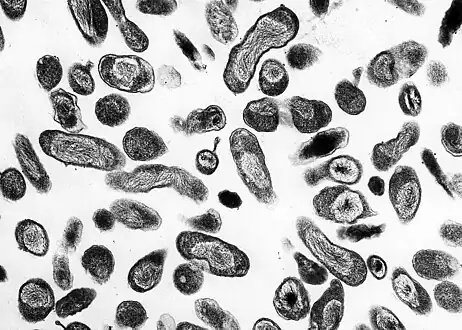
Coccobacillus
A coccobacillus (plural coccobacilli), or bacilluscocco, is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci (spherical bacteria) and bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria). Coccobacilli, then, are very short rods which may be mistaken for cocci.[1]
Haemophilus influenzae, Gardnerella vaginalis, and Chlamydia trachomatis are coccobacilli. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is a Gram-negative coccobacillus prevalent in subgingival plaques. Acinetobacter strains may grow on solid media as coccobacilli. Bordetella pertussis is a Gram-negative coccobacillus responsible for causing whooping cough. Yersinia pestis, the bacterium that causes plague, is also coccobacillus.
Coxiella burnetii is also a coccobacillus.[2] Bacteria from the genus Brucella are medically important coccobacilli that cause brucellosis. Haemophilus ducreyi, another medically important Gram-negative coccobacillus, is observed in sexually transmitted disease, chancroid, of Third World countries.[3]
References
- ↑ Tankeshwar, Acharya (April 11, 2016). "Gram-Negative Cocci and Coccobacilli of Medical Significance; List of Bacteria and Diseases".
- ↑ "persistent rickettsial disease".
- ↑ Schaetchter's Mechanisms of Microbial Disease 4th Edition. ISBN 0-7817-5342-2