Anterior tympanic artery
| Anterior tympanic artery | |
|---|---|
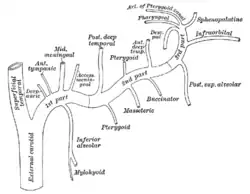 Branches of maxillary artery (anterior tympanic artery at upper left) | |
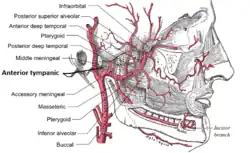 Branches of the maxillary artery | |
| Details | |
| Supplies | Middle ear |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria tympanica anterior |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.055 |
| TA2 | 4425 |
| FMA | 49692 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterior tympanic artery (glaserian artery) is a small artery in the head that supplies the middle ear. It usually arises as a branch of the first part of the maxillary artery.[1] It passes upward behind the temporomandibular articulation, enters the tympanic cavity through the petrotympanic fissure, and ramifies upon the tympanic membrane, forming a vascular circle around the membrane with the stylomastoid branch of the posterior auricular, and anastomosing with the artery of the pterygoid canal and with the caroticotympanic branch from the internal carotid.
Notes
- ↑ Human Anatomy.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 560 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 560 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)
- Mérida Velasco, J. R.; Rodríguez Vázquez, J. F.; Jiménez Collado, J. (1997). "Anterior Tympanic Artery: Course, Ramification and Relationship with the Temporomandibular Joint". Cells Tissues Organs. 158 (3): 222–6. doi:10.1159/000147933. PMID 9394959.
- Wasicky, Richard; Pretterklieber, Michael L. (2000). "The Human Anterior Tympanic Artery: A Nutrient Artery of the Middle Ear with Highly Variable Origin". Cells Tissues Organs. 166 (4): 388–94. doi:10.1159/000016755. PMID 10867441. S2CID 83944308.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.