Stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).[3]
| Stenosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Stenoses |
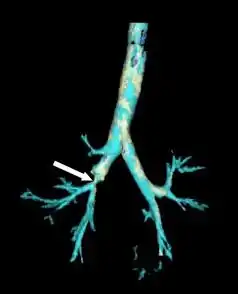 | |
| CT scan of a bronchial stenosis (arrow) that resulted from tracheobronchial injury | |
| Pronunciation | |
Stricture as a term is usually used when narrowing is caused by contraction of smooth muscle (e.g. achalasia, prinzmetal angina); stenosis is usually used when narrowing is caused by lesion that reduces the space of lumen (e.g. atherosclerosis).[4] The term coarctation is another synonym,[5] but is commonly used only in the context of aortic coarctation.[6][7]
Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis after a procedure.[8]
Types
The resulting syndrome depends on the structure affected.
Examples of vascular stenotic lesions include:
- Intermittent claudication (peripheral artery stenosis)
- Angina (coronary artery stenosis)
- Carotid artery stenosis which predispose to (strokes and transient ischaemic episodes)[9]
- Renal artery stenosis
The types of stenoses in heart valves are:
- Pulmonary valve stenosis, which is the thickening of the pulmonary valve, therefore causing narrowing
- Mitral valve stenosis, which is the thickening of the mitral valve (of the left heart), therefore causing narrowing
- Tricuspid valve stenosis, which is the thickening of the tricuspid valve (of the right heart), therefore causing narrowing
- Aortic valve stenosis, which is the thickening of the aortic valve, therefore causing narrowing
Stenoses/strictures of other bodily structures/organs include:
- Pyloric stenosis (gastric outflow obstruction)
- Lumbar, cervical or thoracic spinal stenosis
- Subglottic stenosis (SGS)
- Tracheal stenosis
- Obstructive jaundice (biliary tract stenosis)
- Bowel obstruction
- Phimosis
- Non-communicating hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis
- Stenosing tenosynovitis
- Atherosclerosis
- Esophageal stricture
- Achalasia
- Prinzmetal angina
- Vaginal stenosis
- Meatal stenosis
Causes
- alcohol
- atherosclerosis causes stenotic lesions in arteries.
- birth defects
- calcification
- diabetes
- headbanging – as in the case of Dave Mustaine
- iatrogenic, e.g. secondary to radiation therapy
- infection
- inflammation
- ischemia
- neoplasm – in such cases, the stenosis is often said to be "malignant" or "benign", although this attribute actually refers to the neoplasm itself.
- smoking
- ureteral
- urethral
Diagnosis
Stenoses of the vascular type are often associated with unusual blood sounds resulting from turbulent flow over the narrowed blood vessel. This sound can be made audible by a stethoscope, but diagnosis is generally made or confirmed with some form of medical imaging.
See also
- Atresia
References
- OED 2nd edition, 1989, as /stɪˈnəʊsɪs/.
- Entry "stenosis" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- "Dorlands Medical Dictionary:stenosis". www.mercksource.com. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- "What Is Atherosclerosis? - NHLBI, NIH". www.nhlbi.nih.gov. 22 June 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- "coarctation" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- "Coarctation of the Aorta (CoA)". heart.org.
- Groenemeijer, BE; Bakker, A; Slis, HW; Waalewijn, RA; Heijmen, RH (2008). "An unexpected finding late after repair of coarctation of the aorta". Netherlands Heart Journal. 16 (7–8): 260–3. doi:10.1007/bf03086158. PMC 2516290. PMID 18711614.
- Forgos, Richard N. (August 2004). "Restenosis After Angioplasty and Stenting".
- "Carotid Artery Stenosis". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. 15 March 2021. Retrieved 6 July 2021.
External links
- "Tracheal Stenosis Audio and Video". Archived from the original on 2007-01-12.
- "Symptoms of Urethral Stricture". 20 May 2011. Archived from the original on July 17, 2016.