Chapter 3
Inverse Functions and Advanced Integration
By Boundless
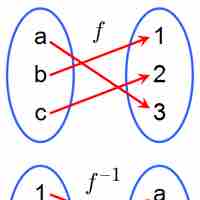
An inverse function is a function that undoes another function.
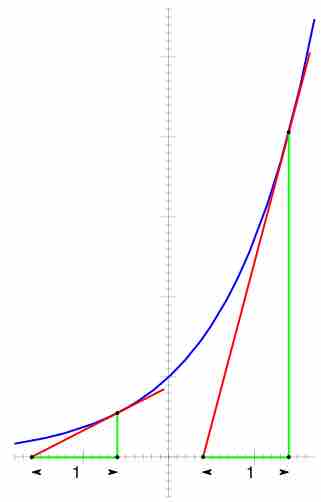
The derivative of the exponential function is equal to the value of the function.
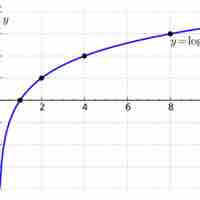
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value must be raised to produce that number.
The general form of the derivative of a logarithmic function is
Differentiation and integration of natural logarithms is based on the property
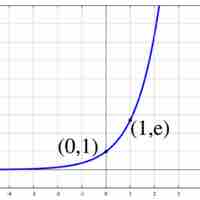
The derivative of the exponential function
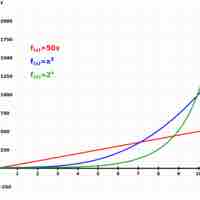
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of the value of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value.
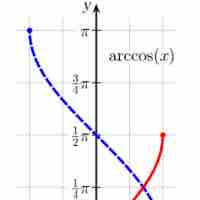
It is useful to know the derivatives and antiderivatives of the inverse trigonometric functions.
Indeterminate forms like
Among all choices for the base
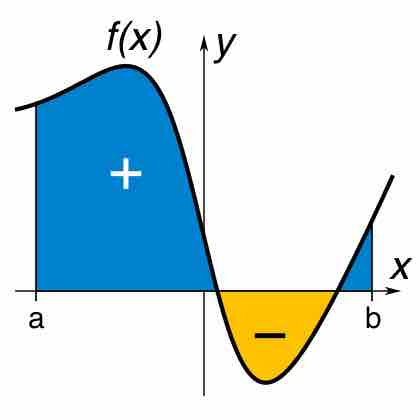
Integration is the process of finding the region bounded by a function; this process makes use of several important properties.
Integration by parts is a way of integrating complex functions by breaking them down into separate parts and integrating them individually.
The trigonometric integrals are a specific set of functions used to simplify complex mathematical expressions in order to evaluate them.
Trigonometric functions can be substituted for other expressions to change the form of integrands and simplify the integration.
Partial fraction expansions provide an approach to integrating a general rational function.
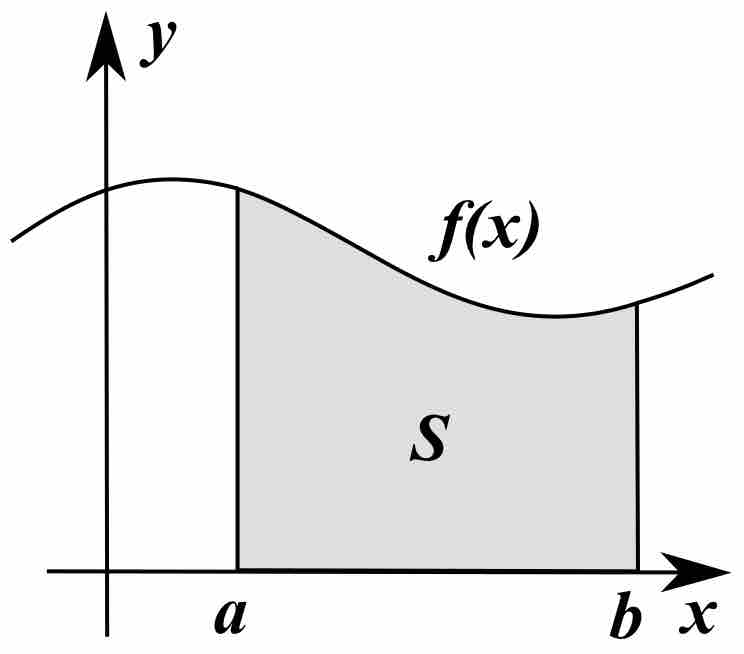
Tables of known integrals or computer programs are commonly used for integration.
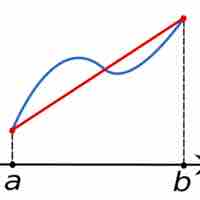
The trapezoidal rule (also known as the trapezoid rule or trapezium rule) is a technique for approximating the definite integral
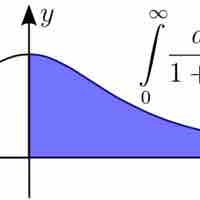
An Improper integral is the limit of a definite integral as an endpoint of the integral interval approaches either a real number or
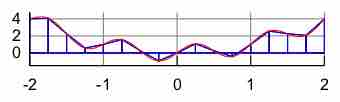
Numerical integration constitutes a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral.
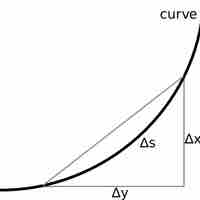
Infinitesimal calculus provides us general formulas for the arc length of a curve and the surface area of a solid.

If the curve is described by the function
Pressure is given as
For a continuous mass distribution, the position of center of mass is given as
Calculus has broad applications in diverse fields of science; examples of integration can be found in economics and biology.
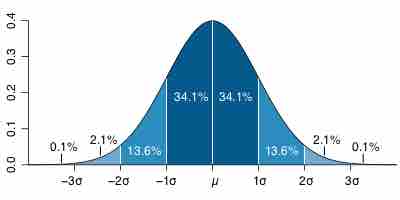
Probability density function describes the relative likelihood, or probability, that a given variable will take on a value.
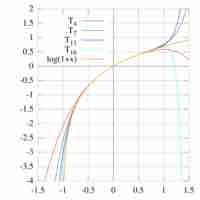
A Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms calculated from the values of the function's derivatives.