HPV-Associated Cancer Trends Among Men by Year
The rate of people getting HPV-associated cancers varies by year and type of cancer. “Incidence rate” means how many people out of a given number get the disease each year.
*Note: This study used cancer registry data to estimate the amount of HPV-associated cancer in the United States by examining cancer in parts of the body and cancer cell types that are more likely to be caused by HPV. Cancer registries do not collect data on the presence or absence of HPV in cancer tissue at the time of diagnosis. In general, HPV is thought to be responsible for more than 90% of anal and cervical cancers; more than 50% of vaginal, vulvar, and penile cancers; and 60% to 70% of oropharyngeal cancers.
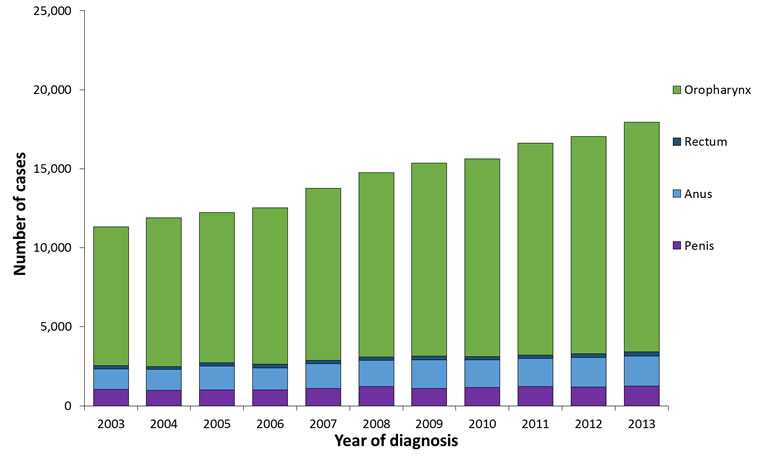
Number of HPV-Associated Cancers Among Men by Year and Cancer Site, United States, 2003–2013
HPV-Associated Cancer Rates Among Men by Year and Cancer Site, United States, 2003–2013
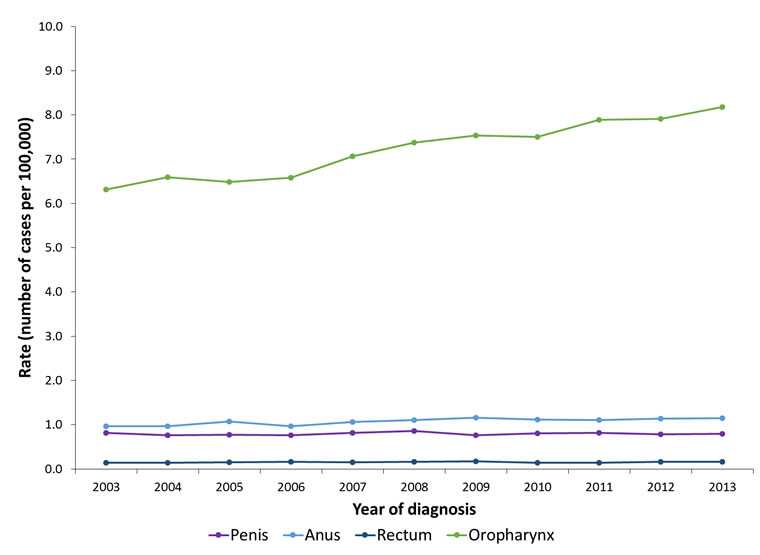
Rates are per 100,000 and age-adjusted to the 2000 U.S. Standard Population (19 age groups — Census P25-1130) standard.
Data are from population-based cancer registries participating in the CDC National Program of Cancer Registries and/or the NCI Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, meeting criteria for high data quality for all years 2003–2013, and covering about 99% of the U.S. population.
HPV-associated cancers were defined as cancers at specific anatomic sites and with specific cellular types in which HPV DNA frequently is found. All cancers were confirmed histologically. Cervical cancers (ICD-O-3 site codes C53.0–C53.9) are limited to carcinomas (ICD-O-3 histology codes 8010–8671, 8940–8941). Vaginal (ICD-O-3 site code C52.9), vulvar (ICD-O-3 site codes C51.0–C51.9), penile (ICD-O-3 site codes C60.0–60.9), anal (ICD-O-3 site code C21.0–C21.9), rectal (ICD-O-3 site code C20.9) and oropharyngeal (ICD-O-3 site codes C01.9, C02.4, C02.8, C05.1, C05.2, C09.0, C09.1, C09.8, C09.9, C10.0, C10.1, C10.2, C10.3, C10.4, C10.8, C10.9, C14.0, C14.2 and C14.8) cancer sites are limited to squamous cell carcinomas (ICD-O-3 histology codes 8050–8084, 8120–8131).
Reference
Viens LJ, Henley SJ, Watson M, Markowitz LE, Thomas CC, Thompson TD, Razzaghi H, Saraiya M, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Human papillomavirus–associated cancers—United States, 2008–2012. MMWR 2016;65(26):661–666.
- Page last reviewed: February 6, 2017
- Page last updated: February 6, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir