Jörmungandr
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr (Old Norse: Jǫrmungandr, lit. 'huge monster',[1]), also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent (Old Norse: Miðgarðsormr), is a sea serpent and the middle child of Loki and the giantess Angrboða. According to the Prose Edda, Odin took Loki's three children by Angrboða—the wolf Fenrir, Hel, and Jörmungandr—and tossed Jörmungandr into the great ocean that encircles Midgard.[2] The serpent grew so large that it was able to surround the Earth and grasp its own tail.[2] It is an example of an ouroboros. As a result of it surrounding the Earth, it is referred to as the World Serpent. When it releases its tail, Ragnarök will begin. Jörmungandr's arch-enemy is the thunder-god, Thor.
Sources
The major sources for myths about Jörmungandr are the Prose Edda, the skaldic poem Húsdrápa, and the Eddic poems Hymiskviða and Völuspá. Other sources include the early skaldic poem Ragnarsdrápa and kennings in other skaldic poems; for example, in Þórsdrápa, faðir lögseims, "father of the sea-thread", is used as a kenning for Loki. There are also several image stones depicting the story of Thor fishing for Jörmungandr.
Stories
There are three preserved myths detailing Thor's encounters with Jörmungandr:
Lifting the cat
In one story, Thor encounters the giant king Útgarða-Loki and has to perform deeds for him, one of which is a challenge of Thor's strength. Útgarða-Loki goads Thor into attempting to lift the World Serpent, disguised by magic as a huge cat. Thor grabs the cat around its midsection but manages to raise the cat only high enough for one of its paws to leave the floor. Útgarða-Loki later explains his deception and that Thor's lifting the cat was an impressive deed, as he had stretched the serpent so that it had almost reached the sky. Many watching became fearful when they saw one paw lift off the ground.[3] If Thor had managed to lift the cat completely from the ground, he would have altered the boundaries of the universe.[4]
Thor's fishing trip
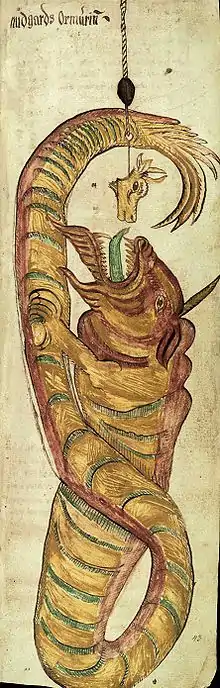
Jörmungandr and Thor meet again when Thor goes fishing with the giant Hymir. When Hymir refuses to provide Thor with bait, Thor strikes the head off Hymir's largest ox to use it. They row to a point where Hymir often sat and caught flatfish and where he drew up two whales. Thor demands to go further out to sea and does so despite Hymir's protest. Thor then prepares a strong line and a large hook and baits it with the ox head, which Jörmungandr bites. Thor pulls the serpent from the water, and the two face one another, Jörmungandr blowing poison.[5] Hymir goes pale with fear. As Thor grabs his hammer to kill the serpent, the giant cuts the line, leaving the serpent to sink beneath the waves and return to its original position encircling the earth.[5][6] The Eddic poem Hymiskviða has a similar ending to the story, but in earlier Scandinavian versions of the myth in skaldic poetry, Thor successfully captures and kills the serpent by striking it on the head.[6][7]
Thor's fishing for Jörmungandr was one of the most popular motifs in Norse art. Four picture stones that are believed to depict the myth are the Altuna Runestone and the Ardre VIII image stone in Sweden, the Hørdum stone in Denmark, and a stone slab at Gosforth, Cumbria by the same sculptor as the Gosforth Cross.[8][9][10] Many of these depictions show the giant cutting the fishing line; on the Altuna stone, Thor is alone, implying he successfully killed the serpent.[6] The Ardre VIII stone may depict more than one stage in the events: a man entering a house where an ox is standing, two men leaving, one with something on his shoulder, and two men using a spear to fish.[11] The image on this stone has been dated to the 8th[8] to 10th[12] century. If the stone is correctly interpreted as a depiction of this myth, it would indicate that the story was preserved essentially unchanged for several centuries prior to the recording of the version in the Prose Edda around the year 1220.[11][7]
Ragnarök
As recounted in Snorri's Gylfaginning based on the Eddic poem Völuspá, one sign of the coming of Ragnarök is the violent unrest of the sea as Jörmungandr releases its tail from its mouth. The sea will flood and the serpent will thrash onto the land.[2] It will advance, spraying poison to fill the air and water, beside Fenrir, whose eyes and nostrils blaze with fire and whose gape touches the earth and the sky. They will join the sons of Muspell to confront the gods on the plain of Vigrid. Here is where the last meeting between the serpent and Thor is predicted to occur. He will eventually kill Jörmungandr but will fall dead after walking nine paces, having been poisoned by the serpent's deadly venom.[13] Thor's final battle with Jörmungandr has been identified, with other scenes of Ragnarök, on the Gosforth Cross.[10]
Analysis
Thor's fishing for Jörmungandr has been taken as one of the similarities between him and the Hindu god Indra, who in Vedic mythology slays the dragon Vritra,[14][15] and has also been related to a Balto-Slavic motif of the storm god combatting a serpent.[16] An alternative analysis of the episode by Preben Meulengracht Sørensen is that it was a youthful indiscretion on the part of Thor, retold to emphasize the order and balance of the cosmos, in which Jörmungandr played a vital role.[17] John Lindow draws a parallel between Jörmungandr's biting of its own tail and the binding of Fenrir, as part of a recurring theme of the bound monster in Norse mythology, where an enemy of the gods is bound but destined to break free at Ragnarök.[18]
Eponym
Asteroid 471926 Jörmungandr was named after the mythological sea serpent.[19] The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center on 25 September 2018 (M.P.C. 111804).[20]
Gallery
_Tors_fiskaf%C3%A4nge_0646.jpg.webp) The Altuna Runestone
The Altuna Runestone Thor fishing for the Midgard Serpent in an illustration from an 18th-century Icelandic manuscript
Thor fishing for the Midgard Serpent in an illustration from an 18th-century Icelandic manuscript Thor Battering the Midgard Serpent (1790) by Henry Fuseli
Thor Battering the Midgard Serpent (1790) by Henry Fuseli Thor and the Midgard Serpent (1905) by Emil Doepler
Thor and the Midgard Serpent (1905) by Emil Doepler The children of Loki (1920) by Willy Pogany
The children of Loki (1920) by Willy Pogany
See also
- Ananta Shesha
- Apep
- Bakunawa
- European dragon
- Germanic dragon
- Horned Serpent
- Lernaean Hydra
- Leviathan
- Makara (Hindu mythology)
- Níðhöggr
- Ophiotaurus
- Ouroboros
- Python (mythology)
- Sea monster
- Typhon
References
- Simek, Rudolf; Hall, Angela (trans.) (2000) [1993]. "Jǫrmungandr". Dictionary of Northern Mythology. Woodbridge, Suffolk / Rochester, New York: D.S. Brewer. p. 179. ISBN 0-85991-513-1.
- Snorri Sturluson; Brodeur, Arthur Gilchrist (trans.) (1916). The Prose Edda. New York: The American-Scandinavian Foundation. Gylfaginning ch.LI , p. 109.
- Snorri Sturluson (1916) Gylfaginning ch. xlvi, xlvii, pp. 65, 67.
- Thury, Eva M.; Devinney, Margaret K. (2017). Introduction to Mythology (4th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 302–03. ISBN 978-0-19-026298-3.
- Snorri Sturluson (1916) Gylfaginning ch. xlviii, pp. 68–70.
- Meulengracht Sørensen, Preben; Williams, Kirsten (trans.) (1986). "Þorr's Fishing Expedition". In Steinsland, Gro (ed.). Words and Objects: Towards a Dialogue Between Archaeology and History of Religion. Oslo: The Institute for Comparative Research in Human Culture; Norwegian University Press. pp. 270–71. ISBN 82-00-07751-9. Meulengracht Sørensen, Preben; Williams, Kirsten (trans.) (2002). "Þorr's Fishing Expedition (Hymiskviða)". In Acker, Paul; Larrington, Carolyne (eds.). The Poetic Edda: Essays on Old Norse Mythology. London / New York: Routledge. pp. 130–31. ISBN 0-8153-1660-7.
- Clunies Ross, Margaret (1989). "Two of Þórr's Great Fights according to Hymiskviða" (PDF). Leeds Studies in English. 20: 8–10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 April 2019.
- Meulengracht Sørensen (1986) p. 260, (2002) p. 123.
- Kopár, Lilla (2018) [2016]. "Eddic poetry and the imagery of stone monuments". In Larrington, Carolyne; Quinn, Judy; Schorn, Brittany (eds.). A Handbook to Eddic Poetry: Myths and Legends of Early Scandinavia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 203–08. ISBN 978-1-316-50129-0.
- Fee, Christopher R.; Leeming, David A. (2001). Gods, Heroes, & Kings: The Battle for Mythic Britain. Oxford University Press. p. 36. ISBN 0-19-513479-6.
- Meulengracht Sørensen (1986) p. 269, (2002) p. 130.
- Kopár, p. 208.
- Snorri Sturluson (2016) Gylfaginning ch. li, pp. 78–80.
- Turville-Petre, E. O. G. (1964). Myth and Religion of the North: The Religion of Ancient Scandinavia. History of Religions. Weidenfeld and Nicolson. p. 104. OCLC 460550410.
- Dumézil, Georges (1952). Les Dieux des Indo-Européens. Mythes et religions (in French). Vol. 29. Presses universitaires de France. p. 24. OCLC 459390464.
- Ivanov, Vjaceslav V.; Toporov, Vladimir N.; Karvovski, A. (trans.) (1970). "Le mythe indo-européen du dieu de l'orage poursuivant le serpent: réconstruction du schéma". In Pouillon, Jean; Maranda, Pierre (eds.). Échanges et communications: mélanges offerts à Claude Lévi-Strauss à l'occasion de son 60ème anniversaire. Studies in general anthropology (in French). Vol. 2. Mouton. pp. 1180–1206. OCLC 849278587.
- Meulengracht Sørensen (1986) p. 272, (2002) p. 132.
- Lindow, John (2002) [2001]. "Bound Monster". Norse Mythology: A Guide to the Gods, Heroes, Rituals, and Beliefs. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 82–83. ISBN 0-19-515382-0.
- "471926 Jormungandr (2013 KN6)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 17 October 2018.