Iodotyrosine désiodase
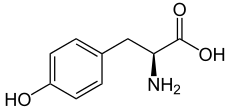
L'iodotyrosine désiodase est une oxydoréductase qui catalyse la désiodation de la monoiodotyrosine (MIT) et de la diiodotyrosine (DIT), dérivés iodés de la tyrosine — un acide aminé protéinogène — intervenant dans la biosynthèse des hormones thyroïdiennes et produits également lors de la dégradation métabolique de ces dernières. Chez l'Homme, cette enzyme est codée par le gène IYD[1],[2], des mutations de ce gène étant associées à l'hypothyroïdie[3].
| N° EC | EC |
|---|---|
| Cofacteur(s) | FMN |
| IUBMB | Entrée IUBMB |
|---|---|
| IntEnz | Vue IntEnz |
| BRENDA | Entrée BRENDA |
| KEGG | Entrée KEGG |
| MetaCyc | Voie métabolique |
| PRIAM | Profil |
| PDB | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBj PDBsum |
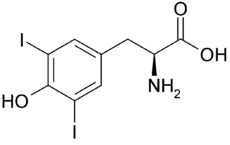
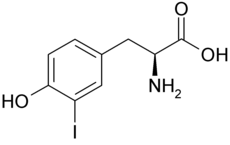
L'iodotyrosine désiodase a pour fonction d'éliminer l'iode des hormones thyroïdiennes une fois celles-ci dégradées en iodotyrosines. Elles diffèrent des iodothyronine désiodases, qui catalysent la désiodation des hormones thyroïdiennes elles-mêmes, et plus généralement des dérivés iodés de la thyronine — et non de la tyrosine.
Contrairement aux iodothyronine désiodases, l'iodotyrosine désiodase n'est pas une sélénoprotéine, c'est-à-dire qu'elle ne contient pas de sélénocystéine, un acide aminé assez rare contenant un atome de sélénium à la place du soufre de la cystéine.
Notes et références
- (en) Sédami Gnidehou, Bernard Caillou, Monique Talbot, Renée Ohayon, Jacques Kaniewski, Marie-Sophie Noël-Hudson, Stanislas Morand, Diane Agnangji, Alphonse Sezan, Françoise Courtin, Alain Virion et Corinne Dupuy, « Iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1 (DEHAL1) is a transmembrane protein involved in the recycling of iodide close to the thyroglobulin iodination site », Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, vol. 18, no 13, , p. 1574–6 (lire en ligne) DOI:10.1096/fj.04-2023fje
- (en) Jessica E. Friedman, James A. Watson Jr., David W.-H. Lam et Steven E. Rokita, « Iodotyrosine Deiodinase Is the First Mammalian Member of the NADH Oxidase/Flavin Reductase Superfamily », Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 281, no 5, , p. 2812-2819 (lire en ligne) DOI:10.1074/jbc.M510365200
- (en) José C. Moreno, Willem Klootwijk, Hans van Toor, Graziella Pinto, Mariella D'Alessandro, Aubène Lèger, David Goudie, Michel Polak, Annette Grüters et Theo J. Visser, « Mutations in the Iodotyrosine Deiodinase Gene and Hypothyroidism », New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 358, no 17, , p. 1811-1818 (lire en ligne) DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa0706819
- (en) Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al., « The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6. », Nature, vol. 425, no 6960, , p. 805–11. DOI:10.1038/nature02055
- (en) Moreno JC, « Identification of novel genes involved in congenital hypothyroidism using serial analysis of gene expression. », Horm. Res., vol. 60 Suppl 3, , p. 96–102. DOI:10.1159/000074509
- (en) Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al., « The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) », Genome Res., vol. 14, no 10B, , p. 2121–7 (PMCID 528928). DOI:10.1101/gr.2596504
- (en) Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al., « Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs », Nat. Genet., vol. 36, no 1, , p. 40–5. DOI:10.1038/ng1285
- (en) Afink G, Kulik W, Overmars H, et al., « Molecular characterization of iodotyrosine dehalogenase deficiency in patients with hypothyroidism », J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., vol. 93, no 12, , p. 4894–901. DOI:10.1210/jc.2008-0865
- (en) Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al., « Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., vol. 99, no 26, , p. 16899–903 (PMCID 139241). DOI:10.1073/pnas.242603899
- (en) Gieger C, Geistlinger L, Altmaier E, et al., « Genetics Meets Metabolomics: A Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolite Profiles in Human Serum », PLoS Genet., vol. 4, no 11, , e1000282 (PMCID 2581785). DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000282
- (en) Thomas SR, McTamney PM, Adler JM, et al., « Crystal Structure of Iodotyrosine Deiodinase, a Novel Flavoprotein Responsible for Iodide Salvage in Thyroid Glands », J. Biol. Chem., vol. 284, no 29, , p. 19659–67 (PMCID 2740591). DOI:10.1074/jbc.M109.013458
- (en) Krause K, Karger S, Gimm O, et al., « Characterisation of DEHAL1 expression in thyroid pathologies », Eur. J. Endocrinol., vol. 156, no 3, , p. 295–301. DOI:10.1530/EJE-06-0596
- (en) Gnidehou S, Lacroix L, Sezan A, et al., « Cloning and characterization of a novel isoform of iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1 (DEHAL1) DEHAL1C from human thyroid: comparisons with DEHAL1 and DEHAL1B », Thyroid, vol. 16, no 8, , p. 715–24. DOI:10.1089/thy.2006.16.715
- (en) Otowa T, Yoshida E, Sugaya N, et al., « Genome-wide association study of panic disorder in the Japanese population », J. Hum. Genet., vol. 54, no 2, , p. 122–6. DOI:10.1038/jhg.2008.17
- Portail de la biochimie
- Portail de la médecine