Chapter 29
APPENDIX A: Diseases, Injuries, and Disorders of the Organ Systems
By Boundless
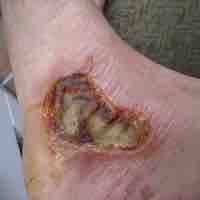
A burn is a type of injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation, or friction.

An allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system.
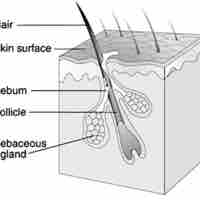
Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is a common human skin disease affecting the skin of the face, upper parts of the chest, and back.
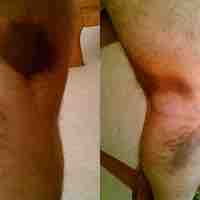
A strain is a tear in tendon fibers resulting from overstretching, while a sprain is an equivalent injury to a ligament.
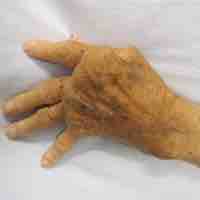
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that affects many tissues and organs, but mainly attacks flexible joints.
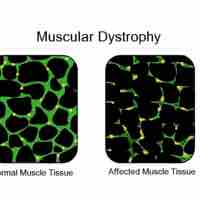
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of muscle diseases characterized by non-functional muscle proteins that impair proper function.

Exercise damages muscles due to eccentric and concentric muscle loading and often results in delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS).
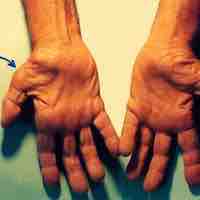
Carpal tunnel syndrome is an entrapment median neuropathy of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel.
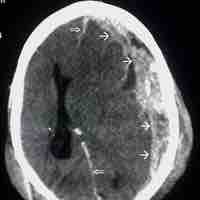
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when an external force injures the brain and can be caused by a direct impact or by acceleration alone.
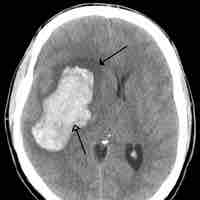
A cerebrovascular accident results from loss of oxygenated blood to a region of the brain and is typically accompanied by neuronal loss.
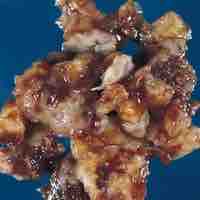
A transient ischemic attack is similar to a stroke; though without permanent damage, it can serve as an important risk factor for stroke.
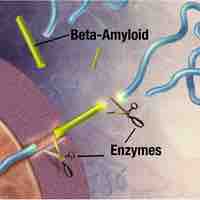
Alzheimer's disease is an age-linked neurodegenerative disorder characterized by marked dementia.
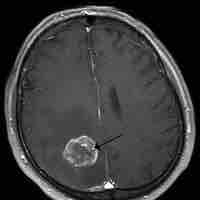
A brain tumor is a pathological abnormal growth of cells in the brain.
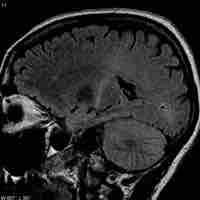
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is caused by degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons, resulting in muscle weakness and atrophy.
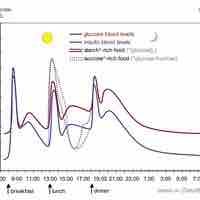
Hyperinsulinism refers to an above-normal level of insulin in the blood of a person or animal.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) develops after exposure to an event that is so stressful for an individual that it becomes traumatic.
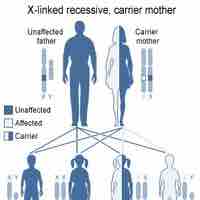
The most common blood disorders involve defects in the amount or activity of factors involved in coagulation.
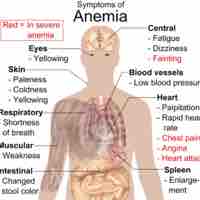
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood resulting in tissue hypoxia.
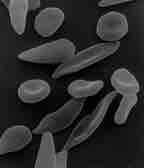
Sickle-cell disease is an autosomal recessive genetic blood disorder in which red blood cells assume a rigid sickle shape.
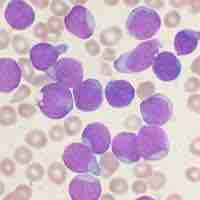
Leukemia is a term covering a spectrum of cancers of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an increase in immature white blood cells.
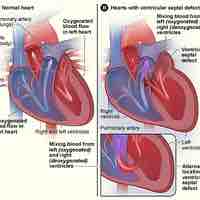
A congenital heart defect is a defect in the structure of the heart and great vessels that is present at birth.
Endocarditis and myocarditis are driven by inflammation of the heart.
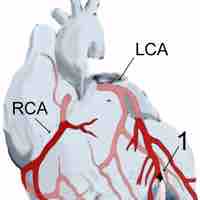
Ischemic heart disease is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, usually due to atherosclerosis, and can lead to a heart attack.
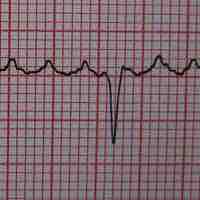
Cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) are a heterogeneous group of conditions involving abnormal electrical activity in the heart.
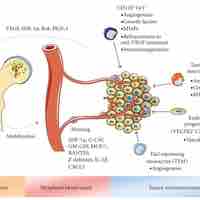
Angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels from existing vessels, contributes to both normal tissue growth and tumorigenesis in cancer.
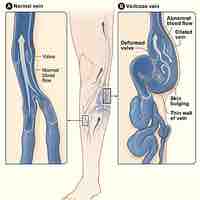
Varicose veins, typically found in the legs, are those that have become enlarged and tortuous due to malfunctioning valves.
Syncope, the medical term for fainting, is a transient loss of consciousness.
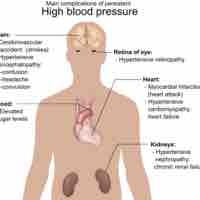
Hypertension is elevated blood pressure, clinically defined as at or greater than 140/90 (systolic/diastolic) mm/Hg.
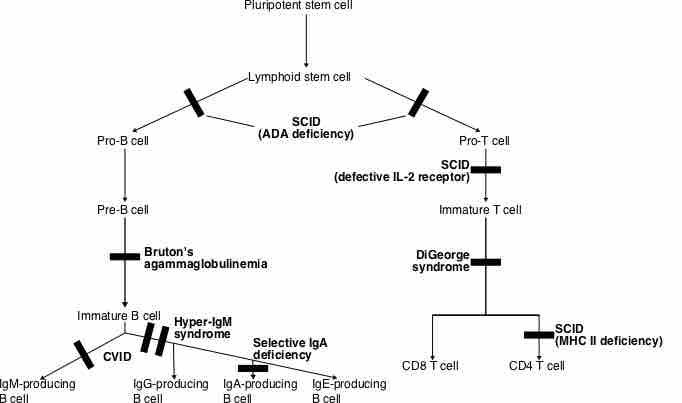
Immunodeficiency is a state where the immune system's ability to fight infectious disease is impaired or absent.
Autoimmune diseases are an inappropriate immune response against tissues in the body.
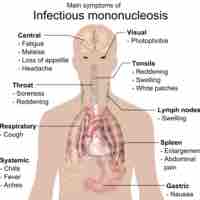
Mononucleosis is an infectious disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and results in flu-like symptoms.
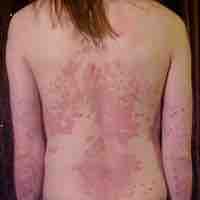
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that affects the skin, caused by faulty immune signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells.

Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by reversible airflow obstruction and bronchospasm.
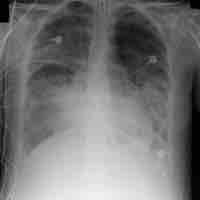
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a serious reaction to various forms of injuries or acute infection to the lung.
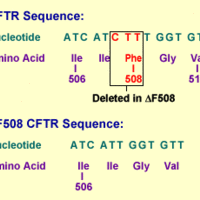
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disorder leading to respiratory congestion, multiple organ failure, and metabolic changes.
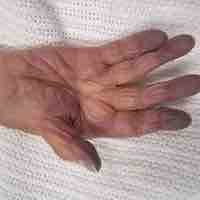
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is inadequate oxygen supply to the body as a whole (generalized hypoxia) or a region of the body (tissue hypoxia).
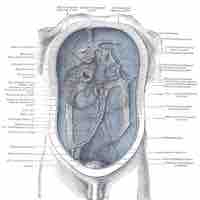
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, usually caused by an infectious organism that is introduced into the abdominal cavity.
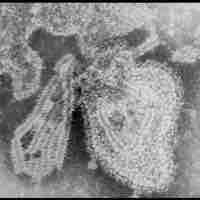
Mumps was a common childhood viral disease, but widespread vaccination has now made it rare in developed countries.

Lactose intolerance is the inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk, due to a lack of the enzyme lactase.
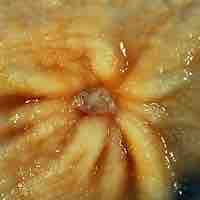
A peptic ulcer, also known as peptic ulcer disease, is an erosion in the wall of the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus.
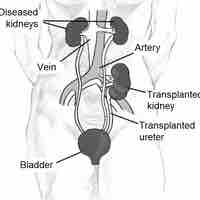
Renal failure uremia is a syndrome of renal failure characterized by elevated levels of urea and creatinine in the blood.
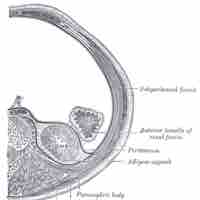
Nephroptosis is an abnormal condition in which the kidney drops down into the pelvis when the patient stands up.
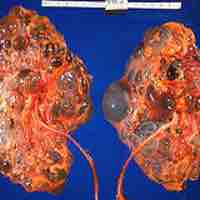
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a cystic genetic disorder of the kidneys.
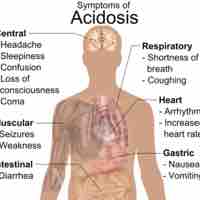
Acidosis describes increased acidity in the blood and other tissues, usually measured as arterial pH below 7.35.
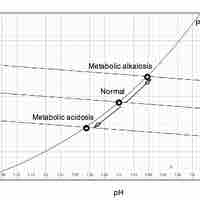
Alkalosis is the increased alkalinity of blood and other tissues, generally occurring when the blood pH is above 7.45.
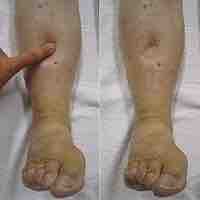
Edema is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling.

A sexually transmitted infection is passed between people during unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to develop or maintain an erection during sexual intercourse.
Cervical cancer is a cancer that originates in the cervix of a female.