Anterior compartment syndrome
| Anterior compartment syndrome of the lower leg | |
|---|---|
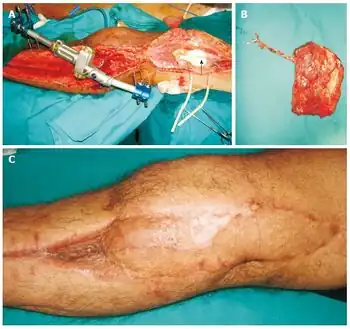 | |
| a-c)Individual with anterior compartment syndrome and vascular bypass, presented with skin and soft tissue defect over the lateral aspect of the knee[1] | |
A compartment syndrome is an increased pressure within a muscular compartment[2] that compromises the circulation to the muscles.
Symptoms and signs
Diffuse tightness and tenderness over the entire belly of the tibialis anterior muscle that does not respond to elevation or pain medication can be early warning signs and suggestive of Anterior Compartment Syndrome. Other common symptoms include excessive swelling that causes the skin to become hot, stretched and glossy. Pain, paresthesias, and tenderness in both the ischemic muscles and the region supplied by the deep common fibular nerve are exhibited by patients with this condition. Sensitivity to passive stretch and active contraction are common, and tend to increase the symptoms.
Pathology
A compartment space is anatomically determined by an unyielding fascial (and osseous) enclosure of the muscles. The anterior compartment syndrome of the lower leg (often referred to simply as anterior compartment syndrome), can affect any and all four muscles of that compartment: tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and peroneus tertius.
This term is often mistakenly used to describe various related/proximal conditions, including Anterior Shin Splints. It is important to distinguish between the two, as shin splints rarely causes serious health problems, while Anterior Compartment Syndrome can lead to irreversible damage.
The true compartment syndrome arises due to increased pressure within the unyielding anterior compartment of the leg. The pressure obstructs venous outflow, which causes further swelling and increased pressure. The resultant ischemia leads to necrosis (death of tissue) of the muscles and nerves. The process can begin with swelling of the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and/or the peroneus tertius muscles in response to strong eccentric contractions sufficient to produce postexercise soreness.
Diagnosis
If these symptoms are observed/experienced it is important to contact a physician specializing in sports medicine (MD/DO), a doctor of podiatric medicine (DPM), or other qualified health care professional immediately so as to get the appropriate advice/treatment before serious damage occurs.
The 5 Ps of Anterior Compartment Syndrome:
- Pain
- Pallor
- Paresthesia
- Pulselessness
- Paralysis (If not treated)
Treatment
The only option to treat acute compartment syndrome is surgery. The procedure, called a fasciotomy, involves a surgeon cutting open the skin and the fascia to relieve the pressure. Options to treat chronic compartment syndrome include physiotherapy, shoe inserts, and anti-inflammatory medications.
References
- ↑ Gravvanis, Andreas; Kyriakopoulos, Antonios; Kateros, Konstantinos; Tsoutsos, Dimosthenis (18 November 2014). "Flap reconstruction of the knee: A review of current concepts and a proposed algorithm". World Journal of Orthopedics. 5 (5): 603–613. doi:10.5312/wjo.v5.i5.603. ISSN 2218-5836. Archived from the original on 29 August 2023. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ↑ Janet G. Travell; David G. Simons (1 October 1992). Myofascial pain and dysfunction: the trigger point manual. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 361. ISBN 978-0-683-08367-5. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- ADAM Health Illustrated Encyclopedia Article, 8/3/2004
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|