Occupational Dermatoses
NOTE: This page is archived for historical purposes and is no longer being maintained or updated.
Slides 101 to 105
Slide 101 - Patch test, read

This illustration shows a positive patch test. When the patches are removed, at least 30 minutes should elapse before the test is read. Readings should be made at 48 and 72 hours and even later to detect delayed responses.
Slide 102 - Walk-through survey
This photo was removed due to privacy concerns.
Nothing can replace the first hand opportunity to examine the task and work environment. A walk-through survey may be the first step in understanding the overall picture by identifying potential hazards in the affected employee's tasks or surroundings.
Slide 103 - Prevention

Prevention of occupational dermatoses can be accomplished by engineering controls, personal protective measures, proper work practices and administrative controls. These methods can be applied individually or minimize skin contact with potential irritants.
Slide 104 - Closed systems
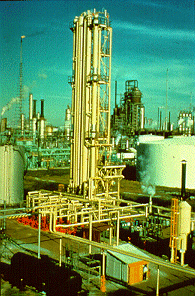
Environmental controls and safety devices that require engineering can be introduced most easily when the plant is being built. Where possible, all potentially hazardous operations should be conducted in systems that are entirely closed. This oil refinery represents an industry using numerous closed systems.
Slide 105 - Ventilation

When processing cannot be entirely enclosed, it is usually possible to install local exhaust systems that collect irritant dust, vapors, fumes and mists. But extensive ventilation systems like this on can be very costly.
- Page last reviewed: January 5, 1998 (archived document)
- Content source:
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Health Effects Laboratory Division (HELD)


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir