Songhay languages
The Songhay, Songhai or Ayneha[3][4] languages ([soŋaj] or [soŋoj]) are a group of closely related languages/dialects centred on the middle stretches of the Niger River in the West African countries of Mali, Niger, Benin, Burkina Faso and Nigeria. In particular, they are spoken in the cities of Timbuktu, Niamey and Gao. They have been widely used as a lingua franca in that region ever since the era of the Songhai Empire. In Mali, the government has officially adopted the dialect of Gao (east of Timbuktu) as the dialect to be used as a medium of primary education.[5]
| Songhay | |
|---|---|
| Songhai, Ayneha | |
| Ethnicity | Songhai |
| Geographic distribution | Niger River valley (Mali, Niger, Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Nigeria); scattered oases (Niger, Mali, Algeria) |
| Linguistic classification | Nilo-Saharan?
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Songhay |
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | son |
| Glottolog | song1307 |
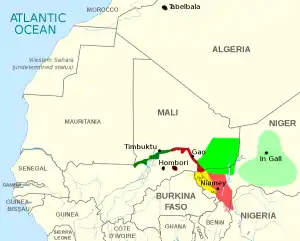 Location of Songhay languages[2] Northwest Songhay: Korandje
Koyra Chiini
Tadaksahak
Tasawaq
Tagdal
Eastern Songhay: Tondi Songway Kiini
Humburi Senni
Koyraboro Senni
Zarma
Songhoyboro Ciine
Dendi | |
Some Songhay languages have little to no mutual intelligibility between each other. For example, Koyraboro Senni, spoken in Gao, is unintelligible to speakers of Zarma in Niger, according to Ethnologue. However, Songhoyboro Ciine,[6] Zarma, and Dendi have high mutual intelligibility within Niger.[7]
For linguists, a major point of interest in the Songhay languages has been the difficulty of determining their genetic affiliation; they are commonly taken to be Nilo-Saharan, as defined by Joseph Greenberg in 1963, but this classification remains controversial. Linguist Gerrit Dimmendaal (2008) believes that for now it is best considered an independent language family.[8] Roger Blench argues that the Songhay and Saharan languages form a Songhay-Saharan branch with each other within the wider Nilo-Saharan linguistic phylum.[1]
Historically, the name Songhay was neither an ethnic nor a linguistic designation for all, but a name for the ruling caste of the Songhai Empire which are the Songhai proper. The term used by the natives to address the languages and people collectively is "Ayneha". Aside the Songhai proper, some speakers in Mali have also adopted the name Songhay as an ethnic designation, [9] while other Songhay-speaking groups identify themselves with other ethnic terms, such as Zarma (Djerma) or Isawaghen (Sawaq).
A few precolonial poems and letters composed in Songhay and written in the Arabic script exist in Timbuktu.[10] However, Songhay is currently written in the Latin script.
Varieties
Percentage of Songhay speakers by population
Researchers classify the Songhay languages into two main branches; Southern and Northern.[11] Southern Songhay is centered on the Niger River. Zarma (Djerma), the most widely spoken Songhay language with two or three million speakers, is a major language of southwestern Niger (downriver from and south of Mali) including in the capital city, Niamey. Koyraboro Senni, with 400,000 speakers, is the language of the town of Gao, the seat of the old Songhai Empire. Koyra Chiini is spoken to its west. The much smaller Northern Songhay is a group of heavily Berber-influenced dialects spoken in the Sahara. Since the Berber influence extends beyond the lexicon into the inflectional morphology, the Northern Songhay languages are sometimes viewed as mixed languages.[12]
Genetic affiliation
Diedrich Hermann Westermann, a missionary and linguist, hesitated between assigning it to Gur or considering it an isolate, and Maurice Delafosse grouped it with Mande. At present, Songhay is normally considered to be Nilo-Saharan, following Joseph Greenberg's 1963 reclassification of African languages; Greenberg's argument is based on about 70 claimed cognates, including pronouns. This proposal has been developed further by, in particular, Lionel Bender, who saw it as an independent subfamily of Nilo-Saharan. Roger Blench notes that Songhay shares the defining singulative–plurative morphology typical of Nilo-Saharan languages. As of 2011, he believes that Songhay is closest to the neighboring Saharan languages and is not divergent.
However, a Nilo-Saharan classification is controversial. Greenberg's argument was subjected to serious criticism by Lacroix, who deemed only about 30 of Greenberg's claimed cognates acceptable, and moreover argued that these held mainly between Zarma and the Saharan languages, thus leading one to suspect them of being loanwords.[13] Certain Songhay–Mande similarities have long been observed (at least since Westermann), and Mukarovsky (1966), Denis Creissels (1981) and Nicolaï (1977, 1984) investigated the possibility of a Mande relationship; Creissels made some 50 comparisons, including many body parts and morphological suffixes (such as the causative in -endi), while Nicolaï claimed some 450 similar words as well as some conspicuous typological traits. However, Nicolaï eventually concluded that this approach was not adequate, and in 1990 proposed a distinctly novel hypothesis: that Songhay is a Berber-based creole language, restructured under Mande influence. In support of this he proposed 412 similarities, ranging all the way from basic vocabulary (tasa "liver") to obvious borrowings (anzad "violin", alkaadi "qadi".) Others, such as Gerrit Dimmendaal, were not convinced, and Nicolaï (2003) appears to consider the question of Songhay's origins still open, while arguing against Bender's proposed etymologies.
Greenberg's morphological similarities with Nilo-Saharan include the personal pronouns ai (cf. Zaghawa ai), 'I', ni (cf. Kanuri nyi), 'you (sg.)', yer (e.g. Kanuri -ye), 'we', wor (cf. Kanuri -wi), 'you (pl.)'; relative and adjective formants -ma (e.g. Kanuri -ma) and -ko (cf. Maba -ko), a plural suffix -an (?), a hypothetical plural suffix -r (cf. Teso -r) which he takes to appear in the pronouns yer and wor, intransitive/passive -a (cf. Teso -o).
The most striking of the Mande similarities listed by Creissels are the third person pronouns a sg. (pan-Mande a), i pl. (pan-Mande i or e), the demonstratives wo "this" (cf. Manding o, wo) and no "there" (cf. Soninke no, other Mande na), the negative na (found in a couple of Manding dialects) and negative perfect mana (cf. Manding má, máŋ), the subjunctive ma (cf. Manding máa), the copula ti (cf. Bisa ti, Manding de/le), the verbal connective ka (cf. Manding kà), the suffixes -ri (resultative - cf. Mandinka -ri, Bambara -li process nouns), -ncè (ethnonymic, cf. Soninke -nke, Mandinka -nka), -anta (ordinal, cf. Soninke -ndi, Mandinka -njaŋ...), -anta (resultative participle, cf. Soninke -nte), -endi (causative, cf. Soninke, Mandinka -ndi), and the postposition ra "in" (cf. Manding lá, Soso ra...)
The Songhay languages are considered to be an independent family by Dimmendaal (2011), although he classifies Saharan as part of Nilo-Saharan.[14]
Grammar
Songhay is mostly a tonal, SOV group of languages, an exception being the divergent Koyra Chiini of Timbuktu, which is non-tonal and uses SVO order.
Songhay has a morpheme -ndi which marks either the causative or the agentless passive. Verbs can even take two instances of the morpheme, one for each meaning. Thus ŋa-ndi-ndi figuratively translates to "[the rice] was made to be eaten [by someone: causee] [by someone: causer]".[15]
Reconstruction of Proto-Songhay
| Proto-Songhay | |
|---|---|
| Reconstruction of | Songhay languages |
Below are some Proto-Songhay reconstructions:[1]
| Gloss | Proto-Songhay |
|---|---|
| person | *bòro |
| bird | *kídòw |
| scorpion, mosquito | *(n)děŋ |
| ashes | *bó:sú |
| stone, mountain | *tóndì |
| year | *gí:rí; *mán(n)à |
| yesterday | *bǐ: |
| ask | *hᘠ|
| bring | *kàte |
| thorn | *kárgí |
| skin | *kú:rú |
| blood | *kúdí |
| year | *gí:rí |
Some Proto-Eastern Songhay reconstructions are:[1]
| Gloss | Proto-Eastern Songhay |
|---|---|
| thatch hut | *bùgù |
| armpit, wing | *fátá |
| thirst | *gèw |
| flank | *kéráw |
| mason wasp | *bímbín(í) |
| sweat | *súŋgáy |
Numerals
Comparison of numerals in individual languages:[16]
| Language | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korandje | affu* | jnka | jnzˁa | rˁəbʕa | χəmsa | sətta | səbʕa | tmənja | təsʕa | ʕəʃrˁa |
| Tadaksahak | a-ˈfːo / a-ˈfːoo-da | hiŋˈka | kaːˈrˤad < Tamasheq | aˈkːoːz < Tamasheq | ʃaˈmːuʃ < Tamasheq | ʃaːˈdˤiʃ < Tamasheq | iˈʃːa < Tamasheq | iˈtˤːam < Tamasheq | tˤaːˈsˤa < Tamasheq | maːˈrˤa < Tamasheq |
| Tasawaq | fó / a-fːó | hínká / à-hínká | hínzà / à-hínzà | táásì / à-tːáásì | xámsà < Arabic | sítːà < Arabic | sábàɣà < Arabic | tàmáníyà < Arabic | tísàɣà < Arabic | ɣàsárà < Arabic |
| Dendi | afɔ | hayinka / ahinka | ahinza | ataki | aɡu | ayidu | ayiye / ahiye | ayiyaku | ayiɡa | aweyi |
| Koyraboro Senni | affoo | ihinka | ihinza | itaatʃi | iɡɡuu | idduu | iyye | iyaaha | iyaɡɡa | iwoy |
| Koyra Chiini | foo / a-foo | hiŋka | hindʒa | taatʃi | ɡuu | iddu | iiye | yaaha | yaɡɡa | woy / wey |
| Zarma, Songhoyboro Ciine | àˈfó | ìˈhíŋká | ìˈhínzà | ìˈtaːcí | ìˈɡú | ˈíddù | ˈijjè | àˈhákˌkù | ˈjǽɡɡà | ìˈwéɪ |
Bibliography
- Dimmendaal, Gerrit. 2008. Language Ecology and Linguistic Diversity on the African Continent. Language and Linguistics Compass 2(5): 843ff.
- Dupuis-Yakouba, Auguste. 1917. Essai pratique de méthode pour l'étude de la langue songoï ou songaï [...]. Paris: Ernest Leroux.
- Hunwick, John O.; Alida Jay Boye. 2008. The Hidden Treasures of Timbuktu. Thames & Hudson.
- Nicolaï, Robert. 1981. Les dialectes du songhay: contribution à l'étude des changements linguistiques. Paris: SELAF. 302 pp.
- Nicolaï, Robert & Petr Zima. 1997. Songhay. LINCOM-Europa. 52 pp.
- Prost, R.P.A. [André]. 1956. La langue sonay et ses dialectes. Dakar: IFAN. Series: Mémoires de l'Institut Français d'Afrique Noire; 47. 627 pp.
Publisher and publication abbreviations:
- CSLI = Center for the Study of Language and Information.
- IFAN = Institut Français d'Afrique Noire (since renamed the Institut Fondamental d'Afrique Noire).
- SELAF = Société d'études linguistiques et anthropologiques de France.
- SUGIA = Sprache und Geschichte in Afrika, journal published by Rüdiger Köppe Verlag, Cologne (Köln).
- Köppe = Rüdiger Köppe Verlag.
On genetic affiliation
- Bender, M. Lionel. 1996. The Nilo-Saharan Languages: A Comparative Essay. München: LINCOM-Europa. 253 pp
- Roger Blench and Colleen Ahland, "The Classification of Gumuz and Koman Languages", presented at the Language Isolates in Africa workshop, Lyons, December 4, 2010
- D. Creissels. 1981. "De la possibilité de rapprochements entre le songhay et les langues Niger–Congo (en particulier Mandé)." In Th. Schadeberg, M. L. Bender, eds., Nilo-Saharan : Proceedings of the First Nilo-Saharan Linguistics Colloquium, Leiden, September 8–10, pp. 185–199. Foris Publications.
- Greenberg, Joseph, 1963. The Languages of Africa (International Journal of American Linguistics 29.1). Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press.
- Lacroix, Pierre-Francis. 1971. "L'ensemble songhay-jerma: problèmes et thèmes de travail". In Acte du 8ème Congrès de la SLAO (Société Linguistique de l’Afrique Occidentale), Série H, Fasicule hors série, 87–100. Abidjan: Annales de l’Université d’Abidjan.
- Mukarovsky, H. G. 1966. "Zur Stellung der Mandesprachen". Anthropos, 61:679-88.
- Nicolaï, Robert. 1977. "Sur l'appartenance du songhay". Annales de la faculté des lettres de Nice, 28:129-145.
- Nicolaï, Robert. 1984. Préliminaires à une étude sur l'origine du songhay: matériaux, problématique et hypothèses, Berlin: D. Reimer. Series: Marburger Studien zur Afrika- und Asienkunde. Serie A, Afrika; 37. 163 pp
- Nicolaï, Robert. 1990. Parentés linguistiques (à propos du songhay). Paris: CNRS. 209 pp
- Nicolaï, Robert. 2003. La force des choses ou l'épreuve 'nilo-saharienne': questions sur les reconstructions archéologiques et l'évolution des langues. SUGIA - Supplement 13. Köln: Köppe. 577 pp
References
- Blench, Roger & Lameen Souag. m.s. Saharan and Songhay form a branch of Nilo-Saharan.
- This map is based on classification from Glottolog and data from Ethnologue.
- Linguistics and Language Behavior Abstracts: LLBA., Volume 33, Issue 3, 1999, retrieved 2021-05-14
- Etudes de lettres, Faculté des lettres de l'Université de Lausanne, 2002, retrieved 2021-05-14
- Heath 2005
- Southern Songhay Speech Varieties In Niger:A Sociolinguistic Survey of the Zarma, Songhay, Kurtey, Wogo, and Dendi Peoples of Niger (PDF), Byron & Annette Harrison and Michael J. Rueck Summer Institute of Linguistics B.P. 10151, Niamey, Niger Republic, 1997, retrieved 2021-02-23
- Ethnologue report for Niger
- Dimmendaal, Gerrit (18 September 2008). "Language Ecology and Linguistic Diversity on the African Continent". Language and Linguistics Compass. 2 (5): 840–858. doi:10.1111/j.1749-818X.2008.00085.x.
- Heath 1999:2
- Hunwick and Boye 2008: ____
- A map of the varieties is provided by Ethnologue at its Web site. See the list of External Links.
- SIL Working Papers on Songhay
- Lacroix 1969: 91–92
- Dimmendaal, Gerrit J. (2011). Historical Linguistics and the Comparative Study of African Languages. John Benjamins. ISBN 978-90-272-8722-9.
- Shopen, T. & Konaré, M. 1970. "Sonrai Causatives and Passives: Transformational versus Lexical Derivations for Propositional Heads", Studies in African Linguistics 1.211–54. Cited in Dixon, R.M.W. (2000). "A Typology of Causatives: Form, Syntax, and Meaning". In Dixon, R.M.W. & Aikhenvald, Alexendra Y. Changing Valency: Case Studies in Transitivity. Cambridge University Press. pp. 31.
- Chan, Eugene (2019). "The Nilo-Saharan Language Phylum". Numeral Systems of the World's Languages.
External links
- Wictionaire, Dictionary Songhai Koyraboro Senni - French, > 3000 Words
- Relative Clauses in Tadaksahak
- Some verb morphology features in Tadaksahak
- PanAfrican L10n page on Songhai & Zarma
- Publications of linguist Jeffrey Heath on Songhay languages
- Language and Culture Djerma
- Maps showing the Songhay languages of Mali and Niger
- Northern Songhay - bibliography and brief description of this subfamily