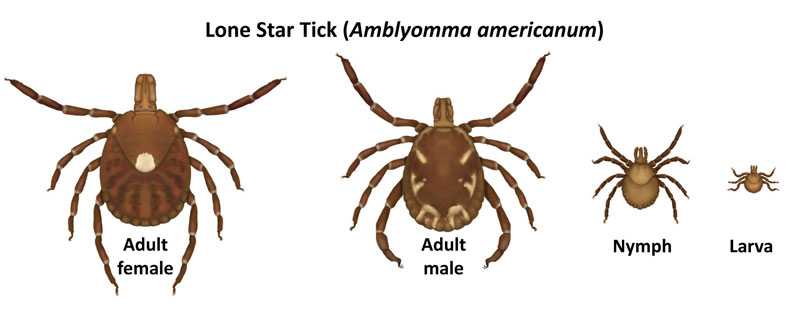
Lone Star tick
 Amblyomma americanum
Amblyomma americanum
Where found: Widely distributed in the southeastern and eastern United States.
Transmits: Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Ehrlichia ewingii (which cause human ehrlichiosis), tularemia, and STARI.
Comments: A very aggressive tick that bites humans. The adult female is distinguished by a white dot or “lone star” on her back. Lone star tick saliva can be irritating; redness and discomfort at a bite site does not necessarily indicate an infection. The nymph and adult females most frequently bite humans and transmit disease.
- Page last reviewed: October 23, 2014
- Page last updated: October 23, 2014
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir