Chapter 6
Thermochemistry
By Boundless
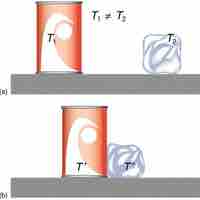
The enthalpy of reaction measures the heat released/absorbed by a reaction that occurs at constant pressure.
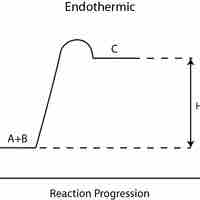
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from the environment, while exothermic reactions release energy to the environment.
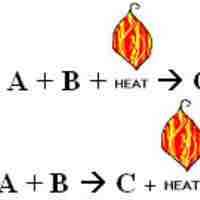
Thermochemical equations are chemical equations which include the enthalpy change of the reaction,
Heat capacity is a measure of the amount of heat energy required to change the temperature of a pure substance by a given amount.
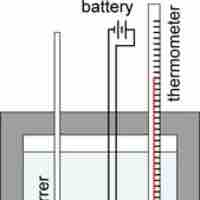
Constant-volume calorimeters, such as bomb calorimeters, are used to measure the heat of combustion of a reaction.
A constant-pressure calorimeter measures the change in enthalpy of a reaction at constant pressure.

The standard enthalpy of formation refers to the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements.
The standard enthalpy of reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs in a system when a chemical reaction transforms one mole of matter under standard conditions.
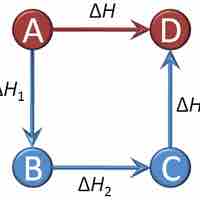
Hess's Law sums the changes in enthalpy for a series of intermediate reaction steps to find the overall change in enthalpy for a reaction.
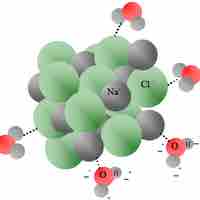
Heat of solution refers to the change in enthalpy when a solute is dissolved into a solvent.
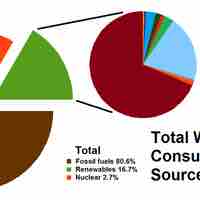
Present sources of energy include fossil fuels, various types of renewable energy, and nuclear power.

Energy consumption is directly related to climate change.
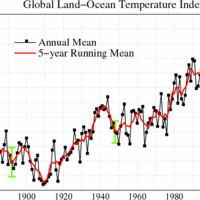
One of the major environmental problems associated with fossil fuel use is global warming.

Alternative and renewable energy sources can reduce the environmental impact of energy production and consumption.