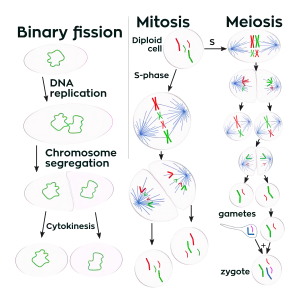
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells.[1] Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division (mitosis), producing daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and a cell division that produces haploid gametes for sexual reproduction (meiosis), reducing the number of chromosomes from two of each type in the diploid parent cell to one of each type in the daughter cells.[2] In cell biology, mitosis (/maɪˈtoʊsɪs/) is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interphase (during which the DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis all together define the mitotic (M) phase of animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two genetically identical daughter cells.[3] Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells by undergoing one round of DNA replication followed by two divisions. Homologous chromosomes are separated in the first division, and sister chromatids are separated in the second division. Both of these cell division cycles are used in the process of sexual reproduction at some point in their life cycle. Both are believed to be present in the last eukaryotic common ancestor.
Prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) usually undergo a vegetative cell division known as binary fission, where their genetic material is segregated equally into two daughter cells, but there are alternative manners of division, such as budding, that have been observed. All cell divisions, regardless of organism, are preceded by a single round of DNA replication.
For simple unicellular microorganisms such as the amoeba, one cell division is equivalent to reproduction – an entire new organism is created. On a larger scale, mitotic cell division can create progeny from multicellular organisms, such as plants that grow from cuttings. Mitotic cell division enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from the one-celled zygote, which itself is produced by fusion of two gametes, each having been produced by meiotic cell division.[4][5] After growth from the zygote to the adult, cell division by mitosis allows for continual construction and repair of the organism.[6] The human body experiences about 10 quadrillion cell divisions in a lifetime.[7]
The primary concern of cell division is the maintenance of the original cell's genome. Before division can occur, the genomic information that is stored in chromosomes must be replicated, and the duplicated genome must be cleanly divided between progeny cells.[8] A great deal of cellular infrastructure is involved in ensuring consistency of genomic information among generations.[9][10][11]
In bacteria

Bacterial cell division happens through binary fission or sometimes through budding. The divisome is a protein complex in bacteria that is responsible for cell division, constriction of inner and outer membranes during division, and remodeling of the peptidoglycan cell wall at the division site. A tubulin-like protein, FtsZ plays a critical role in formation of a contractile ring for the cell division.[13]
In eukaryotes
Cell division in eukaryotes is much more complicated than in prokaryotes. Depending upon chromosomal number reduced or not; Eukaryotic cell divisions can be classified as mitosis (equational division) and meiosis (reductional division). A primitive form of cell division is also found which is called amitosis. The amitotic or mitotic cell division is more atypical and diverse in the various groups of organisms such as protists (namely diatoms, dinoflagellates etc.) and fungi. In Zebra fish, however, skin cells undergo asynthetic fission to expand body surfaces.
 closed
closed
intranuclear
pleuromitosis closed
closed
extranuclear
pleuromitosis closed
closed
orthomitosis semiopen
semiopen
pleuromitosis semiopen
semiopen
orthomitosis open
open
orthomitosis
In mitotic metaphase (see below), typically the chromosomes (each with 2 sister chromatids that they developed due to replication in the S phase of interphase) arranged and sister chromatids split and distributed toward daughter cells.
In meiosis, typically in Meiosis-I the homologous chromosomes are paired and then separated and distributed into daughter cells. Meiosis-II is like mitosis where the chromatids are separated. In human and other higher animals and many other organisms, the meiosis is called gametic meiosis, that is meiosis gives rise to gametes. Whereas in many groups of organisms, especially in plants (observable in lower plants, meiosis but vestigial stage in higher plants), the meiosis gives rise to the kind of spores that germinate into haploid vegetative phase (gametophyte). This kind of meiosis is called sporic meiosis.
Phases of eukaryotic cell division
Interphase
Interphase is the process through which a cell must go before mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis.[14] Interphase consists of three main phases: G1, S, and G2. G1 is a time of growth for the cell where specialized cellular functions occur in order to prepare the cell for DNA replication.[15] There are checkpoints during interphase that allow the cell to either advance or halt further development. One of the checkpoint is between G1 and S, the purpose for this checkpoint is to check for appropriate cell size and any DNA damage . The second check point is in the G2 phase, this checkpoint also checks for cell size but also the DNA replication. The last check point is located at the site of metaphase, where it checks that the chromosomes are correctly connected to the mitotic spindles.[16] In S phase, the chromosomes are replicated in order for the genetic content to be maintained.[17] During G2, the cell undergoes the final stages of growth before it enters the M phase, where spindles are synthesized. The M phase can be either mitosis or meiosis depending on the type of cell. Germ cells, or gametes, undergo meiosis, while somatic cells will undergo mitosis. After the cell proceeds successfully through the M phase, it may then undergo cell division through cytokinesis. The control of each checkpoint is controlled by cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinases. The progression of interphase is the result of the increased amount of cyclin. As the amount of cyclin increases, more and more cyclin dependent kinases attach to cyclin signaling the cell further into interphase. At the peak of the cyclin, attached to the cyclin dependent kinases this system pushes the cell out of interphase and into the M phase, where mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis occur.[18] There are three transition checkpoints the cell has to go through before entering the M phase. The most important being the G1-S transition checkpoint. If the cell does not pass this checkpoint, it results in the cell exiting the cell cycle.[19]
Prophase
Prophase is the first stage of division. The nuclear envelope is broken down in this stage, long strands of chromatin condense to form shorter more visible strands called chromosomes, the nucleolus disappears, and microtubules attach to the chromosomes at the disc-shaped kinetochores present in the centromere.[20] Microtubules associated with the alignment and separation of chromosomes are referred to as the spindle and spindle fibers. Chromosomes will also be visible under a microscope and will be connected at the centromere. During this condensation and alignment period in meiosis, the homologous chromosomes undergo a break in their double-stranded DNA at the same locations, followed by a recombination of the now fragmented parental DNA strands into non-parental combinations, known as crossing over.[21] This process is evidenced to be caused in a large part by the highly conserved Spo11 protein through a mechanism similar to that seen with toposomerase in DNA replication and transcription.[22]
Metaphase
In metaphase, the centromeres of the chromosomes convene themselves on the metaphase plate (or equatorial plate), an imaginary line that is at equal distances from the two centrosome poles and held together by complexes known as cohesins. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell by microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs) pushing and pulling on centromeres of both chromatids thereby causing the chromosome to move to the center. At this point the chromosomes are still condensing and are currently one step away from being the most coiled and condensed they will be, and the spindle fibers have already connected to the kinetochores.[23] During this phase all the microtubules, with the exception of the kinetochores, are in a state of instability promoting their progression toward anaphase.[24] At this point, the chromosomes are ready to split into opposite poles of the cell toward the spindle to which they are connected.[25]
Anaphase
Anaphase is a very short stage of the cell cycle and it occurs after the chromosomes align at the mitotic plate. Kinetochores emit anaphase-inhibition signals until their attachment to the mitotic spindle. Once the final chromosome is properly aligned and attached the final signal dissipates and triggers the abrupt shift to anaphase.[24] This abrupt shift is caused by the activation of the anaphase-promoting complex and its function of tagging degradation of proteins important toward the metaphase-anaphase transition. One of these proteins that is broken down is securin which through its breakdown releases the enzyme separase that cleaves the cohesin rings holding together the sister chromatids thereby leading to the chromosomes separating.[26] After the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, the spindle fibers will pull them apart. The chromosomes are split apart while the sister chromatids move to opposite sides of the cell.[27] As the sister chromatids are being pulled apart, the cell and plasma are elongated by non-kinetochore microtubules.[28]
Telophase
Telophase is the last stage of the cell cycle in which a cleavage furrow splits the cells cytoplasm (cytokinesis) and chromatin. This occurs through the synthesis of a new nuclear envelope that forms around the chromatin gathered at each pole. The nucleolus reforms as the chromatin reverts back to the loose state it possessed during interphase.[29][30] The division of the cellular contents is not always equal and can vary by cell type as seen with oocyte formation where one of the four daughter cells possess the majority of the cytoplasm.[31]
Cytokinesis
The last stage of the cell division process is cytokinesis. In this stage there is a cytoplasmic division that occurs at the end of either mitosis or meiosis. At this stage there is a resulting irreversible separation leading to two daughter cells. Cell division plays an important role in determining the fate of the cell. This is due to there being the possibility of an asymmetric division. This as a result leads to cytokinesis producing unequal daughter cells containing completely different amounts or concentrations of fate-determining molecules.[32]
In animals the cytokinesis ends with formation of a contractile ring and thereafter a cleavage. But in plants it happen differently. At first a cell plate is formed and then a cell wall develops between the two daughter cells.
In Fission yeast (S. pombe) the cytokinesis happens in G1 phase [33]
Variants

Cells are broadly classified into two main categories: simple non-nucleated prokaryotic cells and complex nucleated eukaryotic cells. Due to their structural differences, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells do not divide in the same way. Also, the pattern of cell division that transforms eukaryotic stem cells into gametes (sperm cells in males or egg cells in females), termed meiosis, is different from that of the division of somatic cells in the body. Image of the mitotic spindle in a human cell showing microtubules in green, chromosomes (DNA) in blue, and kinetochores in red.
In 2022, scientists discovered a new type of cell division called asynthetic fission found in the squamous epithelial cells in the epidermis of juvenile zebrafish. When juvenile zebrafish are growing, skin cells must quickly cover the rapidly increasing surface area of the zebrafish. These skin cells divide without duplicating their DNA (the S phase of mitosis) causing up to 50% of the cells to have a reduced genome size. These cells are later replaced by cells with a standard amount of DNA. Scientists expect to find this type of division in other vertebrates.[35]
Degradation
Multicellular organisms replace worn-out cells through cell division. In some animals, however, cell division eventually halts. In humans this occurs, on average, after 52 divisions, known as the Hayflick limit. The cell is then referred to as senescent. With each division the cells telomeres, protective sequences of DNA on the end of a chromosome that prevent degradation of the chromosomal DNA, shorten. This shortening has been correlated to negative effects such as age-related diseases and shortened lifespans in humans.[36][37] Cancer cells, on the other hand, are not thought to degrade in this way, if at all. An enzyme complex called telomerase, present in large quantities in cancerous cells, rebuilds the telomeres through synthesis of telomeric DNA repeats, allowing division to continue indefinitely.[38]
History
.jpg.webp)
A cell division under microscope was first discovered by German botanist Hugo von Mohl in 1835 as he worked over the green alga Cladophora glomerata.[39]
In 1943, cell division was filmed for the first time[40] by Kurt Michel using a phase-contrast microscope.[41]
See also
- Cell fusion
- gametic fusion
- Cell growth
- Cyclin-dependent kinase
- Labile cells, cells that constantly divide
References
- Martin EA, Hine R (2020). A dictionary of biology (6th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199204625. OCLC 176818780.
- Griffiths AJ (2012). Introduction to genetic analysis (10th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman and Co. ISBN 9781429229432. OCLC 698085201.
- "10.2 The Cell Cycle - Biology 2e | OpenStax". openstax.org. Retrieved 2020-11-24.
- Gilbert SF (2000). "Spermatogenesis". Developmental Biology (6th ed.).
- Gilbert SF (2000). "Oogenesis". Developmental Biology (6th ed.).
- Maton, Anthea (1997). Cells : building blocks of life (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. pp. 70–74. ISBN 978-0134234762. OCLC 37049921.
- Quammen D (April 2008). "Contagious Cancer". Harper's Magazine. ISSN 0017-789X. Retrieved 2019-04-14.
- Golitsin, Yuri N.; Krylov, Mikhail C. C. (2010). Cell division : theory, variants, and degradation. New York: Nova Science Publishers. p. 137. ISBN 9781611225938. OCLC 669515286.
- Fletcher, Daniel A.; Mullins, R. Dyche (28 January 2010). "Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton". Nature. 463 (7280): 485–492. Bibcode:2010Natur.463..485F. doi:10.1038/nature08908. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 2851742. PMID 20110992.
- Li, Shanwei; Sun, Tiantian; Ren, Haiyun (27 April 2015). "The functions of the cytoskeleton and associated proteins during mitosis and cytokinesis in plant cells". Frontiers in Plant Science. 6: 282. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00282. ISSN 1664-462X. PMC 4410512. PMID 25964792.
- Hohmann, Tim; Dehghani, Faramarz (18 April 2019). "The Cytoskeleton—A Complex Interacting Meshwork". Cells. 8 (4): 362. doi:10.3390/cells8040362. ISSN 2073-4409. PMC 6523135. PMID 31003495.
- Hugonnet JE, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Monton A, den Blaauwen T, Carbonnelle E, Veckerlé C, et al. (October 2016). "Escherichia coli". eLife. 5. doi:10.7554/elife.19469. PMC 5089857. PMID 27767957.
- Cell Division: The Cycle of the Ring, Lawrence Rothfield and Sheryl Justice, CELL, DOI
- Marieb EN (2000). Essentials of human anatomy and physiology (6th ed.). San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 978-0805349405. OCLC 41266267.
- Pardee AB (November 1989). "G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation". Science. 246 (4930): 603–8. Bibcode:1989Sci...246..603P. doi:10.1126/science.2683075. PMID 2683075.
- Molinari M (October 2000). "Cell cycle checkpoints and their inactivation in human cancer". Cell Proliferation. 33 (5): 261–74. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2184.2000.00191.x. PMC 6496592. PMID 11063129.
- Morgan DO (2007). The cell cycle : principles of control. London: New Science Press. ISBN 9780199206100. OCLC 70173205.
- Lindqvist A, van Zon W, Karlsson Rosenthal C, Wolthuis RM (May 2007). "Cyclin B1-Cdk1 activation continues after centrosome separation to control mitotic progression". PLOS Biology. 5 (5): e123. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050123. PMC 1858714. PMID 17472438.
- Paulovich AG, Toczyski DP, Hartwell LH (February 1997). "When checkpoints fail". Cell. 88 (3): 315–21. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81870-X. PMID 9039258. S2CID 5530166.
- Schermelleh L, Carlton PM, Haase S, Shao L, Winoto L, Kner P, et al. (June 2008). "Subdiffraction multicolor imaging of the nuclear periphery with 3D structured illumination microscopy". Science. 320 (5881): 1332–6. Bibcode:2008Sci...320.1332S. doi:10.1126/science.1156947. PMC 2916659. PMID 18535242.
- Lewontin RC, Miller JH, Gelbart WM, Griffiths AJ (1999). "The Mechanism of Crossing-Over". Modern Genetic Analysis.
- Keeney S (2001). Mechanism and control of meiotic recombination initiation. Current Topics in Developmental Biology. Vol. 52. Elsevier. pp. 1–53. doi:10.1016/s0070-2153(01)52008-6. ISBN 9780121531522. PMID 11529427.
- "Researchers Shed Light On Shrinking Of Chromosomes". ScienceDaily. Retrieved 2019-04-14.
- Walter P, Roberts K, Raff M, Lewis J, Johnson A, Alberts B (2002). "Mitosis". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.).
- Elrod S (2010). Schaum's outlines : genetics (5th ed.). New York: Mcgraw-Hill. p. 8. ISBN 9780071625036. OCLC 473440643.
- Brooker AS, Berkowitz KM (2014). "The roles of cohesins in mitosis, meiosis, and human health and disease". Cell Cycle Control. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1170. New York: Springer. pp. 229–66. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-0888-2_11. ISBN 9781493908875. PMC 4495907. PMID 24906316.
- "The Cell Cycle". www.biology-pages.info. Retrieved 2019-04-14.
- Urry LA, Cain ML, Jackson RB, Wasserman SA, Minorsky PV, Reece JB (2014). Campbell Biology in Focus. Boston (Massachusetts): Pearson. ISBN 978-0-321-81380-0.
- Dekker J (2014-11-25). "Two ways to fold the genome during the cell cycle: insights obtained with chromosome conformation capture". Epigenetics & Chromatin. 7 (1): 25. doi:10.1186/1756-8935-7-25. PMC 4247682. PMID 25435919.
- Hetzer MW (March 2010). "The nuclear envelope". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2 (3): a000539. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000539. PMC 2829960. PMID 20300205.
- Gilbert SF (2000). "Oogenesis". Developmental Biology (6th ed.).
- Guertin DA, Trautmann S, McCollum D (June 2002). "Cytokinesis in eukaryotes". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 66 (2): 155–78. doi:10.1128/MMBR.66.2.155-178.2002. PMC 120788. PMID 12040122.
- The Cell, G.M. Cooper; ed 2 NCBI bookshelf, The eukaryotic cell cycle, Figure 14.7
- "Phase Holographic Imaging of Cell Division". Internet archive. Archived from the original on 29 June 2013.
- Chan KY, Yan CC, Roan HY, Hsu SC, Tseng TL, Hsiao CD, et al. (April 2022). "Skin cells undergo asynthetic fission to expand body surfaces in zebrafish". Nature. 605 (7908): 119–125. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04641-0. PMID 35477758. S2CID 248416916.
- Jiang H, Schiffer E, Song Z, Wang J, Zürbig P, Thedieck K, et al. (August 2008). "Proteins induced by telomere dysfunction and DNA damage represent biomarkers of human aging and disease". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 (32): 11299–304. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10511299J. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801457105. PMC 2516278. PMID 18695223.
- Cawthon RM, Smith KR, O'Brien E, Sivatchenko A, Kerber RA (February 2003). "Association between telomere length in blood and mortality in people aged 60 years or older". Lancet. 361 (9355): 393–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12384-7. PMID 12573379. S2CID 38437955.
- Jafri MA, Ansari SA, Alqahtani MH, Shay JW (June 2016). "Roles of telomeres and telomerase in cancer, and advances in telomerase-targeted therapies". Genome Medicine. 8 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s13073-016-0324-x. PMC 4915101. PMID 27323951.
- Biographie, Deutsche. "Mohl, Hugo von - Deutsche Biographie". www.deutsche-biographie.de (in German). Retrieved 2019-04-15.
- Masters BR (2008-12-15). "History of the Optical Microscope in Cell Biology and Medicine". Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0003082. ISBN 978-0470016176.
- ZEISS Microscopy (2013-06-01), Historic time lapse movie by Dr. Kurt Michel, Carl Zeiss Jena (ca. 1943), archived from the original on 2021-11-07, retrieved 2019-04-15
Further reading
- Morgan HI. (2007). "The Cell Cycle: Principles of Control" London: New Science Press.
- J.M.Turner Fetus into Man (1978, 1989). Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-30692-9
- Cell division: binary fission and mitosis
- McDougal, W. Scott, et al. Campbell-Walsh Urology Eleventh Edition Review. Elsevier, 2016.
- The Mitosis and Cell Cycle Control Section from the Landmark Papers in Cell Biology (Gall JG, McIntosh JR, eds.) contains commentaries on and links to seminal research papers on mitosis and cell division. Published online in the Image & Video Library of The American Society for Cell Biology
- The Image & Video Library Archived 2011-06-10 at the Wayback Machine of The American Society for Cell Biology contains many videos showing the cell division.
- The Cell Division of the Cell Image Library
- Images : Calanthe discolor Lindl. - Flavon's Secret Flower Garden
- Tyson's model of cell division and a Description on BioModels Database
- WormWeb.org: Interactive Visualization of the C. elegans Cell Lineage - Visualize the entire set of cell divisions of the nematode C. elegans