Inactivity Related to Chronic Disease in Adults with Disabilities
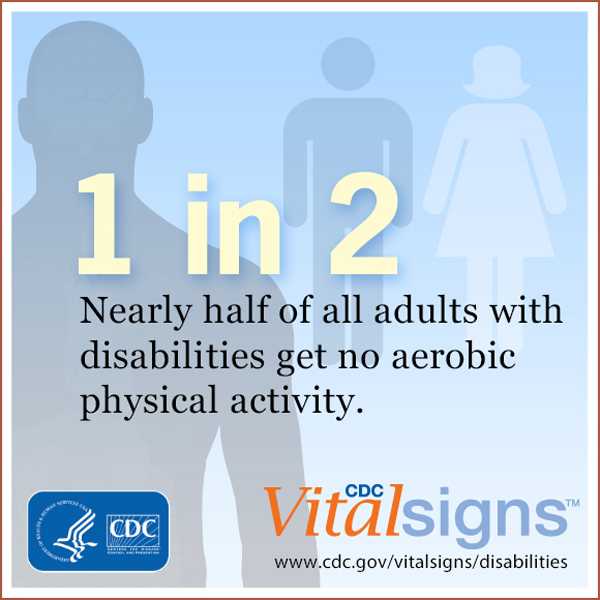
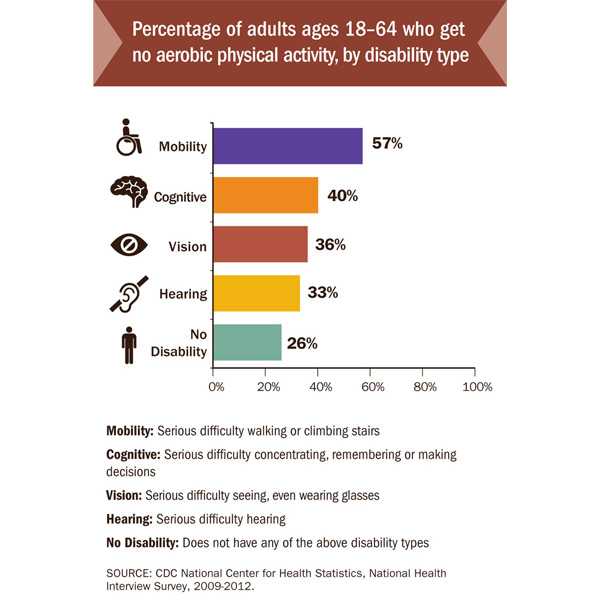
Half of adults with disability get no aerobic physical activity
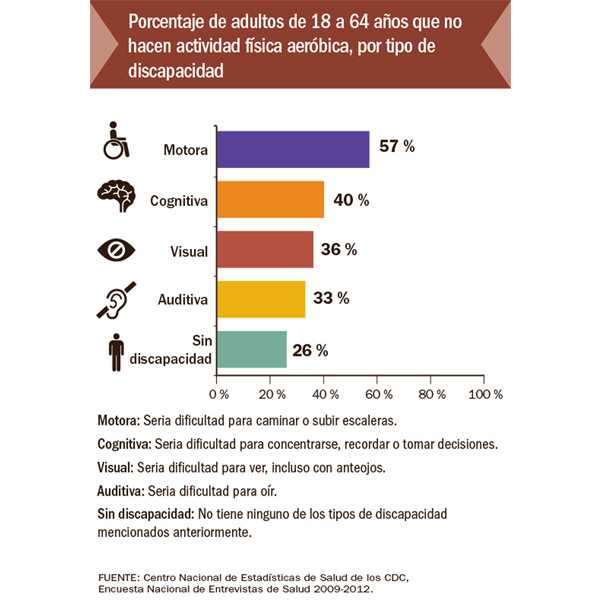
Working age adults with disabilities who get no aerobic physical activity are 50 percent more likely to have a chronic disease such as cancer, diabetes, stroke, or heart disease than their active peers, according to a Vital Signs report released today by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Most adults with disabilities are able to participate in physical activity, yet nearly half (47 percent) of them get no aerobic physical activity. An additional 22 percent aren’t active enough. However, only about 44 percent of adults with disabilities who saw a doctor in the past year got a recommendation for physical activity.
The key findings of the report include:
- Working age adults with disabilities are three times more likely to have heart disease, stroke, diabetes or cancer than adults without disabilities.
- Nearly half of adults with disabilities get no aerobic physical activity, an important protective health behavior to help avoid these chronic diseases.
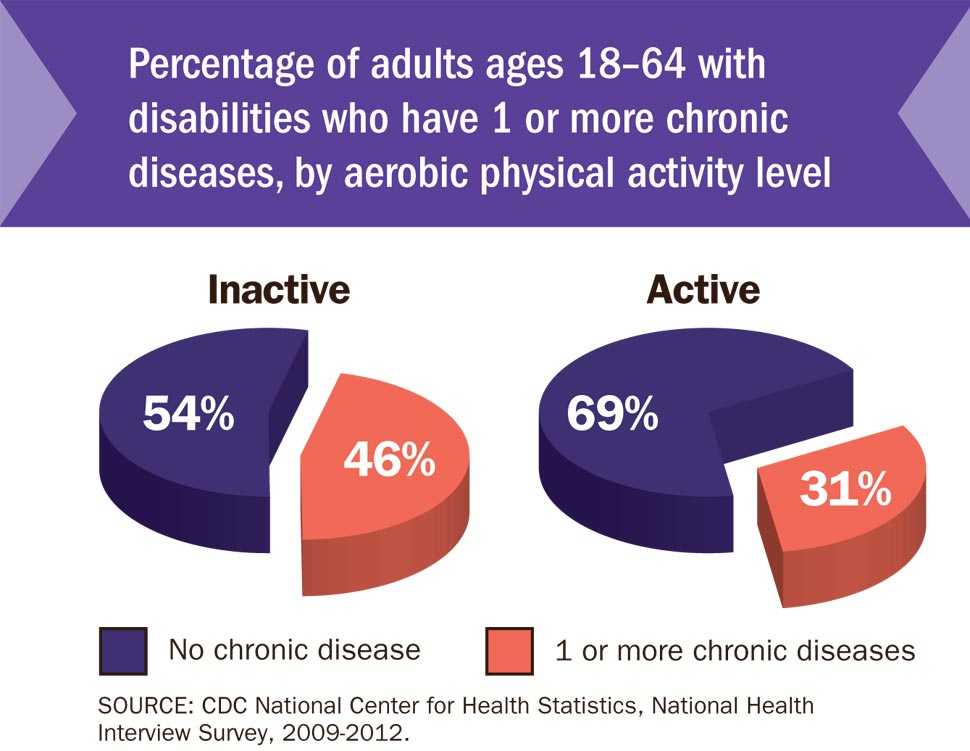
- Inactive adults with disabilities were 50 percent more likely to report at least one chronic disease than were active adults with disabilities.
- Adults with disabilities were 82 percent more likely to be physically active if their doctor recommended it.
Aerobic physical activity can help all adults, including those with disabilities, avoid chronic disease. Physical activity is for everybody – and everybody can help.
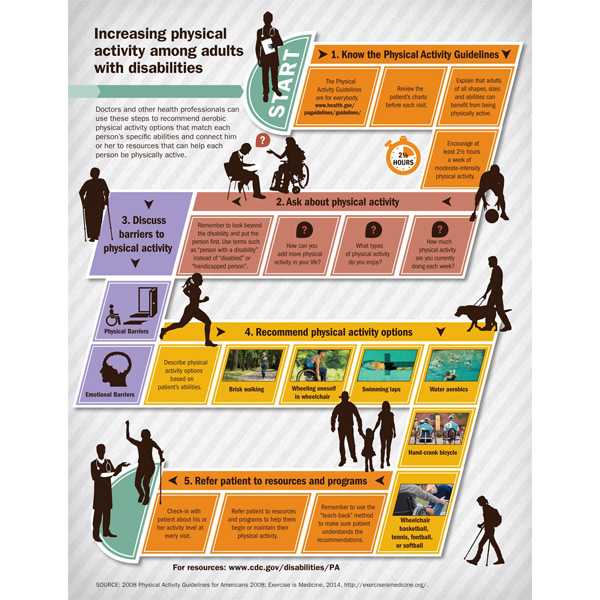
- Adults with disabilities can talk to their doctor about how much and what kind of physical activity is right for them.
- Doctors and other health professionals can recommend aerobic physical activity options that match each person’s specific abilities and connect him or her to resources that can help each person be physically active.
- States and communities can bring together adults with disabilities, health professionals, and community leaders to address resource needs to increase physical activity.
CDC has set up a dedicated resource page for doctors and other health professionals with information to help them recommend aerobic physical activity to their adult patients with disabilities.
Contact Information
CDC Media Relations
(404) 639-3286
media@cdc.gov
Vital Signs Links
Factsheet:
English [PDF-2.65MB]
Spanish [PDF-1.16MB]
Dianna D. Carroll, PhD, MS

“Physical activity is for everyone. Adults with disabilities, health professionals and community leaders need to continue working together to address resource needs that will increase physical activity options for all abilities.”
Dianna D. Carroll, PhD, MS – Senior Health Scientist, Division of Human Development and Disability, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
- Disability and Physical Activity: Resources for Doctors and Other Health Professionals
- Press Release: Inactivity Related to Chronic Disease in Adults with Disabilities: English | Spanish
- CDC Feature: 10 Things to Know about Physical Activity among Adults with Disabilities
- MMWR – Vital Signs: Disability and Physical Activity – United States, 2009-2012 | PDF [356.6 KB]
- Vital Signs: Home | May 2014 Vital Signs | Factsheet PDF [2.65MB] | Issues
- Vital Signs (Spanish): Home | Factsheet PDF [1.16MB] | Issues
Videos
- What’s Disability to Me?
- Where in health is disability? Public health practices to include people with disabilities
- Mark’s Story (short version)
Podcasts
- Vital Signs – Adults with Disabilities: English | Spanish
- Vital Signs – Adults with Disabilities (PSA)
- Page last reviewed: May 6, 2014
- Page last updated: July 21, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir