Section 8
Valuing Bonds
By Boundless
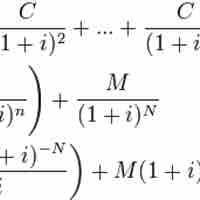
The value of a bond is obtained by discounting the bond's expected cash flows to the present using an appropriate discount rate.
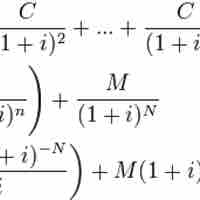
Par value is stated value or face value, with a typical bond making a repayment of par value at maturity.
Yield to maturity is the discount rate at which the sum of all future cash flows from the bond are equal to the price of the bond.
An inflation premium is the part of prevailing interest rates that results from lenders compensating for expected inflation.
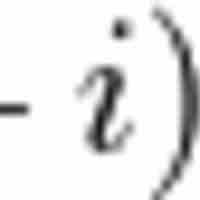
Nominal rate refers to the rate before adjustment for inflation; the real rate is the nominal rate minus inflation: r = R - i or, 1+r = (1+r)(1+E(r)).
"Time to maturity" refers to the length of time before the par value of a bond must be returned to the bondholder.
The yield to maturity is the discount rate that returns the bond's market price: YTM = [(Face value/Bond price)1/Time period]-1.
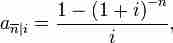
Payment frequency can be annual, semi annual, quarterly, or monthly; the more frequently a bond makes coupon payments, the higher the bond price.

Refunding occurs when an entity that has issued callable bonds calls those debt securities to issue new debt at a lower coupon rate.