Chapter 10
The Media
By Boundless
Media in the United States has taken multiple forms and grown in power due to its for-profit nature.

Broadcasting media has been regulated since the 1920s to ensure balanced and fair coverage, along with coverage of relevant, local issues.
Media consolidation has resulted in fewer companies owning more media sources, thereby increasing the concentration of ownership.

While local news is still available, it is becoming increasingly nationalized and local outlets are being purchased larger, national networks.

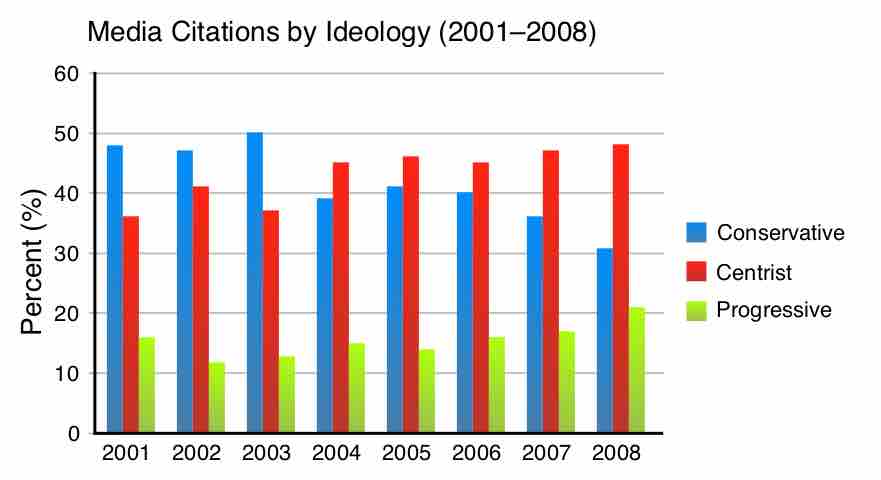
Agenda-setting is a psychological process whereby the media continuously covers an issue so viewers think its a top-priority issue.

Adversarial journalism, or gotcha journalism, seeks to reveal wrongdoings of public officials through a variety of premeditated methods.

Media of the United States consists of television, radio, cinema, newspapers, magazines, and Internet-based Web sites.
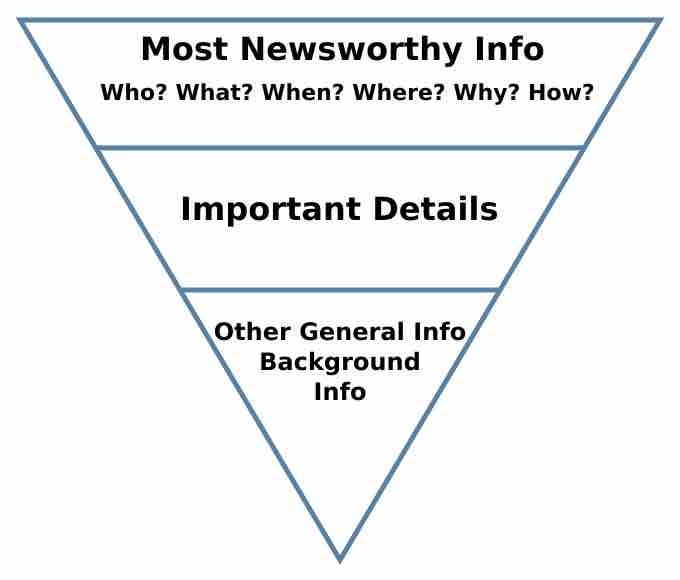
Journalism ethics and standards describe the principles of ethics and good practice journalists adopt in response to specific challenges.

A regulation is a legal provision that creates, limits, or constrains a right, creates or limits a duty, or allocates a responsibility.

The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent regulatory agency of the United States government.

Political advertising is a form of campaigning used by political candidates to reach and influence voters.

From 1960 onward, televised debates have become an important aspect of every presidential election.

Media coverage strongly influences people's perception of politics, society, and culture.

The growth of the Internet and its associated technologies has made a profound impact on contemporary political campaigns.

The main form of print media is the newspaper, which is a scheduled publication containing news of current events, and informative articles.

Stations dedicated to news will often feature newscasts, or bulletins, usually at the top of the hour, between 3 and 8 minutes in length.

A news bulletin or newscast is a television program that provides updates on world, national, or local news events.
An important promise of new media is the "democratization" of the creation, publishing, distribution and consumption of media content.
A journalist collects, writes, and distributes news and other information, and his or her work is referred to as journalism.

Blogs and podcasts are forms of media that exist within cyberspace and encourage interactions among people.