Hypothiocyanite
L'hypothiocyanite est un anion de formule semi-développée −O-S-C≡N naturellement présent dans les muqueuses. On a identifié l'importance de son rôle et de son action tout d'abord dans le lait, puis dans la salive et en 2006, dans les sécrétions pulmonaires. L'hypothiocyanite, avec la lactoferrine, le lysozyme fait partie des premières lignes de défense du système immunitaire du corps humain face l'attaque d'agents infectieux et en particulier des microorganismes pathogènes. Ce composé antimicrobien est absent chez les malades atteints de mucoviscidose[1].
Chimie
L'hypothiocyanite est la base conjuguée de l'acide hypothiocyanique (H–O–S–C≡N). Il peut être considéré comme un composé inorganique faisant partie de la famille des thiocyanates car il contient le groupe fonctionnel SCN−. L'OSCN− est formé quand un atome d'oxygène est lié au groupe thiocyanate via une catalyse enzymatique
L'hypothiocyanite (également appelé hypothiocyanate) est produit par la mise en contact de peroxyde d'hydrogène et de thiocyanate en présence d'une peroxydase[2] (myéloperoxydase, lactoperoxydase).
H2O2 + SCN− → OSCN− + H2O
Bactéricide
L'hypothiocyanite est produit naturellement par le système immunitaire antimicrobien des muqueuses dans une réaction d'oxydo-réduction réalisée par une peroxydase. Il est étudié intensivement pour ses capacités antimicrobiennes importantes a distinguo des antibiotiques car il est inoffensif pour les cellules du corps humain tout en étant cytotoxique pour les bactéries
Mode d'action
Pruitt. et al. (Pruitt KM, 1982) ont montré que les produits de catalyse de la lactoperoxydase avaient des actions antibactériennes. Le principal produit d'oxydation, l'anion hypothiocyanite, OSCN− est produit pour une quantité d'environ 1 mole par mole de peroxyde d'hydrogène. Au pH optimal de 5,3, l'OSCN−est en équilibre avec HOSCN. L'acide HOSCN est considéré comme le plus bactéricide des deux formes (Thomas EL, 1983). À un pH de 7, on a évalué que HOSCN représente 2 % à comparer OSCN−98 % (Thomas EL, 1981)
L'action d'OSCN− sur les bactéries est signalé comme une action sur les groupements sulfhydryls (SH) (Aune et Thomas, 1978[3]; Ekstrand. Et al. 1985). Ainsi, il a un mode d'action sur les micro-organismes complètement différent des antibiotiques. L'anion hypothiocyanite n'attaque pas l'ADN et n'est pas mutagène (White et al[4], 1983). L'hypothiocyanite ne génère pas d'antibiorésistance.
L'OSCN− a également été identifié comme un agent antimicrobien important dans le lait, la salive[5], les larmes…
Lien avec la mucoviscidose
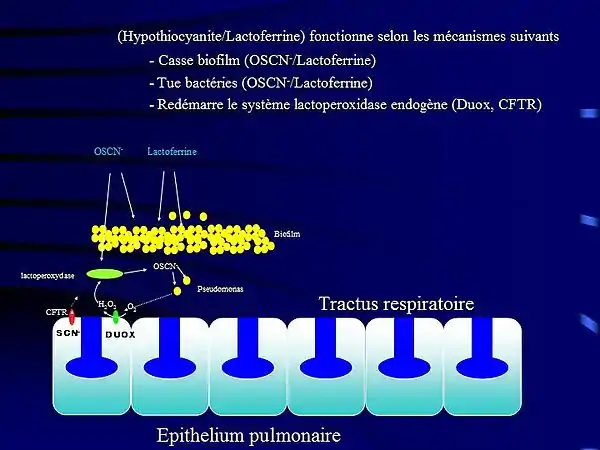
Initialement, il a été découvert que le composé hypothiocyanite OSCN− était manquant chez les personnes atteintes de mucoviscidose (Banfi 2007[6]) et de ce fait, le système de défense immunitaire antimicrobien du poumon[7] ne pouvait fonctionner correctement. Dès lors, le mucus se développe, les bactéries ne sont plus ni évacuées ni tuées. Le manque d'OSCN− ajouté au déficit en lactoferrine (Singh[8], Nature 2002) conduit ensuite à une difficulté a évacuer le mucus et à des infections bactériennes. En parallèle, on assiste à des inflammations répétées des muqueuses, inflammations générées non seulement par les bactéries mais également par le peroxyde d'hydrogène H2O2 produit par les protéines duox[9] et non détoxifiées par les lactoperoxydases (Conner et al [10],[11], Rada et al [12],[13], Fisher et al[14] )
Un produit contenant de l'hypothiocyanite OSCN−/ lactoferrine, Meveol a reçu récemment le statut de médicament orphelin pour le traitement de la mucoviscidose à la fois par l'agence européenne EMEA et la FDA américaine.
Large efficacité
Liste non exhaustive
Bactéries (+Gram, -Gram) • ''Acinetobacter species • Aeromonas hydrophila • Bacillus brevis • Bacillus Cereus • Bacillus megaterium • Bacillus subtilis • Burkholderia cepacia • Campylobacter jejuni • Capnocytophaga ochracea • Corynebacterium xerosis • Enterobacter cloacae • Escherichia coli • Haemophilus influenzae • Helicobacter Pylori • Klebsiella oxytoca • Klebsiella pneumoniae • Legionella • Listeria monocytogenes • Micrococcus luteus • Mycobacterium smegmatis • MRSA • Neisseria species • Pseudomonas aeruginosa • Pseudomonas pyocyanea • Salmonella species • Selenomonas sputigena • Shigella sonnei • Staphylococcus aerogenes • Staphylococcus Aureus • Streptococcus agalactiae • Streptococcus faecalis • Streptococcus mutans • Wolinella recta • Xanthomonas campestris • Yersinia enterocolitica
Virus[15] • Herpes simplex virus, HSV • Immunodeficient virus, HIV • Respiratory Syncytial virus, RSV • Echovirus 11 • Influenza virus
Levures et moisissures • Candida albicans • Aspergillus niger • Colletotrichum musae • Colletotrichum gloeosporioide • Botryodiplodia theobromae • Fusarium monoliforme • Fusarium oxysporum • Rhodotula rubra • Byssochlamys fulva • Sclerotinia
Références
- Furtmüller PG, Zederbauer M, Jantschko W, Helm J, Bogner M, Jakopitsch C, Obinger C. Active site structure and catalytic mechanisms of human peroxidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006 Jan 15;445(2):199-213. Epub 2005 Oct 26
- Thomas EL, Aune TM. Lactoperoxidase, peroxide, thiocyanate antimicrobial system : correlation of sulfhydryl oxidation with antimicrobial action. Infect. Immun. (1978); 20(2):456-63. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC421877/pdf/iai00197-0132.pdf
- White WE Jr, Pruitt KM, Mansson-Rahemtulla B. Peroxidase-Thiocyanate-Peroxide Antibacterial System Does Not Damage DNA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983; 23(2): 267–272. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC186035/pdf/aac00203-0085.pdf
- Tenovuo J. Clinical applications of antimicrobial host proteins lactoperoxidase, lysozyme and lactoferrin in xerostomia: efficacy and safety. Oral Dis. 2002 Jan;8(1):23-9. Review
- Mowska, Patryk, Daniel Lorentzen, Katherine Excoffon, Joseph Zabner, Paul B. McCray, William M. Nauseef, Corinne Dupuy, and Botond Bánfi. A novel host defense system of airways is defective in cystic fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 1er novembre 2006. Web. 26 novembre 2009. http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/reprint/175/2/174.pdf
- Al Obaidi AH. Role of airway lactoperoxidase in scavenging of hydrogen peroxide damage in asthma. Ann Thorac Med. 2007 Jul;2(3):107-10
- Singh PK, Parsek MR, Greenberg EP, Welsh MJ. A component of innate immunity prevents bacterial biofilm development. Nature. 2002;417:552-5
- Gattas MV, Forteza R, Fragoso MA, Fregien N, Salas P, Salathe M, Conner GE. Oxidative epithelial host defense is regulated by infectious and inflammatory stimuli. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Nov 15;47(10):1450-8. Epub 2009 Aug 22
- Conner GE, Salathe M, Forteza R Lactoperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide metabolism in the airway, AmJ Respir Crit Care Med 2002 Dec 15;166 (12 Pt2):S57-1 Review http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/reprint/166/12/S1/S57
- Conner GE, Wijkstrom-Frei C, Randell SH, Fernandez VE, Salathe M. The lactoperoxidase system links anion transport to host defense in cystic fibrosis. FEBS Lett. 2007;581(2):271-8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1851694/pdf/nihms16911.pdf
- Rada B, Lekstrom K, Damian S, Dupuy C, Leto TL. The Pseudomonas toxin pyocyanin inhibits the dual oxidase-based antimicrobial system as it imposes oxidative stress on airway epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2008 Oct 1;181(7):4883-93. http://www.jimmunol.org/cgi/reprint/181/7/4883
- Rada B, Leto TL. Oxidative innate immune defenses by Nox/Duox family NADPH oxidases. Contrib. Microbiol. 2008;15:164-87. Review. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2776633/pdf/nihms156206.pdf
- Fischer H. Mechanism and function of DUOX in epithelia of the lung. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(10):1-13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19358684
- Mikola H, Waris M, Tenovuo J. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1, respiratory syncytial virus and echovirus type 11 by peroxidase-generated hypothiocyanite. Antiviral Res. 1995 Mar;26(2):161-71.
Bibliographie
- Mowska, Patryk, Daniel Lorentzen, Katherine Excoffon, Joseph Zabner, Paul B. McCray, William M. Nauseef, Corinne Dupuy, et Botond banfi. A novel host defense system of airways is defective in cystic fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, . Web. . <http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/reprint/175/2/174.pdf>.
- Hypothiocyanite/Lactoferrine : Orphan designation by the EMEA for the treatment of cystic fibrosis.
- Hypothiocyanite/Lactoferrin : Orphan druggranted by the FDA for the treatment of cystic fibrosis.
- Childers M, Eckel G, Himmel A, Caldwell J., A new model of cystic fibrosis pathology: lack of transport of glutathion and its thiocyanate conjugates. Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(1):101-1.
- Conner GE, Wijkstrom-Frei C, Randell SH, Fernandez VE, Salathe M., The lactoperoxidase system links anion transport to host defense in cystic fibrosis. FEBS Lett. 2007;581(2):271-8.
- Minarowski Ł, Sands D, Minarowska A, Karwowska A, Sulewska A, Gacko M, Chyczewska E. Thiocyanate concentration in saliva of cystic fibrosis patients. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2008;46(2):245-6.
- Rada B, Leto TL, Redox warfare between airway epithelial cells and Pseudomonas : dual oxidase versus pyocyanin. Immunol. Res. 2008
- Conner GE, Salathe M, Forteza R, Lactoperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide metabolism in the airway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(12 Pt 2):S57-61. Review.
- Eastvold JS. Hypothiocyanous acid : an overview. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2005;77:22.
- Fischer H, Mechanism and function of DUOX in epithelia of the lung. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(10):1-13.
- Kussendrager KD, Van Hooijdonk ACM, Lactoperoxidase: physico-chemical properties, occurrence, mechanism of action and applications. Br. J. Nutr. 2000; 84, suppl. 1, S19-S25.
- Pedemonte N, Caci E, Sondo E, Caputo A, et al, Thiocyanate transport in resting & IL-4-stimulated human bronchial epithelial cells: role of pendrin and anion channels. J Immunol. 2007;178(8):5144-53.
- Pruitt KM, Tenovuo J, Andrews RW, Mc Kane T, Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed oxidation of thiocyanate: polarographic study of the oxidation products. Biochemistry. 1982;21(3): 562-7.
- Rada B, Leto TL, Redox warfare between airway epithelial cells and Pseudomonas : dual oxidase versus pyocyanin. Immunol. Res. 2009; 43 (1-3) :198-209.
- Rada B, Leto TL, Oxidative innate immune defenses by Nox/Duox family NADPH oxidases. Contrib. Microbiol. 2008;15:164-87. Review.
- Reiter B, Härnulv G, Lactoperoxidase antibacterial system: Natural occurrence, Biological functions and Practical applications. J. Food Protect. 1984;47:724-32.
- Rogan MP, Taggart CC, Greene CM, Murphy PG, O'Neill SJ, McElvaney NG. Loss of microbicidal activity and increased formation of biofilm due to decreased lactoferrin activity in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 2004 Oct 1;190(7):1245-53. Epub 2004 Aug 26. http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/pdf/10.1086/423821?cookieSet=1
- Shin K, Wakabayashi H, Yamauchi K, Teraguchi S, Tamura Y, Kurokawa M, Shiraki K, Effects of orally administered bovine lactoferrin and lactoperoxidase on influenza virus infection in mice. J Med Microbiol. 2005;54(Pt 8):717-23.
- Thomas EL, Aune TM, Lactoperoxidase, peroxide, thiocyanate antimicrobial system : correlation of sulfhydryl oxidation with antimicrobial action. Infect. Immun. (1978); 20(2):456-63.
- Thomas EL, Bates KP, Jefferson MM, Hypothiocyanite ion : detection of the antimicrobial agent in human saliva. J. Dent. Res. 1980; 59(9):1466-72.
- Thomas EL, Lactoperoxidase-catalysed oxidation of, thiocyanate : equilibria between oxidised forms of thiocyanate. Biochemistry. 1981; 20:3273-80.
- Thomas EL, Pera KA, Smith KW, et al, Inhibition of streptococcus mutans by the lactoperoxidase antimicrobial system. Infect. Immun. 1983; 39(2):767-78.
- White WE Jr, Pruitt KM, Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Peroxidase-Thiocyanate-Peroxide Antibacterial System Does Not Damage DNA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983; 23(2): 267–272.
- Wijkstrom-Frei C, El-Chemaly S, Ali-Rachedi R, Gerson C, Cobas MA, Forteza R, Salathe M, Conner GE, Lactoperoxidase and human airway host defense. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2003;29(2):206-12.
- Xu Y, Szep S, Lu Z, The antioxidant role of thiocyanate in the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis and other inflammation related diseases, PNAS. 2009; Early edition, November 16th.
- Singh PK, Shaefer AL, Parsek MR, Moninger TO, Welsh MJ, Greenberg EP. Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms. Nature. 2000;407:762-4.
- Singh PK, Parsek MR, Greenberg EP, Welsh MJ. A component of innate immunity prevents bacterial biofilm development. Nature. 2002;417:552-5.
- Travis SM, Conway BA, Zabner J, Smith JJ, Anderson NN, Singh PK, Greenberg EP, Welsh MJ. Activity of abundant antimicrobials of the human airway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 May;20(5):872-9.
- Portail de la médecine
- Portail de la chimie