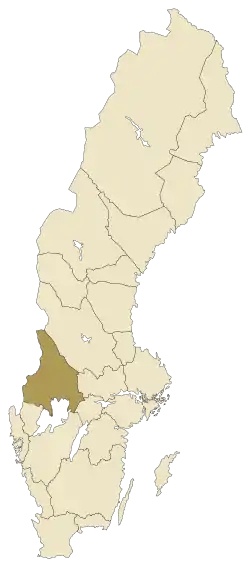
Värmland
Värmland (Swedish pronunciation: [ˈvæ̌rmland] (![]() listen)) also known as Wermeland, is a landskap (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are Varmelandia,[2] Vermelandia,[3] Wermelandia,[4] Værmalandia, Værmolandia, Virmolandia and Vermillandia.
listen)) also known as Wermeland, is a landskap (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are Varmelandia,[2] Vermelandia,[3] Wermelandia,[4] Værmalandia, Værmolandia, Virmolandia and Vermillandia.
Värmland | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Country | Sweden |
| Land | Svealand |
| Counties | Värmland County Örebro County Västra Götaland County |
| Area | |
| • Total | 18,164 km2 (7,013 sq mi) |
| Population (2016)[1] | |
| • Total | 318,341 |
| • Density | 18/km2 (45/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Värmlänning |
| Ethnicity | |
| • Languages | Värmländska Götamål |
| Culture | |
| • Flower | Chickweed wintergreen |
| • Animal | Wolf |
| • Bird | Red-throated diver |
| • Fish | Smelt |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
Some of the Latinised forms show the origin of the name to come from the large local lake by the name of Värmeln (from older *Virmil); others from the river name *Værma, the main outlet of that lake.[5] The province was originally part of Götaland, and became part of Svealand in 1815.[6]
Geography
The largest lake is Vänern. Most streams of importance lead to Vänern. However, the province is rich in small lakes, ponds and streams. The scenery, with mountains and lakes, is usually regarded as picturesque and has inspired painters and writers.
Western Värmland
There are several mountain plateaus in the western part of Värmland, which is in the Scandinavian Mountains. The highest elevations are found in the northern parts, with plateaus of 500–700 metres (1,600–2,300 ft). The highest peak is also located here, Granberget at Höljes, 701 metres (2,300 ft).
Eastern Värmland
The eastern part of Värmland is counted as part of the Bergslagen, the Central Swedish Mining District. Its terrain is rather hilly, with a few high hills: Hvitklinten (414 m.), Dalkarlsberget (450 m.) and Vålbergsrös (476 m.).
This part of Värmland is rich in minerals, most notably iron ore which exists in large quantities. Some notable sites in this area are around Långban and Nordmark Hundred. In the southeast, the ridge of Kilsbergen marks the border with Närke.
.jpg.webp) Sunset on the lake Foxen located in the borderland between southwest Värmland and Norway.
Sunset on the lake Foxen located in the borderland between southwest Värmland and Norway. The view from Granberget.
The view from Granberget. Klarälven seen from Ullerud Church, near Deje.
Klarälven seen from Ullerud Church, near Deje. The Värmland sheep is one of the oldest Swedish sheep breeds.
The Värmland sheep is one of the oldest Swedish sheep breeds. Cottage at Sannsatra outside Torsby.
Cottage at Sannsatra outside Torsby. Sysslebäck.
Sysslebäck. Fish ladder for Salmon near the power station in Gullspång.
Fish ladder for Salmon near the power station in Gullspång. The ski resort Branäs.
The ski resort Branäs.
Population
The population of Värmland is 318,341 as of 31 December 2016. It is distributed over three counties as follows:[1]
| County | Population |
|---|---|
| Värmland County, partly | 279,334 |
| Örebro County, partly | 38,575 |
| Västra Götaland County, peripherally | 432 |
History
The province was sparsely populated in the pre-historic age compared to Sweden's southern half. Its 5,500 registered ancient remains are few, compared to other areas. The province was considered to be of minor importance in the Swedish Realm. There are, however, interesting histories told by Snorri Sturlasson about Värmland in the 13th century. It extends back to Ingjald Illråde a legendary king in the 7th century. These stories say that Olof Trätälja, the son of Ingjald, was not accepted as king and had to flee and settled in the then sparsely populated Värmland. More men had to flee the brutal successor of Ingjald and settled in Värmland. Archaeology shows that there was at this time a large increase of population, and construction of some big memorials of powerful men. According to Snorri and other Icelandic sources, Värmland came under Norwegian control in the late 9th and through the 10th century. However, by the time of Adam of Bremen in the 11th century the region is described as Swedish. In Adam's account, the värmlänningar are described as a distinct "Swedish tribe" along with the Sviar, Geats and Skridfinnar (commonly taken to be Sami people).
The early history strongly influenced was not only by the proximity to Västergötland, but also by its western neighbour Norway. Sweden's war with Norway had a strong effect on Värmland too. In 1225, Haakon IV of Norway (Haakon the Old) invaded Sweden and burnt down all villages if they did not pay a ransom. This feud was eventually settled in 1249.
Värmland was originally considered a part of Götaland, and had a strong connection to its southern neighbour Västergötland. Eastern Värmland traditionally belongs to the Bergslagen area, Sweden's central mining district.

In 1582, Värmland was granted its first city privileges, Kristinehamn, but those were revoked. The second city, Karlstad, on the north shore of lake Vänern, was granted by Duke Charles, later king Charles IX of Sweden, in 1584. It became the capital of the province and its name is derived from the King, and literally means Charles' City. The third city was Filipstad in 1611; however, its privilege was revoked in 1694 after a devastating fire. King Charles IX took great personal interest in expanding mining in the province and the industry developed significantly during his reign.
The early 17th century marked the beginning of substantial immigration from Finland. The areas where they centred were known as Finnskog. They kept their Finnish customs and language until the late 19th century. The last native resident to speak Finnish here died in the 1980s.
The most significant coup d'état of modern Swedish history had its beginning in Karlstad. The man behind the uprising was a liberal nobleman and a prominent man of the opposition, major general Georg Adlersparre. He was backed up by the radical guards captain Carl Henrik Anckarsvärd and used the part of the western army that was stationed in Värmland to occupy Karlstad on the night of 7 March 1809. From there he officially proclaimed a revolution, a proclamation which held the view that wars and oppression had ruined the country and the government therefore had to be overthrown. On 9 March, Adlersparre and his enthusiastic soldiers (many of Finnish origin) finally began their march towards Stockholm, and in the events that followed, the king Gustav IV Adolf abdicated under pressure.[7]
Under the Continental system (1806–1814), the timber industry flourished in Värmland and continuing into the modern era, forestry became industrialized and is still the economic backbone of the province.

Bordering on Norway, Värmland was affected by Sweden's last war, Crown Prince Jean Baptiste Bernadottes military campaign against Norway in 1814. The province saw large troop movement and many soldiers originating from the province were involved in battles. The Värmland Regiment had three battalions attached to the 9th Brigade under Colonel Klingspor and one battalion attached to the 10th Brigade under Colonel Gahn af Colqhoun. Both brigades were part of the 5th Army Division under Major General Rosenblad. The 9th Brigade crossed the border to Norway on 30 July 1814 and participated in the siege of Fredrikstad Fortress, which capitulated on 4 August, while other parts of the regiment a few days later followed later Lieutenant General Vegesacks department north and participated in battles at Rakkestad and Langenäs on 6 August 1814 and Askim on 9 August 1814. A battalion of the regiment, commanded by Major Lagerlöv, managed to fight back a Norwegian attack from the bridgehead at Langenäs. The 10th Brigade crossed the border on 1 August 1814 and went in the direction of Morast. It participated in the Battle of Lier south of Kongsvinger on 2 August 1814 and then retreated to the border, where the battalion participated in the battle of Midskog on 5 August 1814 and suffered heavy losses.[8]


During World War II, western Värmland was again an area of heavy military deployment. A major part of the Swedish Armed Forces was concentrated to Värmland following the German invasion of Norway. Approximately 150,000 military personnel were mobilised to Värmland in June 1941, by the time of German demands to transport the fully armed Division Engelbrecht through the country and before the launch of Operation Barbarossa, and with several large military exercises being conducted in the province during the period. Even more military personnel, possibly as many as 250,000, were mobilised to Värmland in the fall of 1943, due to the pending Swedish announcement to end German military transits and fear of a German attack.[9]
An agreement from the dissolution of the union with Norway in 1905 stated that no fortification was allowed on the border between the two nations, but after the German occupation of Norway, old fortifications were renovated and many new constructed. Notably is the fortification Skansen Hultet (Skans 153 Hultet) in Eda Municipality, constructed 1940-1941 (although improvements continued until 1945), and equipped with a network of machine gun emplacements, casemates and other concrete bunkers, surrounded by barbed wire, walls and several lines of tank traps. The fortifications have been renovated by locals and are now open to the public.[10] Formerly classified Swedish military documents shows that the Swedish Armed Forces spent approximately SEK 30 million on fortifications in Värmland during the 1940s.[11] There are around 12,000 military objects, including 123 fortified sites, in Värmland dating from World War II.[11][12]
The film Gränsen (Eng. Beyond the Border) from 2011, telling the story about the life of the young soldiers guarding the border between Sweden and German-occupied Norway in 1942, takes place in northern Värmland and was filmed near Torsby.[13]
 The runestone Skramlestenen found outside Gunnarskog is dated to early Viking Age, between the 5th and 6th century.
The runestone Skramlestenen found outside Gunnarskog is dated to early Viking Age, between the 5th and 6th century. The mining area Långban in eastern Värmland, active between 1711 and 1972.
The mining area Långban in eastern Värmland, active between 1711 and 1972. A workforce of log drivers ("Loggers") transporting timber on Klarälven, near Forshaga in 1918.
A workforce of log drivers ("Loggers") transporting timber on Klarälven, near Forshaga in 1918. The Skoghall Mill, production of carton board owned by Stora Enso.
The Skoghall Mill, production of carton board owned by Stora Enso. The Military Barracks of the Värmland Regiment in 1920.
The Military Barracks of the Värmland Regiment in 1920.
Culture and literature

The province has powerful literary and musical traditions and has spawned some of the most well-known and loved authors of Sweden. In the 19th century several leading authors had their origin here, and retained links to Värmland, among them Erik Gustaf Geijer, Esaias Tegnér, Gustaf Fröding and Nobel Prize winner Selma Lagerlöf. Lagerlöf's novel, Gösta Berlings Saga, is a neo-romantic saga that takes place in Värmland in the 1820s and 1830s. It was also made into a film starring Greta Garbo. It was also made into an opera, I cavalieri di Ekebù, by Italian composer Riccardo Zandonai in 1925.
Education, theatre and a somewhat glamorous lifestyle were buoyed by the landed gentry and the wealth being generated through a lively local iron trade, and also by the position of the landscape on the edge between civilization and wilderness, which inspired art, literature and folklore. During the second half of the 19th century, the iron processing industry was largely put out of business by the revolution in the steel industry which made Central Europe and the United States vastly superior in this field, and the overall economic crisis throughout Europe of the 1870s and 1880s, and the subsequent emigration to North America, shook the landscape. The consequence, however, was to make authors like Lagerlöf and Fröding more aware of the heritage of their province, and they both drew on what they felt to be an oral tradition of story-telling and local legends. This emphasis on richly textured, often romantic or burlesque tales which nonetheless transcend the local has remained a focus of later writers, such as Göran Tunström (1937–2000) and Lars Andersson (b. 1954).
The musical traditions have inspired a number of prominent musicians, such as singers Zarah Leander, Monica Zetterlund and Rigmor Gustafsson.
Dukes
Since 1772, Sweden's Princes have been created Dukes of various provinces in Sweden. This is solely a nominal title.
- Prince Carl Adolf (1798)
- Crown Prince Gustaf (from his birth in 1858 until he became King in 1907)
- Prince Carl Philip (1979-)
Chartered cities
- Arvika (town charter 1811, city charter 1911)
- Filipstad (city charter 1611–1695, town charter 1720, city charter 1835)
- Hagfors (city charter 1950)
- Karlskoga (city charter 1940)
- Karlstad (city charter 1584)
- Kristinehamn (city charter 1582–1584, city charter 1642)
- Säffle (town charter 1882, city charter 1951)
Provincial districts
- Fryksdal
- Färnebo
- Gillberg
- Grums
- Jösse
- Karlskoga
- Karlstad
- Kil
- Nordmark
- Nyeds (ceded from Kil, 1681)
- Näs
- Visnums
- Väse
- Älvdal
- Ölme
Notable natives




- Adam Alsing, (1968 in Karlstad – 2020) TV and radio presenter
- Johanna Anderson, (1856—1904) Baptist missionary in Burma
- Adolph Olson Eberhart, (1870 in Kil – 1944), Swedish-American Governor of Minnesota
- August Hjalmar Edgren (1840 in Östanås – 1903), Swedish-American linguistics professor
- John Alexis Edgren (1839 in Östanås – 1908), Swedish-American Minister
- Nils Ericson (1802 in Langbanshyttan – 1870), inventor and mechanical engineer
- John Ericsson (1803 in Langbanshyttan – 1889), inventor and mechanical engineer.[14]
- Lars Magnus Ericsson, (1846 in Värmskog – 1926) inventor, founder of Ericsson
- Tage Erlander, (1901 in Ransäter – 1985) Prime Minister of Sweden, 1946-1969
- Nils Ferlin, (1898 in Karlstad - 1961) poet and lyricist.
- Gustaf Fröding, (1860 in Alster – 1911) poet and writer
- Erik Gustaf Geijer, (1783 in Ransäter – 1847) writer, historian, poet, philosopher and composer.[15]
- Göran Hägglund, (born 1959 in Degerfors) Minister for Social Affairs, 2006-2014
- Selma Lagerlöf, (1858 in Mårbacka – 1940) author and teacher
- Zarah Leander, (1907 in Karlstad – 1981) singer and actress
- Bruce Magnuson, (1909–1995) former leader of the Communist Party of Canada
- Oscar F. Mossberg, (1866–1937) Swedish-American manufacture of firearms, co-founder of O.F. Mossberg & Sons[16]
- Adolf Noreen, (1854 in Östra Ämtervik – 1925) linguist
- Harry Nyquist, (1889 in Filsby – 1976) physicist and electronic engineer
- Victor Sjöström, (1879 in Årjäng – 1960) film director, screen writer and actor
- Mia Skäringer, (born 1976 in Kristinehamn) actress and comedian
- Esaias Tegnér (1782 in Kyrkerud – 1846) writer, professor of the Greek language and bishop.[17]
- Sten Tolgfors, (born 1966 in Forshaga) arms lobbyist and former Minister for Defence
- Göran Tunström, (1937 in Borgvik – 2000) author.
- Östen Undén, (1886 in Karlstad – 1974) Minister for Foreign Affairs, 1924–1926 and 1945–1962
- Monica Zetterlund, (1937 in Hagfors – 2005) jazz singer and actress.
Sport
- Gunnar Andersson, (1928 in Arvika – 1969) former footballer, famous in Olympique de Marseille
- Marcus Berg, (born 1986 in Torsby) footballer in FC Krasnodar
- Andreas Bergwall, (born 1974) bandy goalkeeper
- Kenny Bräck, (born 1966 in Arvika) a former race car driver, 1999 Indy 500 Winner
- Sven-Göran Eriksson, (born 1948 in Sunne) football coach, former England head coach
- Bengt-Åke Gustafsson, (born 1958 in Karlskoga) former ice hockey player and head coach of Sweden men's national ice hockey team
- Stefan Holm, (born 1976 in Forshaga) high jumper, gold medallist at the 2004 Summer Olympics
- Willy Lindström, (born 1951 in Grums) former ice hockey player and twice winner of Stanley Cup
- Lina Länsberg, (born 1982 in Karlstad) mixed martial artist and twice IFMA gold medalist
- Ola Toivonen, (born 1986 in Degerfors) footballer in Malmö FF
- Thomas Wassberg, (born 1956 in Lennartsfors) retired cross-country skier, four times Olympic gold medallist
Sub-divisions
Sweden's provinces were sub-divided into hundreds or districts. Värmland was historically divided into chartered cities and districts. One district formed part of Bergslagen and was a mountain district, and all the other districts were hundreds.
- Edsberg Hundred
- Fryksdal Hundred
- Färnebo Hundred
- Gillberg Hundred
- Grums Hundred
- Jösse Hundred
- Karlstad Hundred
- Karlskoga Mountain District
- Kil Hundred
- Nordmark Hundred
- Nyed Hundred
- Näs Hundred
- Visnum Hundred
- Väse Hundred
- Älvdal Hundred
- Ölme Hundred
Sports
Football in the province is administered by Värmlands Fotbollförbund. Ice hockey is also popular, with Färjestads BK.
The area hosts the Rally Sweden[18][19] and is the site of the Höljesbanan rallycross circuit.
Notes
- Citations
- "Folkmängd i landskapen den 31 december 2016" (in Swedish). Statistics Sweden. 21 March 2017. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- "... de Varmelandia a Suecis occupata ..." vide p. 142 at Google Books
- Fredrik Fryxell as per Svenskt biografiskt lexikon below pdf here Archived 12 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Graesse
- The entry Värmland in Svensk etymologisk ordbok by Elof Hellquist (1922).
- Dahlbäck, Göran (1996). "Värmland • Historia". Nationalencyklopedin. Vol. 20. Bokförlaget Bra Böcker AB. p. 141. ISBN 91-7024-620-3.
- Norberg, p. 56-57
- Högman, Hans (21 December 2018). "Värmlands regemente, I22/I2". www.hhogman.se (in Swedish). Sollentuna: Hans Högman. Retrieved 29 January 2019.
- Klang, Ingvar; Dyegård, Carl Henrik; Modin, Sven-Åke (5 February 2007). "Foredrag: Bredskapsperioden ur ett Värmländskt perspektiv". oslomilsamfund.no (in Swedish). Oslo: Oslo Militære Samfund. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
- http://www.varmland.org/event.asp?typ=detail&id=11815&ty=3&su=29&lang=
- Skoglund, Tomas (29 December 2011). "Miljardsatsning skulle skydda Värmland". Värmlands Folkblad (in Swedish). Karlstad: Värmlands Folkblad Drift AB. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- Rung Klint, Gunilla (6 September 2016). "Här skulle Hitler stoppas". Nya Wermlands-Tidningen (in Swedish). Karlstad: Nya Wermlands-Tidningens AB. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- Segerpalm, Erik (21 January 2011). "En krigsfilm från Värmlandsskogarna". Värmlands Folkblad (in Swedish). Karlstad: NWT Gruppen AB. Retrieved 29 January 2019.
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 9 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 740.
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 551–552.
- Sandqvist, Anders (27 October 2016). "Svenska släkten som har beväpnat Amerika" [The Swedish family that has armed America]. Expressen (in Swedish). Stockholm: AB Kvällstidningen Expressen. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- Gosse, Edmund William (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 26 (11th ed.). pp. 505–506.
- "Visit Karlstad - Varmt välkommen till solstaden Karlstad!".
- "Svenska Rallyt 2021".
References
- Norberg, Johan (1999), Den Svenska Liberalismens historia, Timbro, ISBN 91-7566-429-1
External links
- (in Swedish) Värmland - Tourist site
