Artesunate is available to treat severe malaria in the United States
Currently, only one non-oral drug is FDA-approved and available to treat severe malaria cases in the United States. However, the drug can harm the heart and is often not available. An investigational new drug protocol makes intravenous artesunate available for the treatment of patients with severe malaria.
Treatment of Severe Malaria in the United States
Approximately 1,700 cases of malaria are diagnosed in the United States each year. Approximately 10% of them are cases of severe malaria, which have a significantly higher chance of death.
Intravenous quinidine gluconate had been the only parenteral (administered by a non-oral route such as by injection) drug available in the United States for the treatment of severe malaria. However, quinidine, an antiarrhythmic drug with antimalarial action, can be harmful to the heart and has become less and less available in U.S. hospitals with the advent of newer antiarrhythmic drugs.

Artesunate is in the class of medications known as artemesinins, which are derivatives from the “quinghaosu” or sweet wormwood plant (Artemisia annua). Photographer: Emmet J. Judziewicz , University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point and Madison
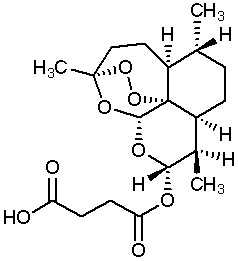
The chemical structure of artesunate is shown here.
Artesunate and the New IND
Artesunate is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) in preference to quinidine for the treatment of severe malaria and has been used worldwide for many years. Artesunate is in the class of medications known as artemisinins, which are derivatives from the “quinghaosu” or sweet wormwood plant (Artemisia annua).
On June 21, 2007, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved investigational new drug (IND) protocol # 76,725, entitled Intravenous Artesunate for Treatment of Severe Malaria in the United States. This IND makes a new class of antimalarial medication, artemisinins, available in the United States for the first time.
The Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR) has been conducting studies in several countries using artesunate, and has agreed to provide a supply of this medication to CDC.
High quality-intravenous artesunate is available only to malaria patients hospitalized in the United States who need intravenous treatment because of:
- severe malaria disease
- high levels of malaria parasites in the blood
- inability to take oral medications
- lack of timely access to intravenous quinidine
- quinidine intolerance or contraindications
- quinidine failure
The drug will be provided to the hospitals, upon request and on an emergency basis, by the CDC Drug Service or by one of the CDC Quarantine Stations located around the country.
How to Obtain Artesunate
To enroll a patient with severe malaria in this treatment protocol, contact the CDC Malaria Hotline: 770-488-7788 (M-F, 8am-4:30pm, eastern time) or after hours, call 770-488-7100 and request to speak with a CDC Malaria Branch clinician.
Malaria Resources for Health-Care Providers
Health-care providers are encouraged to use CDC resources for malaria management advice. These include a Malaria Hotline, which provides access to CDC malaria experts 24 hours a day, 365 days a year; and Web-based, continuously updated information for clinicians on diagnosis and treatment of malaria.
- Page last reviewed: July 10, 2017
- Page last updated: July 14, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir