Through finance, distances in timespace between production and consumption are then posible.[3]
References
- Hayes, Adam. "Finance". Investopedia. Retrieved 2022-08-03.
- Gippel, Jennifer K (2012-11-07). "A revolution in finance?". Australian Journal of Management. 38 (1): 125–146. doi:10.1177/0312896212461034. ISSN 0312-8962.
- Allen, Michael; Price, John (2000). "Monetized time-space: derivatives – money's 'new imaginary'?". Economy and Society. 29 (2): 264-284. doi:10.1080/030851400360497. S2CID 145739812. Retrieved 3 June 2022.
- See e.g., Bank of Finland. "Financial system".
- "Introducing the Financial System | Boundless Economics". courses.lumenlearning.com. Retrieved 2020-05-18.
- "What is the financial system?". Economy.
- "Personal Finance - Definition, Overview, Guide to Financial Planning". Corporate Finance Institute. Retrieved 2019-10-23.
- Publishing, Speedy (2015-05-25). Finance (Speedy Study Guides). Speedy Publishing LLC. ISBN 978-1-68185-667-4.
- "Personal Finance - Definition, Overview, Guide to Financial Planning". Corporate Finance Institute. Retrieved 2020-05-18.
- Snowdon, Michael, ed. (2019), "Financial Planning Standards Board", Financial Planning Competency Handbook, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 709–735, doi:10.1002/9781119642497.ch80, ISBN 9781119642497, S2CID 242623141
- Kenton, Will. "Personal Finance". Investopedia. Retrieved 2020-01-20.
- Pamela Drake and Frank Fabozzi (2009). What Is Finance?
- See Aswath Damodaran, Corporate Finance: First Principles
- Irons, Robert (July 2019). The Fundamental Principles of Finance. Google Books: Routledge. ISBN 9781000024357. Retrieved 3 April 2021.
- Doss, Daniel; Sumrall, William; Jones, Don (2012). Strategic Finance for Criminal Justice Organizations (1st ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-1439892237.
- Doss, Daniel; Sumrall, William; Jones, Don (2012). Strategic Finance for Criminal Justice Organizations (1st ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 53–54. ISBN 978-1439892237.
- Sharon Kioko and Justin Marlowe (2016). Financial Strategy for Public Managers. Rebus Foundation. ISBN 978-1-927472-59-0.
- Board of Governors of Federal Reserve System of the United States. Mission of the Federal Reserve System. Federalreserve.gov Accessed: 2010-01-16. (Archived by WebCite at Archived 2010-01-14 at the Wayback Machine)
- Investment Management, Investopedia
- Portfolio Management: An Overview, CFA Institute
- Peter F. Christoffersen (22 November 2011). Elements of Financial Risk Management. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-374448-7.
- Allan M. Malz (13 September 2011). Financial Risk Management: Models, History, and Institutions. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-02291-7.
- John Hampton (2011). The AMA Handbook of Financial Risk Management. American Management Association. ISBN 978-0814417447
- See generally, Roy E. DeMeo (N.D.) Quantitative Risk Management: VaR and Others
- See discussion here: "Careers in Applied Mathematics" (PDF). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
- See the discussion re finance theory by Fama and Miller under § Notes.
- "Finance" Farlex Financial Dictionary. 2012
- "Is finance an art or a science?". Investopedia. Retrieved 2015-11-11.
- A. Pinkasovitch (2021). Using Decision Trees in Finance
- W. Kenton (2021). "Harry Markowitz", investopedia.com
- For an overview, see "Financial Economics", William F. Sharpe (Stanford University manuscript)
- "The History of the Black-Scholes Formula", priceonomics.com
- Research Area: Financial Mathematics and Engineering, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
- For a survey, see "Financial Models", from Michael Mastro (2013). Financial Derivative and Energy Market Valuation, John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1118487716.
- See for example III.A.3, in Carol Alexander, ed. (January 2005). The Professional Risk Managers' Handbook. PRMIA Publications. ISBN 978-0976609704
- Bloomfield, Robert and Anderson, Alyssa. "Experimental finance". In Baker, H. Kent, and Nofsinger, John R., eds. Behavioral finance: investors, corporations, and markets. Vol. 6. John Wiley & Sons, 2010. pp. 113-131. ISBN 978-0470499115
- "Behavioral Finance - Overview, Examples and Guide". Corporate Finance Institute. Retrieved 2020-09-21.
- Zahera, Syed Aliya; Bansal, Rohit (2018-05-08). "Do investors exhibit behavioral biases in investment decision making? A systematic review". Qualitative Research in Financial Markets. 10 (2): 210–251. doi:10.1108/QRFM-04-2017-0028. ISSN 1755-4179.
- Shefrin, Hersh (2002). Beyond greed and fear: Understanding behavioral finance and the psychology of investing. New York: Oxford University Press. p. ix. ISBN 978-0195304213. Retrieved 8 May 2017.
growth of behavioral finance.
- Fergusson, Nial. The Ascent of Money. United States: Penguin Books.
- "Herodotus on Lydia". World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2021-05-13.
- "babylon-coins.com". babylon-coins.com. Retrieved 2021-05-13.
- "ScienceGarden.de - deutschlands größtes Wissenschaftsmagazin".
- [visitantwerpen.be/en/sightseeing/architecture-monuments/new-exchange-handelsbeurs "New Exchange Handelsbeurs"]. Visit Antwerpen. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - "Our History". London Stock Exchange. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- Library of Congress https://guides.loc.gov/wall-street-history/exchanges. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
Further reading
- Graham, Benjamin; Jason Zweig (2003-07-08) [1949]. The Intelligent Investor. Warren E. Buffett (collaborator) (2003 ed.). HarperCollins. front cover. ISBN 0-06-055566-1.
- Graham, B. and Dodd, D. and Dodd, D.L.F. (1934). Security Analysis: The Classic 1934 Edition. McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN 978-0-070-24496-2. LCCN 34023635.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Rich Dad Poor Dad: What the Rich Teach Their Kids About Money That the Poor and Middle Class Do Not!, by Robert Kiyosaki and Sharon Lechter. Warner Business Books, 2000. ISBN 0-446-67745-0
- Bogle, John Bogle (2007). The Little Book of Common Sense Investing: The Only Way to Guarantee Your Fair Share of Stock Market Returns. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 216. ISBN 9780470102107.
- Buffett, W. and Cunningham, L.A. (2009). The Essays of Warren Buffett: Lessons for Investors and Managers. John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Limited. ISBN 978-0-470-82441-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Stanley, Thomas J. and Danko, W.D. (1998). The Millionaire Next Door. Gallery Books. ISBN 978-0-671-01520-6. LCCN 98046515.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Soros, George (1988). The Alchemy of Finance: Reading the Mind of the Market. A Touchstone book. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-66238-7. LCCN 87004745.
- Fisher, Philip Arthur (1996). Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits and Other Writings. Wiley Investment Classics. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-11927-2. LCCN 95051449.
External links
- Finance Definition - Investopedia
- Finance Definition - Corporate Finance Institute
- Hypertextual Finance Glossary (Campbell Harvey)
- Corporate finance resources (Aswath Damodaran)
- Financial management resources (James Van Horne)
- Financial mathematics, derivatives, and risk management resources (Don Chance)
- Personal finance resources (Financial Literacy and Education Commission, mymoney.gov)
- Public Finance resources (Governance and Social Development Resource Centre, gsdrc.org)