Chapter 28
Reproduction, Chromosomes, and Meiosis
By Boundless
Gene expression is a highly complex, regulated process that begins with DNA transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into protein.
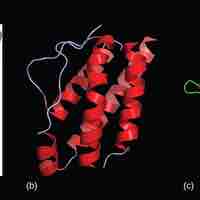
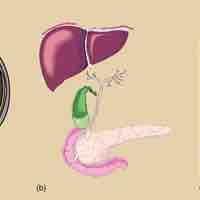
Proteins, encoded by individual genes, orchestrate nearly every function of the cell.

The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance identified chromosomes as the genetic material responsible for Mendelian inheritance.
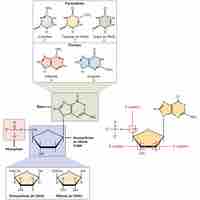
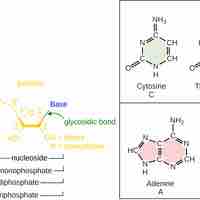
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular processes, especially the regulation and expression of genes.
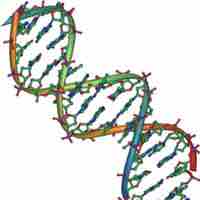
The DNA double helix looks like a twisted staircase, with the sugar and phosphate backbone surrounding complementary nitrogen bases.
DNA packaging is an important process in living cells. Without it, a cell is not able to accommodate the large amount of DNA that is stored inside.
RNA is the nucleic acid that makes proteins from the code provided by DNA through the processes of transcription and translation.
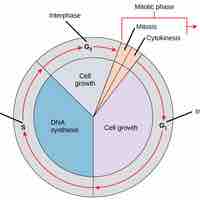
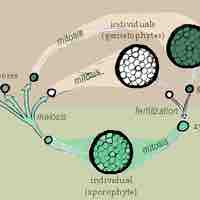
The cell cycle allows multiicellular organisms to grow and divide and single-celled organisms to reproduce.

The genome of an organism consists of its entire complement of DNA, which encodes the genes that control the organism's characteristics.
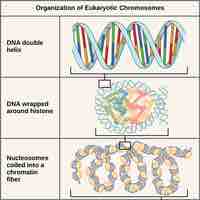
Chromosomes must coil to pack DNA into the cell during cell division, a process involving 3 levels of compaction.

Genetic variation is a measure of the variation that exists in the genetic makeup of individuals within population.
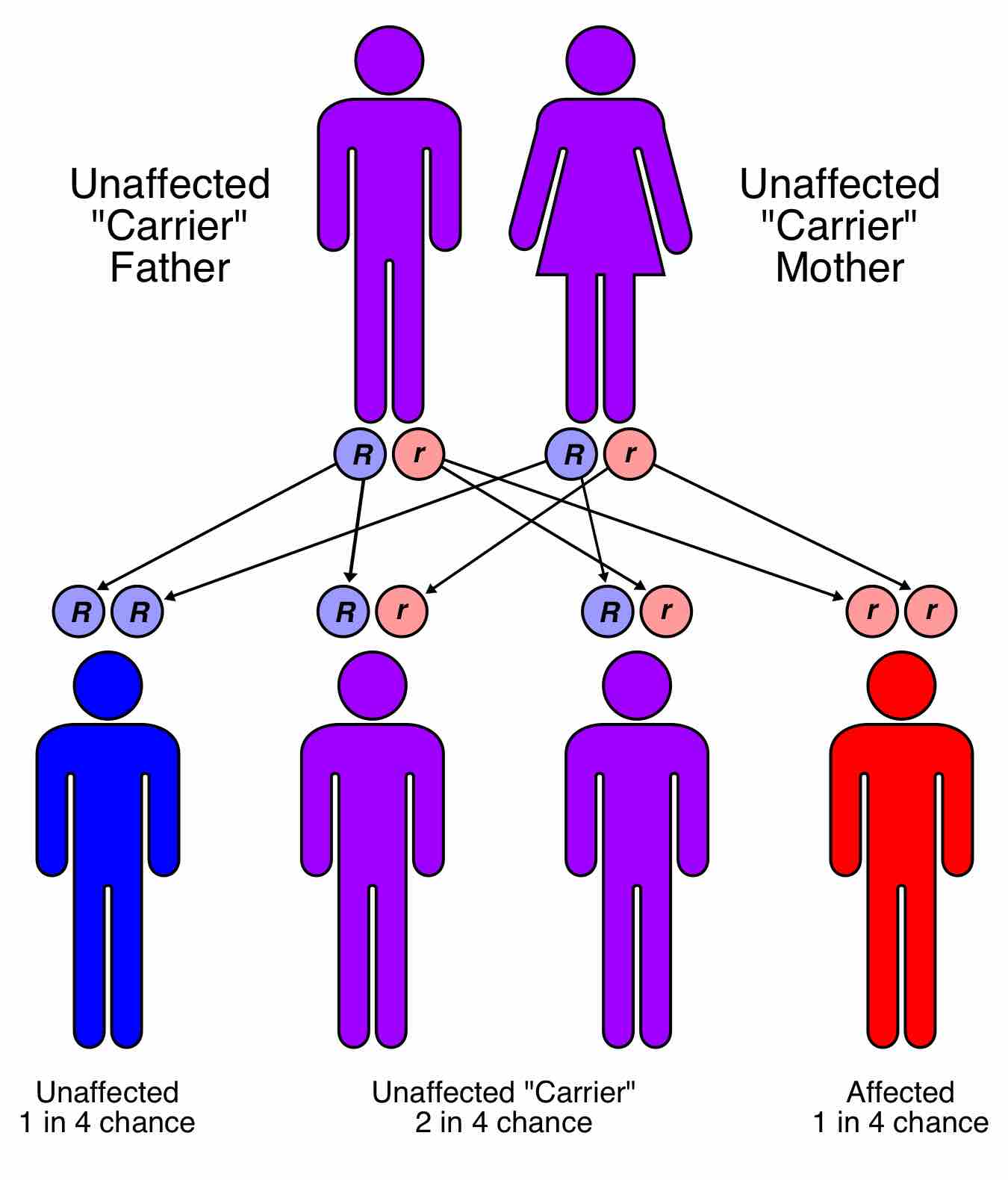
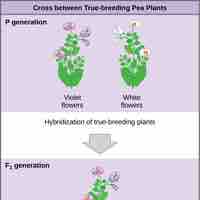
Mendel's Law of Segregation states that a diploid organism passes a randomly selected allele for a trait to its offspring, such that the offspring receives one allele from each parent.
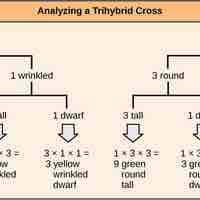
Independent assortment allows the calculation of genotypic and phenotypic ratios based on the probability of individual gene combinations.
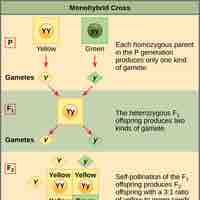
A Punnett square applies the rules of probability to predict the possible outcomes of a monohybrid cross and their expected frequencies.
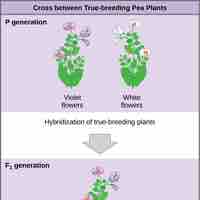
The observable traits expressed by an organism are referred to as its phenotype and its underlying genetic makeup is called its genotype.

The garden pea has several advantageous characteristics that allowed Mendel to develop the laws of modern genetics.

Linked genes can become unlinked during recombination; the probability of genes separating depends on their distance from each other.
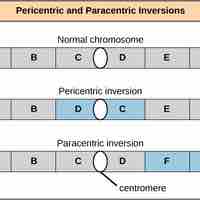
Structural rearrangements of chromosomes include both inversions and translocations, which may have detrimental effects on an organism.