Bremerhaven
Bremerhaven (German pronunciation: [ˌbʁeːmɐˈhaːfn̩] (![]() listen), lit. 'Bremener Harbor', Low German: Bremerhoben) is a city at the seaport of the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, a state of the Federal Republic of Germany.
listen), lit. 'Bremener Harbor', Low German: Bremerhoben) is a city at the seaport of the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, a state of the Federal Republic of Germany.
Bremerhaven | |
|---|---|
City | |
 Bremerhaven in July 2013 | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
Location of Bremerhaven  | |
 Bremerhaven  Bremerhaven | |
| Coordinates: 53°33′0″N 8°35′0″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Bremen |
| Founded | 1827 |
| Subdivisions | 2 boroughs with 9 districts |
| Government | |
| • Lord mayor | Melf Grantz (SPD) |
| • Governing parties | SPD / CDU / FDP |
| Area | |
| • Total | 93.82 km2 (36.22 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 2 m (7 ft) |
| Population (2020-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 113,557 |
| • Density | 1,200/km2 (3,100/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 27568-27580 |
| Dialling codes | 0471 |
| Vehicle registration | HB (with 1 letter and 4 digits) |
| Website | bremerhaven.de |
.jpg.webp)
It forms a semi-enclave in the state of Lower Saxony and is located at the mouth of the River Weser on its eastern bank, opposite the town of Nordenham. Though a relatively new city, it has a long history as a trade port and today is one of the most important German ports, playing a role in Germany's trade.
History

.jpg.webp)
The town was founded in 1827, but neighboring settlements such as Lehe were in the vicinity as early as the 12th century, and Geestendorf was "mentioned in documents of the ninth century".[2] These tiny villages were built on small islands in the swampy estuary. In 1381, the city of Bremen established de facto rule over the lower Weser stream, including Lehe, later therefore called Bremerlehe. Early in 1653, Swedish Bremen-Verden's troops captured Bremerlehe by force.
The Emperor Ferdinand III ordered his vassal Christina of Sweden, then Duchess regnant of Bremen-Verden, to restitute Bremerlehe to Bremen. However, Swedish Bremen-Verden began the First Bremian War (March – July 1654). In the subsequent peace treaty (First Stade Recess; November 1654) Bremen had to cede Bremerlehe and its surroundings to Swedish Bremen-Verden. The latter developed plans to found a fortified town on the site, and much later this location became the present-day city of Bremerhaven. In 1672, under the reign of Charles XI of Sweden, in personal union Duke of Bremen-Verden—colonists tried unsuccessfully to erect a castle (named Carlsburg after Charles XI) there; this fortified structure was meant to protect, as well as control shipping heading for Bremen.
Finally, in 1827, the city of Bremen under Burgomaster Johann Smidt bought the territories at the mouth of the Weser from the Kingdom of Hanover. Bremen sought this territory to retain its share of Germany's overseas trade, which was threatened by the silting up of the Weser around the old inland port of Bremen. Bremerhaven (literally in English: Bremener Haven/Harbour) was founded to be a haven for Bremen's merchant marine, becoming the second harbour for Bremen, despite being 50 km (31 mi) downstream. Due to trade with, and emigration to North America, the port and the town grew quickly. In 1848, Bremerhaven became the home port of the German Confederation's Navy under Karl Rudolf Brommy.
The Kingdom of Hanover founded a rival town next to Bremerhaven and called it Geestemünde (1845). Both towns grew and established the three economic pillars of trade, shipbuilding and fishing. Following inter-state negotiations at different times, Bremerhaven's boundary was several times extended at the expense of Hanoveran territory. In 1924, Geestemünde and the neighbouring municipality of Lehe were united to become the new city of Wesermünde, and in 1939 Bremerhaven (apart from the overseas port) was removed from the jurisdiction of Bremen and made a part of Wesermünde, then a part of the Prussian Province of Hanover.
Bremerhaven was one of the important harbours of emigration in Europe.[3]
As possibly the most critical North Sea base of the Nazi War Navy, the Kriegsmarine, 79%[4] of the city was destroyed in the Allied air bombing of Bremen in World War II; however, key parts of the port were deliberately spared by the Allied forces to provide a usable harbour for supplying the Allies after the war. All of Wesermünde, including those parts which did not previously belong to Bremerhaven, was a postwar enclave run by the United States within the British zone of northern Germany. Most of the US military units and their personnel were assigned to the city's Carl Schurz Kaserne. One of the longest based US units at the Kaserne was a US military radio and TV station, an "Amerikanischer Soldatensender", AFN Bremerhaven, which broadcast for 48 years. In 1993, the Kaserne was vacated by the US military and returned to the German government.
In 1947 the city became part of the federal state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen and was consequently renamed from Wesermünde to Bremerhaven. Today, Bremerhaven is a city in its own right, but also part of the city-state of Bremen, which is for all intents and purposes a state comprising two cities. In addition to being part of the federal state, the city of Bremen has owned the "overseas port" within Bremerhaven since 1927. This and other parts of Bremerhaven owned by the city of Bremen are known as stadtbremisch. To complicate matters, a treaty between the two cities (as mentioned in Section 8 of Bremerhaven's municipal constitution) makes Bremerhaven responsible for the municipal administration of those parts owned directly by Bremen.[5]
Trade
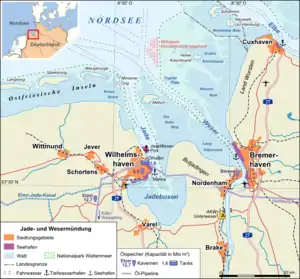
The port of Bremerhaven is the sixteenth-largest container port in the world and the fourth-largest in Europe with 4.9 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU) of cargo handled in 2007[6] and 5,5 million in 2015.[7] The container terminal is situated on the bank of the river Weser opening to the North Sea. In the wet dock parts, accessible by two large locks, more than 2 million cars are imported or exported every year with 2,3 million in 2014. Bremerhaven imports and exports more cars than any other city in Europe. Another million tons of "High-and-Heavy" goods are handled with ro-ro ships. In 2011 a new panamax-sized lock has replaced the 1897 Kaiserschleuse, then the largest lock worldwide.
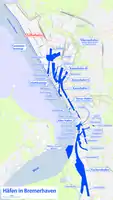 Harbors of Bremerhaven
Harbors of Bremerhaven The river Weser flows by Bremen to the estuary at Bremerhaven (top)
The river Weser flows by Bremen to the estuary at Bremerhaven (top) Skyline of Havenwelten-district
Skyline of Havenwelten-district Overseas port of Bremerhaven
Overseas port of Bremerhaven The MSC Venezuela docking at Bremerhaven's container port
The MSC Venezuela docking at Bremerhaven's container port Locks and docks around Lloyd Werft
Locks and docks around Lloyd Werft
Climate
Bremerhaven has a temperate maritime climate; severe frost and heat waves with temperatures above 30 °C (86 °F) are rare. On average, the city receives about 751 mm (29.6 in) of precipitation distributed throughout the year, with a slight peak in the summer months between June and August and a slightly drier season in late winter and early spring. Snow does fall in winter and early spring and, more rarely, in autumn. However, it usually doesn't stay on the ground for long. The hottest temperature ever recorded was 35.9 °C (96.6 °F) on 20 July 2022, and the coldest was −18.6 °C (−1.5 °F) on 25 February 1956.[8]
| Climate data for Bremerhaven (Averages 1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.5 (40.1) |
5.1 (41.2) |
8.3 (46.9) |
13.2 (55.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
19.6 (67.3) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.7 (56.7) |
8.5 (47.3) |
5.3 (41.5) |
13.1 (55.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
5.3 (41.5) |
9.4 (48.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.1 (61.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.4 (65.1) |
15.0 (59.0) |
10.8 (51.4) |
6.5 (43.7) |
3.4 (38.1) |
10.1 (50.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.5 (32.9) |
0.6 (33.1) |
2.5 (36.5) |
5.8 (42.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.7 (54.9) |
15.0 (59.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
8.1 (46.6) |
4.2 (39.6) |
1.5 (34.7) |
7.3 (45.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.0 (2.44) |
46.5 (1.83) |
48.4 (1.91) |
36.4 (1.43) |
50.1 (1.97) |
68.1 (2.68) |
83.7 (3.30) |
80.0 (3.15) |
72.8 (2.87) |
67.7 (2.67) |
63.3 (2.49) |
72.4 (2.85) |
751.4 (29.59) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 47.0 | 69.9 | 121.7 | 181.1 | 218.7 | 204.2 | 219.6 | 198.9 | 146.3 | 107.8 | 51.4 | 37.9 | 1,604.5 |
| Source: European Climate Assessment and Dataset[9] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Bremerhaven (Averages 1961–1990, Extremes 1949–) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.1 (55.6) |
17.2 (63.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
28.9 (84.0) |
31.7 (89.1) |
34.3 (93.7) |
35.9 (96.6) |
35.8 (96.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
18.8 (65.8) |
14.0 (57.2) |
35.9 (96.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.0 (37.4) |
3.8 (38.8) |
6.9 (44.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
16.1 (61.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
17.6 (63.7) |
13.2 (55.8) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.3 (39.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.1 (34.0) |
1.6 (34.9) |
4.1 (39.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.3 (54.1) |
15.4 (59.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
14.2 (57.6) |
10.3 (50.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
2.5 (36.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1 (30) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
4.3 (39.7) |
8.5 (47.3) |
11.9 (53.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
13.5 (56.3) |
11.1 (52.0) |
7.7 (45.9) |
3.5 (38.3) |
0.4 (32.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.2 (1.0) |
−18.6 (−1.5) |
−14.6 (5.7) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.1 (44.8) |
7.5 (45.5) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−10.2 (13.6) |
−15.6 (3.9) |
−18.6 (−1.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 56.0 (2.20) |
36.1 (1.42) |
50.3 (1.98) |
47.8 (1.88) |
56.3 (2.22) |
73.1 (2.88) |
78.7 (3.10) |
71.7 (2.82) |
67.9 (2.67) |
65.3 (2.57) |
71.4 (2.81) |
66.9 (2.63) |
741.5 (29.18) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 40.0 | 65.1 | 101.4 | 160.3 | 208.9 | 207.2 | 194.6 | 192.4 | 134.3 | 94.9 | 48.2 | 32.9 | 1,480.2 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst,[10] European Climate Assessment and Dataset,[9] and Dekadenrekorde deutscher Städte[11] | |||||||||||||
Transport
Roads
Due to its unique geographic situation, Bremerhaven suffers from a few transportational difficulties. The city has been connected to the autobahn network since the late 1970s. The A 27 runs north–south, east of the city, connecting Bremerhaven to Bremen and Cuxhaven. Road connections to Hamburg, however, are poor. The Bundesstraße 71 and secondary roads therefore carry most of the heavy lorry traffic. A proposed solution is the construction of the A 22, the so-called Küstenautobahn (or "coastal motorway"), which would link Bremerhaven to Hamburg and Wilhelmshaven/Oldenburg (using the Weser tunnel). Roads leading to the overseas port are regularly overloaded with freight traffic, and solutions are presently being discussed, including a deep-cut road favoured by the city government and various interest groups.
Railway
Bremerhaven has three active passenger rail stations, Bremerhaven Hauptbahnhof in the city centre, Bremerhaven-Lehe north of the centre and Bremerhaven-Wulsdorf in the southern part of the city. A fourth station, Bremerhaven-Speckenbüttel near the border to Langen has been out of service since 1988, though it might reopen when the Bremen S-Bahn scheme becomes operational. Bremerhaven's central station lost its last long-distance train in 2001. Now only regional connections to Bremen, Cuxhaven, Osnabrück and Hannover are available. The railways in Bremerhaven, however, still carry a heavy load of freight traffic, mostly new cars, containers and food.
Tram

Bremerhaven owned a tram from 1881 to 1982.[12] In the heyday, 1949, there were 6 lines.[13] The last line was the 2 from the north of the city to the main train station. The tram was shut down on July 30, 1982.[14]
.jpg.webp)
Bus
Bremerhaven has 2020 a bus network with 19 bus lines operated by BREMERHAVEN BUS. Two of the bus lines are night lines that only go on weekends. In addition, there is the so-called Schnellbus-Line S, which serves selected stops and is therefore faster.[15] BREMERHAVEN BUS operates up to 87 regular buses through the company Verkehrsgesellschaft Bremerhaven AG (VGB).[16] There are numerous regional buses operated by other companies that depart from Bremerhaven Central Station, to Bad Bederkesa, Beverstedt, Hagen, Nordholz and Otterndorf. In addition, Bremerhaven is also served by buses from Flixbus.
Tourist attractions


Bremerhaven has only a few historical buildings, and the high street and city centre are almost entirely post-war. The main attractions for tourists are found at the Havenwelten and include an attraction about climate change, the Klimahaus Bremerhaven 8° Ost, the German Emigration Center (since August 8, 2005) and the German Maritime Museum (Deutsches Schiffahrtsmuseum) by Hans Scharoun from 1975, featuring the Hansekogge, a vintage cog dating from 1380, excavated in Bremen in 1962, and the historical harbour (Museumshafen) with a number of museum ships, such as the Type XXI U-boat Wilhelm Bauer (a museum of its own), the Seute Deern (a wooden three-masted sailing vessel), and the salvage tug Seefalke from 1924. The Bremerhaven Zoo reopened on 27 March 2004, after a lengthy renovation. It features Arctic wildlife, both terrestrial and marine. The latest addition is the Klimahaus from 2009, simulating travel adventure along the 8th line of longitude and dealing with climate issues. Two gazebos can be found on top of the Atlantic Hotel Sail City and the Radar Tower. Another tourist spot is the Fischereihafen (fishing port) in Geestemünde which also houses an aquarium (the Atlanticum). The Lloyd Werft shipyard is renowned for building and renovating large cruise liners, for example Norway.
Every five years Sail Bremerhaven is held, a large sailing convention that attracts tall ships from all over the world. The last time it was held was in 2015 with over 270 vessels and 3,500 crew members.[17] In 2011 Bremerhaven set the record for the largest ever parade of boats, with 327 vessels in the parade. This record was broken in 2012 by the Thames Diamond Jubilee Pageant, with 1,000 boats.[18]
The passenger terminal Columbuskaje, built at the Weser bank in 1927 to avoid time-absorbing locking, has been transferred into a cruise terminal (Columbus Cruise Center Bremerhaven/CCCB). Also three marinas are available, the latest accessible through a new lock at Neuer Hafen.
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1845 | 3,000 | — |
| 1875 | 12,296 | +309.9% |
| 1900 | 20,315 | +65.2% |
| 1925 | 23,896 | +17.6% |
| 1933 | 25,779 | +7.9% |
| 1950 | 114,070 | +342.5% |
| 1956 | 130,492 | +14.4% |
| 1961 | 141,849 | +8.7% |
| 1970 | 143,918 | +1.5% |
| 1980 | 138,728 | −3.6% |
| 1990 | 130,446 | −6.0% |
| 2000 | 120,822 | −7.4% |
| 2010 | 113,366 | −6.2% |
| 2015 | 114,025 | +0.6% |
| 2019 | 117,746 | +3.3% |
| Foreign residents | |
|---|---|
| Nationality | Population (31.12.2019) |
| 3,975 | |
| 3,110 | |
| 2,410 | |
| 2,290 | |
| 1,485 | |
| 1,240 | |
| 765 | |
| 570 | |
| 525 | |
| 420 |
Politics
Bremerhaven has a city council with 49 members. It also elects 15 members of the Bürgerschaft of Bremen.
Sport
The Fischtown Pinguins, also known as REV Bremerhaven, are a professional ice hockey team in the DEL, Germany's top ice hockey league.
Eisbären Bremerhaven (Polar Bears), founded 2001, is a basketball team playing in the German second-tier level league ProA.
The American Football team is the Bremerhaven Seahawks which play in the German Regio Nord of the 3rd League. The Seahawks are the second oldest team in Germany.
Local association football clubs are Leher TS, SFL Bremerhaven and until 2012 FC Bremerhaven. TSV Wulsdorf and OSC Bremerhaven also have a football teams but as part of a multi-sport club.
Research and education
Bremerhaven is home to the Alfred Wegener Institute, a national research institute which is concerned with maritime sciences and climate and keeps a number of research vessels, amongst them the heavy research icebreaker RV Polarstern. It also runs the Neumayer-Station III in the Antarctic.
The Fraunhofer Society Institute for Wind Energy and Energy System Technology maintains research laboratories in Bremerhaven for development and testing of Wind Power components.[19]
The German Maritime Museum is part of the German Leibniz Association.
The Bremerhaven University of Applied Sciences (Hochschule Bremerhaven) was founded in 1975 and is expanding since with more than 3.000 students in 2009. The university is attended by a large number of overseas students from all over the world. Among the courses offered are Process Engineering, Information Technology and the BA Entrepreneurship, Innovation, Leadership programme, the first programme modelled after the Finnisch Team Academy format in a German language higher education institution.[20]
Twin towns – sister cities

Bremerhaven is twinned with:[21]
 Cherbourg-en-Cotentin, France (1960)
Cherbourg-en-Cotentin, France (1960) Grimsby, North East Lincolnshire, England, UK (1963)
Grimsby, North East Lincolnshire, England, UK (1963) Pori, Finland (1969)
Pori, Finland (1969) Frederikshavn, Denmark (1979)
Frederikshavn, Denmark (1979) Szczecin, Poland (1990)
Szczecin, Poland (1990) Kaliningrad, Russia (1992)
Kaliningrad, Russia (1992)
The three roads connecting the city of Bremerhaven to the Autobahn 27 consequently are named after the original three twin towns:
- Cherbourger Straße (AS Bremerhaven-Überseehafen)
- Grimsbystraße (AS Bremerhaven-Mitte)
- Poristraße (AS Bremerhaven-Geestemünde)
In addition to that, there are also streets which earlier had been named after Szczecin (Stettiner Straße) and Kaliningrad (Königsberger Straße).
Notable people




- Hans Joachim Alpers (1943–2011), writer and editor of science fiction and fantasy
- Lale Andersen (1905–1972), singer and actress, sang WW2 song "Lili Marleen"
- Roger Asmussen (1936–2015), politician (CDU), German Minister of Economy and Transport in 1987
- Uwe Beckmeyer (born 1949), politician (SPD)
- Adolf Butenandt (1903–1995), biochemist
- Jeanne Córdova (1948–2016), American pioneer lesbian and gay rights activist
- Jenny Dolfen (born 1975), illustrator and teacher
- Volker Engel (born 1965), visual effects supervisor and producer
- Heino Ferch (born 1963), actor
- Wolfgang Gaede (1878–1945), physicist and pioneer of vacuum engineering
- Johanna Goldschmidt (1807–1884), social activist, writer and philanthropist
- Werner Grübmeyer (1926-2018), politician
- Corinna Harney (born 1972), German-American model and actress
- Carl Hermann (1898–1961), professor of crystallography
- Christoph Maria Herbst (born 1966), actor and comedian at Stadttheater Bremerhaven 1992–1996
- Carola Höhn (1910–2005), stage and movie actress
- Eberhard Jäckel (1929–2017), historian, studied role of Adolf Hitler in German history
- Lou Jacobs (1903–1992), American clown and entertainer
- Erich Koch-Weser (1875–1944), lawyer and politician
- Sigrid Lorenzen Rupp (1943–2004), German-American architect
- Norman Paech (born 1938), university professor and politician (The Left)
- Johannes Piersig (1907–1998), Kantor, docent af music educator
- Betty Schade (1895–1982), German-born American actress of the silent era
- Hans Joachim Schliep (born 1945), Lutheran theologian, pastor and author
- André Werner (born 1960), composer of classical music
- Anders Levermann (born 1973), environmental scientist and climatologist
- Felix Magath (born 1953), football player and coach
- Herta Müller (born 1953), writer and Nobel Prize for Literature 2009, 1989 Scholarship in Bremerhaven
- Stephan Remmler (born 1946), grew up in Bremerhaven, singer, composer and music producer
- Willi Reimann (born 1949), former footballer at TuS Bremerhaven 93, football coach
- Karl-Georg Saebisch (1903–1984), German-language theater, film and television actor, director and honorary member of the Municipal Theatre Bremerhaven
- Hans Scharoun (1893–1972), grew up in Bremerhaven, architect and exponent of organic architecture
- Gottfried Semper (1803–1879), architect, volunteer at the port construction
- Wolfgang Wippermann (born 1945), historian[22]
- Helmut Yström (1881–1963), politician, Senator in Bremen, 1945–1948, local chief of police
Sport
- Bernd Brexendorf (born 1954), footballer and doctor
- Egon Coordes (born 1944), football player and trainer
- Hendrik Feldwehr (born 1986), swimmer
- Eduard Pendorf (1892–1958), footballer
- Walter Schmidt (born 1937), footballer
- Clemens Schoppenhauer (born 1992), footballer
- Tomas Seyler (born 1974), darts player
- Esra Sibel Tezkan (born 1993), Turkish-German footballer
- Lars Toborg (born 1975), football player
References and notes
- "Bevölkerungsentwicklung im Land Bremen" (PDF). Statistisches Landesamt Bremen (in German). June 2021.
- Dierks, August, Dr.; von Garvens, Eugenie (1954), Bremerhaven: Busy – Breezy – Booming – Town, Bremerhaven: The Chamber of Commerce and Industry p. 8. Fourth revised edition. Translated into English from the original German edition titled Bremerhaven – tätige Stadt im Noordseewind
- Evans, Nicholas J. (2001). "Work in progress: Indirect passage from Europe Transmigration via the UK, 1836–1914". Journal for Maritime Research. 3: 70–84. doi:10.1080/21533369.2001.9668313.
- Archives, The National. "The National Archives – World War II – Western Europe 1939–1945: Hamburg – Why did the RAF bomb cities?". www.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 20 March 2018.
- Verfassung für die Stadt Bremerhaven (VerfBrhv Archived May 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine); § 8(1) Zum Stadtgebiet gehören alle Grundstücke, Fluß- und Hafenanlagen der ehemaligen Stadt Wesermünde. Gemeindeverwaltungsmäßig wird die Stadt Bremerhaven im Gebiet des stadtbremischen Überseehafens aufgrund eines Vertrages zwischen den Städten Bremen und Bremerhaven zuständig.
- Van Marle, Gavin (2008-01-31). "Europe Terminals stretched to limit". Lloyds List Daily Commercial News. pp. 8–9.
- "weser.de – Seehäfen & Seeschifffahrt: Bremische Häfen". www.weser.de. Archived from the original on 2014-03-29. Retrieved 2016-08-08.
- "Wetter und Klima – Deutscher Wetterdienst – Startseite". www.dwd.de.
- "Indices data". www.ecad.eu. Retrieved 20 March 2018.
- "Extreme Temperatures". wettergefahren-fruehwarnung.de. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- Paul Homann. "Bremerhavener Streckennetze - Tram and bus route networks since 1881" (PDF). p. 3 & 46. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-08-28.
- "VGB Fahrplan 1949 - Original Timetable from the year 1949 // Book Archive from Paul Homann, Bremerhaven" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-25.
- Paul Homann. "Bremerhavens Nahverkehr, Chronik - recent history since 1980 - German text" (PDF). p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-04-19.
- Paul Homann. "Bremerhavener Streckennetze - Tram and bus route networks since 1881" (PDF). p. 109. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-08-28.
- Paul Homann. "VGB-Linienbusse - Buses for the town bus network" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-01-01.
- "SAIL – Bremerhaven". www.sail-bremerhaven.de. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- "Diamond Jubilee Thames Pageant cheered by crowds". BBC News. 3 June 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2012.
- "Fraunhofer IWES Laboratories". Archived from the original on April 19, 2012.
- https://startblog.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Studiengangsbroschüre-GIF-2019.pdf
- "Städtepartnerschaften". bremerhaven.de (in German). Bremerhaven. 21 September 2016. Retrieved 2021-02-10.
- Wolfgang Wippermann, German wiki retrieved 26 March 2018
